Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes Cells
advertisement

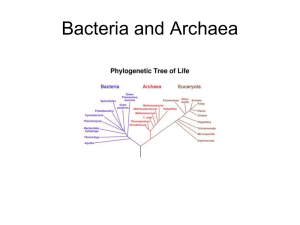
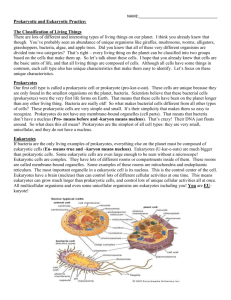
Sb1a..(standard) Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes Cells Eukaryotes/Prokaryotes asgn. # 2 Last:_____________________________First_______________________________Pd_____ Project Manager Last:_________________________________First____________________ 1. Membrane bound Nucleus 2. DNA 3. Lysosomes 4. Mitochondria 5. Flagella 6. Smooth ER 7. Rough ER 8. Golgi Apparatus 9. Cytoplasm 10. Ribosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Cell Wall 13. Vacuole 14. Chloroplast Bacteria Prokaryotes Plant Eukaryotes Animal Eukaryotes Found In (check ) Function Sketch Sb1a..(standard) Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cell Model Group project: Eukaryotes/Prokaryotes asgn. # 4 1. Form a group of 4 members close to where you’re seated, select a Project Manager. 2. As a group, complete Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Cells asgn. #2 3. As a group, complete Cell Simile asgn. #3 4. As a group create a Cell Model asgn #4 with representations for the Cell Functions. Your model must match your Simile Chart 5. Project Manager pick up 2 magazines & scissors from supply area, group members cut pics to match your Simile chart from magazines provided…If you are a talented artist, you may draw and use magazine pics. 6. Cut 14 squares to set up your similes, your set up should look like the example below Mitochondria & Battery provides ENERGY 7. Project Manager pick up1 poster sheet of paper from supply area, cut it in the shape of SQUARE for plant cell model CIRCLE for the animal cell and for the bacteria cell 8. Use your color pencils or word art on computers to make a heading for your MODEL. It should read a. EUKARYOTIC ANIMAL CELL b. EUKARYOTIC PLANT CELL c. PROKARYOTIC BACTERIA CELL 9. Write the Cell Theory along the bottom margin of your poster paper 10. Create side boarders of different types of organisms to represent a. EUKARYOTIC ANIMALS b. EUKARYOTIC PLANTS c. PROKARYOTIC BACTERIA 11. ANSWER Essential Questions IN COMPLETE SENTENCES ONLY. 12. Your model is reading for grading when posted outside, be sure all 4 names are printed clearly for grading Grading Rubric Name Exceed Meets NI INC No Expect. Expectation Work 4 3 2 1 0 Design – Boarder (visuals reflect examples of prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms) Design – Headings, Labels & Standards (accurate, easy to read) Design -Complexity (number of organelles represented, effort) Design -Accuracy (simile visuals are accurate and done according to example) Design - Effort, overall appearance Design- Writing (Essential Questions answered in complete Sentences & The Cell Theory) Assessment- Group members can do verb quiz with EQ’s TOTAL ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How many times larger is a eukaryotic cell than a prokaryotic cell? Which type of cell has membrane bound organelles? What’s one difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Which cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA? What are the structures within a eukaryotic cell that carries out specific activities called? 6. Which organelle moves proteins and other substances through the cell? 7. A cell that requires a lot of energy might contain large numbers of which organelles? 8. What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? Sb1a..(standard) Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes Coding Eukaryotes/Prokaryotes asgn. # 1 Last:_____________________________First_______________________________Pd_____ Prokaryotes cells are the simplest of all the cells. Bacteria are prokaryotes and they fall into two major categories: The Kingdom Eubacteria and the Kingdom Archaebacteria. Eubacteria are common types that occur all around us, usually they are on surfaces and in the soil. You can only find Archaebacteria in extreme environments, like hot sulfur springs. Archaebacteria are thought to be some of the oldest life forms on earth. Most bacteria don't make their own food. That means they have to rely on other organisms to provide them with food. These bacteria have to break down, or decompose, other living things to obtain energy. When most people hear the word bacteria, they think of something that is bad for you. In fact, very few bacteria cause illness. Some bacteria actually help you! Bacteria are used to make food, such as cheese and yogurt, and they can also help us break down harmful substances in the environment. Scientists created a type of bacteria that could gobble up oil from oil spills. Some bacteria live inside the guts of animals and help them to digest food. Unfortunately, there are many types of bacteria that can make us ill. Salmonella bacteria can cause food poisoning, and certain types of bacteria are responsible for other infections. You might have had some experience with Streptococcus, the bacteria that causes strep throat. Bacteria have a very simple cell design. Most of them have a thick outer covering called the cell wall. On the picture, color the cell wall purple (it’s the outermost layer). Just within the cell wall is the cell membrane. Color the cell membrane pink. Along the surface of the bacteria cell, you might encounter structures called pilus, whose job is to help the bacteria stick to surfaces. Color all the pilus light green. Bacteria might also need to move around in their environment, so they can have structures called flagella, which resemble tails. Find the two flagella pictured and color them dark green. The watery interior of the cell is called cytoplasm, and it has the texture of jello. Color the cytoplasm light blue. Sprinkled throughout the cell are small roundish structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes make proteins for the cell. Color all of the ribosomes red. Every prokaryote cell has DNA floating within the cytoplasm, which usually looks like a twisted strand of spaghetti. DNA contains the instructions for the cell, basically it is the control center. Find the DNA and color it yellow. Name the organelles and assign them a color (by groups) 1._________________________gr. color 3._________________________gr color 5._________________________gr color 7._________________________gr color 2.____________________gr color 4.____________________gr color 6.____________________gr color 1. What bacteria causes strep throat? _______________________________________ 2. What are the oldest life forms on earth? ___________________________________ 3. What type of bacteria causes food poisoning?________________________________ 4. What part of the bacteria cell helps it stick to surfaces?_________________________ 5. Name two foods that bacteria help make:_____________________________________ 6. What does “decompose” mean?_____________________________________________ 7. What is the control center of the bacteria cell?__________________________________ 8. What part of the bacteria cell helps it move?____________________________________ 9. Where do Archaebacteria live?______________________________________________ 10. To what kingdom do common bacteria belong? ________________________________ Animal Cell Coloring I. Directions: Color each part of the cell its designated color. Cell Membrane(light brown) Nucleolus (black) Mitochondria (orange) Cytoplasm (light yellow) Golgi Apparatus (pink) Lysosome (purple) Nucleoplasm (pink) Flagella (red/blue striped) Microtubules (dark green) Nuclear Membrane(dark brown) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (dark blue) Ribosome (red) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum( light blue) II. Briefly describe the function of the cell parts. 1. Cell membrane ______________________________________________ 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum _________________________________________ 3. Ribosome ____________________________________________________ 4. Golgi Apparatus ____________________________________________________ 5. Lysosome ____________________________________________________ 6. Microtubule ____________________________________________________ 7. Mitochondria ____________________________________________________ 8. Nucleus ____________________________________________________ Name:_______________________________________ Plant Cell Coloring Cell Membrane (orange) Nucleoplasm (yellow) Mitochondria (red) Vacuole (lt. Blue) Chromatin (gray) Cell Wall (dark green) Nucleolus (brown) Chloroplasts (light green) Ribosome (purple) Cytoplasm (white) Golgi Apparatus (dk blue) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (pink) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (pink) Analysis 1. Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell: 2. How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? 3. What is the function of the chloroplasts? 4. What is the function of the vacuole?