pediatric emergency
advertisement

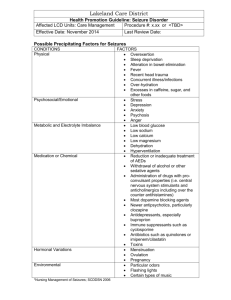
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY The ABCD The A Arousal Alertness Activity Apathy The B Breathing difficulties The C Poor Color (pale) Circulation (Cold peripheries) The D Decreased fluids intake (fewer than half a normal intake) and Decreased urine output (fewer than 4 wet nappies a day) Level of Awareness (AVPU) A - Alert V - Responds to Voice P - Responds to Pain U - Unresponsive Neonatal Resuscitation Adrenaline IV: 10 – 30 mcg / kg Apgar Score Appearance Pulse Grimace Activity Respiration Shock Definition: Inadequate circulation to meet the tissues’ demands Etiology: Hypervolemia Viral gastroenteritis Maldistribution of fluid: o Sepsis o Anaphylaxis Symptoms: EARLY (Compensated shock) o Tachypnea and tachycardia o Sunken eyes and fontanels o Mottled, pale, cold skin o Decreased skin turgor o Decreased capillary refill (> 2 sec) o Decreased urinary output (< 1 ml/kg/h) LATE (Decompensated shock) o Confusion / depressed cerebral state o Bradycardia o Hypotension o Blue peripheries o Absent urine output Hypervolemia (Treatment) 0.9 % saline IV Blood if trauma Septicemia (Meningococcal Purpura) Poor State Fever Rash Negative Glass Test Severe State Positive Glass Test Fever Poor feeding Irritability, lethargy Tachycardia Tachypnea Hypotension Shock, multi organ failure Purple rash Seizures Definition: Uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain, which may produce a physical convulsion. Status epileptics: Seizure lasting 30 min Successive frequent seizures with unconsciousness Febrile seizures: Seizure accompanied by a fever in absence of intracranial infection Etiology: Febrile seizures – any infections & fever Metabolic: o Hypoglycemia, o Hypocalcaemia o Hypomagnesaemia o Hypo/hypernatremia Meningitis and encephalitis Cerebral trauma or tumor Toxins (poison, metabolic disorders) Epilepsy and others Dyspnea – Croup Definition: The degree of subcostal, intercostal and sternal recession is a more useful indicator of severity of upper airways obstruction than the respiratory rate. Symptoms: Viral 6 months to 6 years Harsh Loud stridor Cold Mild fever Dyspnea – Asthma Examination: History of allergy or asthma Symptoms: Too breathless to eat or talk Use of accessory muscles Distended chest Wheeze or silent chest Cyanosis and alter level of consciousness Anaphylaxis Definition: Severe, whole – body reaction to an allergen, after being previously exposed to this allergen (sensitization to it). This reaction happen very quickly. Examination: • History of allergy / anaphylaxis • Food or insect sting venom allergy Symptoms: Airways: o Swelling o Hoarseness o Stridor Breathing: o Tachypnea o Wheeze o Cyanosis (SpO2< 92 %) Circulation: o Pale o Clammy o Hypotension o Drowsy o Coma