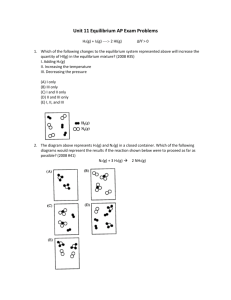
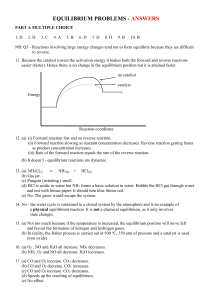
III. Equilibrium (pg. 2a) AP Chemistry 1) Given the reaction below at
advertisement

III. Equilibrium (pg. 2a) AP Chemistry 1) Given the reaction below at equilibrium, state and explain the effect (increase, decrease or no change) the quantity on the right hand column, given the operation in the left column below. Each operation is to be considered separately. 2 Cl2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) ↔ 4 HCl (g) + O2 (g) ∆H = + 27 kJ What type of reaction, in terms of heat, is the above reaction? Stress a) increasing volume of container Shift Effect concentration of water b) increase concentration of chlorine value of equilibrium constant c) Increase concentration of chlorine concentration of HCl d) increase concentration of oxygen concentration of water e) increase concentration of oxygen concentration of HCl f) increase concentration of oxygen value of equilibrium constant g) decrease volume of container concentration of chlorine h) decrease volume of container concentration of oxygen i) raising temperature concentration of water j) raising temperature concentration of HCl k) lower temperature value of equilibrium constant l) adding He concentration of oxygen m) adding a catalyst concentration of chlorine n) lowering temperature concentration of water o) adding HCl amount of heat p) taking away HCl as it is formed concentration of oxygen 2) Given the reaction below at equilibrium, state and explain the effect (increase, decrease or no change) the quantity on the right hand column, given the operation in the left column below. Each operation is to be considered separately. 2 C (s) + O2 (g) ↔ 2 CO (g) ∆H = - 26.41 kJ What type of reaction, in terms of heat, is the above reaction? Stress a) increasing volume of container Shift Effect concentration of oxygen b) increase concentration of oxygen concentration of carbon c) increase concentration of oxygen concentration of CO d) decrease volume of container amount of heat e) decrease volume of container value of equilibrium constant f) raising temperature value of equilibrium constant g) raising temperature concentration of CO h) raising temperature concentration of oxygen i) adding He concentration of CO j) adding a catalyst concentration of carbon k) lowering the temperature concentration of CO l) increase concentration of CO amount of heat m) taking away CO as it is formed concentration of oxygen 3) You are given a box in which PCl5 (g), PCl3 (g) and Cl2 (g) are in equilibrium with each other at 546 K. Assuming that the decomposition of PCl5 to PCl3 and Cl2 is endothermic, what effect would there be on the concentration of PCl 5 in the box if each of the following changes were made a) add Cl 2 to the box, b) reduce volume of the box and c) raise the temperature of the system d) add PCl5 to the reaction e) remove Cl2 as it is formed f) add Ar at constant pressure g) add Ar at constant volume 4) Consider the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g) ↔ 2 NO2 (g) ∆H = 58.0 kJ In what direction will the equilibrium shift when each of the following changes is made to the system at equilibrium: a) add N2O4; b) remove NO2; c) increase the total pressure by adding N2 (g); d) increase the volume; e) decrease the temperature? f) add Ar at constant pressure g) add Ar at constant volume