Fossil Study Guide
advertisement

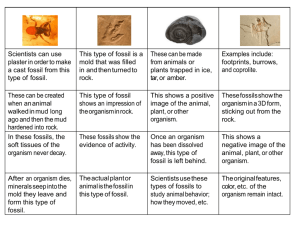
Fossil Study Guide Define the following vocabulary words: 1. Fossil: 2. Extinct: 3. Paleontologist: 4. Explain how a fossil is formed. 5. Are there more animal or plant fossils? Why? 6. What can scientists learn by looking at an animal’s fossil? 7. What can scientists learn about the area (environment) they find a fossil in? 8. How is making a model fossil with clay similar to how fossils are actually formed? 9. List the different types of fossils and explain each type. Define the following vocabulary words: 1. Fossil: the hardened remains of an animal or plant that lived long ago 2. Extinct: a living organism such as a plant or animal that no longer exists 3. Paleontologist: a scientist who studies fossils and organisms that lived long ago 4. Explain how a fossil is formed. First, an organism dies. Second, the soft parts of the organism decay or rot away. Third, dirt/mud covers the remains of the organism. Fourth, minerals replace the bones and fill any spaces left in the remains. Finally, the earth shifts and brings fossils to the surface. 5. Are there more animal or plant fossils? Why? There are more animal fossils because the soft parts of plants are easily destroyed as rocks form. Animals have bones and teeth that are not easily destroyed. 6. What can scientists learn by looking at an animal’s fossil? Scientists can learn the size and shape of animals that no longer exist. They can also learn how animals have changed over time. Fossil teeth can tell scientists what the animal ate. Scientists can learn that certain animals and plants lived at the same time if they are found in the same rocks. They can also study the rock layers to determine how old a fossil is. 7. What can scientists learn about the area (environment) they find a fossil in? Scientists can tell what that place was like long ago. For example, they can tell if that area was once under water if bones and teeth of sea creatures are found there. 8. How is making a model fossil with clay similar to how fossils are actually formed? Pressing an object into clay leaves an imprint of the object in the clay. The imprint is a mold of the object. If you fill the imprinted area with glue and let it harden. The hardened glue can be removed from the imprint. This represents a cast of the object. 9. List the different types of fossils and explain each type. Trace – marks left behind (dinosaur tracks in mud) Mold – the shape of a once living organism left in sediment (soil/mud) when rock formed. The organism that made the mold decays, leaving only a space shaped like the animal or plant. Cast – the actual shape of an organism formed when mud or minerals fill a mold





![F3-4 Study Guide for QUIZ [1/28/2016]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006814899_1-56a576b1a51c0f876f28a8da0f15de89-300x300.png)