CONCEPT 3: APPLYING THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF

CONCEPT 3: APPLYING THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE TO ANALYZE THE EFFECTS OF SEX CHROMOSOMES,
LINKED GENES, AND RECOMBINED RECOMBINES GENES
Campbell: Chapter 15
Goal: to analyze mechanisms of chromosomal inheritance
You must know:
How the chromosome theory of inheritance connects the physical movement of chromosomes in meiosis to
Mendel’s laws of inheritance
The unique pattern of inheritance in sex-linked and linked genes
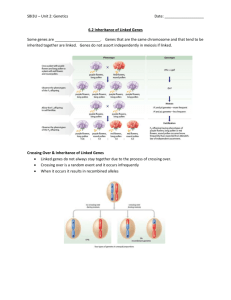
Remember...Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
What is the relationship between a pair of alleles and a homologous pair of chromosomes?
Since genes have specific locations on chromosomes (loci), when chromosomes segregate and assort independently so do the genes!
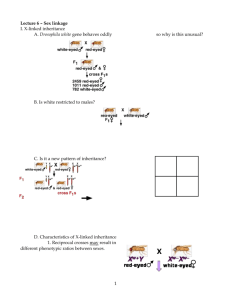
Sex-Linked Genes : A sex linked gene is a gene located on the X sex chromosome.
Would this individual be a male or a female? How do you know?
Morgan’s Sex-Linked Discovery in 1910!
Conclusion?
The gene for fly eye colour is found on the “X” sex chromosome!
Sex-Linked Genes – Checking in
Can Fathers pass sex-linked genes to their sons?
For males, do the terms homozygous and heterozygous apply?
Do most genes on the “X” sex chromosomes have to do with sex characteristics?
Colour Blindness: Sex-Linked Gene
What happens if you cross a normal female with a colour blind male?
What happens if you cross a carrier female with a normal male?
What happens if you cross a carrier female with a colour-blind male?
Other examples of Sex-Linked Genes:
Duchene Muscular Dystrophy
Hemophilia
Try This!
Neither Tom nor Rhonda has muscular distrophy, but their firstborn son has it. What is the probability that a second child will have this disease?
What if the child was a boy?
A girl?
X-Inactivation
Since females get two copies of the “X” sex chromosomes, they need to inactivate one of them!
Done by adding methyl groups to DNA... ______________________
Happens randomly in each cell when the female is an embryo
Inactive chromosome is called a ___________________________
Example of X-Inactivation: Calico Cats!
The kitten on the left (see the presentation slide) “CC” is an identical clone of the cat on the right “Rainbow”.
How can you explain the different colouring?
Why aren’t half of female’s colour blind?
AP Biology 11
Mendelian Genetics – Concept 3 (Part 1: Sex linked)
Name:____________________
Date:____________ Bl:_____
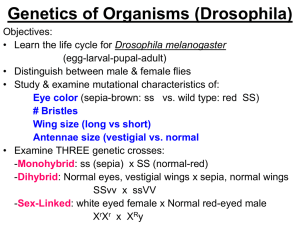
Try This! A culture of white-eyed fruit flies ( Drosophila melanogaster ) was maintained for many generations. Females from the stock white-eyed culture were crossed with red-eyed (wild-type) males. The F1 females were crossed with the white-eyed males from the original culture. The resulting phenotypes of the progeny are summarized below.
Parental Generation Cross
White-eyes x red eyed
females males
F1 Generation (500 flies)
100% females red-eyed
100% of males white-eyed
F1 Generation Cross
F1 red-eyed x white-eyed
females males
50% females red-eyed
50% females white-eyed
50% males red-eyed
50% males white-eyed
1. The best explanation for the red-eyed F1 females is
(A) mutation (B) culture contamination (C) dominance (D) multiple loci (E) sex-linked dominance
2. There are white-eyed females in the F2 generation because
(A) white is a dominant allele (B) the white allele is autosomal (C) a mutation has occurred
(D) these F2 females have two white alleles (E) the white allele is located in the Y chromosome
3. Which of the following best describes the mode of inheritance of eye-colour in the white culture?
(A) autosomal (B) dominant (C) located on Y chromosome (D) sex-linked (E) lethal