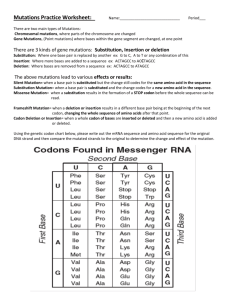
12.4 Mutations What are Mutations? Changes in the DNA (genetic
advertisement

12.4 Mutations What are Mutations? • Changes in the _____________________________of DNA (genetic material) • May occur in _________________________________ (aren’t passed to offspring) • May occur in __________________________________(eggs & sperm) and be passed to offspring Kinds of Mutations Mutations that produce changes in___________________________________________ _________________________________________. Mutations that produce changes in _______________________________are known as ___________________________________________________. Gene Mutations Gene mutations involving a change in one or a few nucleotides are known as _____________________________because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. Point mutations include_________________________________________________________. Substitutions usually affect no more than a single amino acid. _________________________________________ _____________________________________________. An example of a disorder from substitution is: The effects of insertions or deletions are more dramatic. The addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a shift in the grouping of codons, therefore______________________________________________________________. Changes like these are called_____________________________________. In an insertion, an _____________________________________________________. In a__________________, the loss of a ___________________________________and the reading frame is shifted. Amino Acid Sequence Changed. Chromosomal Mutations Chromosomal mutations involve__________________ ______________________________________, break or are lost during mitosis or meiosis. Chromosomal mutations include deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Deletions involve the loss of all or part of a chromosome. Duplications produce extra copies of parts of a chromosome (sequence repeated). Inversions reverse the direction of parts of chromosomes. Translocations occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another. Are Mutations Helpful or Harmful? • Mutations happen ____________________________ • Almost all mutations are ____________________ • Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations • Many mutations are ______________________________________. – Do you remember the name of that enzyme? • • _____________________________________ Some type of ________________________________result from ___________(body cell) mutations • Some mutations may _____________________________________(beneficial) Q: The type of point mutation that usually affects only a single amino acid is called a. a deletion. b. a frameshift mutation. c. an insertion. d. a substitution. Q: A mutation that affects every amino acid following an insertion or deletion is called a(an) a. frameshift mutation. b. point mutation. c. chromosomal mutation. d. inversion. Q: A mutation that affects every amino acid following an insertion or deletion is called a(an) a. frameshift mutation. b. point mutation. c. chromosomal mutation. d. inversion.