USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson
advertisement

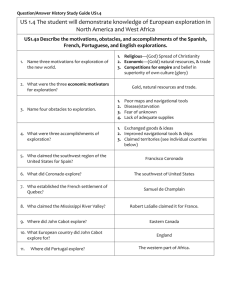
2012-13 DO NOT LOSE THIS STUDY GUIDE! DO NOT TRASH! USI.4 [USI.4 EUROPEAN EXPLORATION STUDY GUIDE TARA JOHNSON] [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document. Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.] USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 American Indians established their own diverse (different) cultures in America long before the Europeans arrived. The Indians walked the paths through the land and learned the land by experience. They know of the waters, the trees, the landforms, and the various animals. They tilled the earth and grew plants for food, dyes, medicines, and cloth. They domesticated (tamed) animals, established patterns of trade, built towns, produced architecture, developed systems of beliefs, and created systems of government. American Indians related to diverse and demanding environments, not only by adapting their ways to it, but also by shaping the physical environment to meet their needs. For example, by building irrigation (water) systems and using fire to clear brush, they prepared land to grow crops and helped the growth of wild game. They were the first people to inhabit this land. It was their homeland. After the arrival of European explorers, American Indians struggled to preserve their cultures while adapting to rapidly changing conditions. The Europeans brought many diseases from their countries, such as smallpox, the most deadly. The Europeans established permanent settlements in America and forced the Indians to move away from their Tribal homelands. The Indians believed that the land was to be used and shared but not owned, while the Europeans, particularly the English, claimed private ownership of land. This disagreement resulted in a serious conflict between the American Indians and the Europeans. The relationship between Europeans and American Indians sometimes led to cooperation (getting along) and other times resulted in conflict (problems). Let’s look at how the Spanish, the French, and the English brought changes to the settlers and the Indians. Study the graph on the next page. 1|Page USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson Spanish French Conquered and enslaved American Indians Brought Christianity to the New World Brought European diseases to American Indians Established trading post Spread Christianity religion English Established settlements and claimed ownership of land Learned farming techniques from American Indians Traded with American Indians How did they (explorers and American Indians) get along? Areas of cooperation existed between the cultures: 1. Europeans brought weapons and metal farm tools to the American Indians. 2. Trade 3. Crop What did they (explorers and American Indians) disagree over? Areas of conflict existed between the cultures: 1. Land 2. Competition for trade 3. Differences in cultures 4. Diseases 5. Language differences 2|Page 2012-13 American Indians Taught farming techniques to Europeans settlers Believed that land was to be used and shared but not owned USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 Why explore? There were several motivational forces for countries to explore. A motivation is a reason to want to do something. The first motivation for exploration is economic. Countries wanted gold, natural resources, and trade. Second, is religiously motivated. Countries wanted to spread Christianity in the New World. Last, competitions for empire and belief in superiority of own culture. The idea that more is bigger and better. There were several obstacles in exploration. Poor maps and navigational tools often misguided exploration. Explorers would often die of disease or starvation. Explorers lacked supplies and feared the unknown. Although there were several obstacles in explorations, there were also many accomplishments. Cultures were able to exchanges goods and ideas. They learned to improve navigational tools and ships. Each country; Spain, France and England, were able to claim territories in the New World for themselves. 3|Page USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 Let’s look at these three countries, who they sent to explore for them and what they claimed. Explorer What did he claim? Spain France France England Francisco Coronado Robert La Salle Samuel De Champlain John Cabot 4|Page Claimed southwest United States for Spain Claimed the Mississippi River Valley Explored the Great Lakes Claimed a huge area of land , from the Appalachian Mnts, to the Rocky Mtns. And from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico Established a French settlement in Quebec Explored Eastern Canada Explored what is now Newfoundland USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 On the maps below, locate and label each explorer’s claim. Coronado’s Route for Spain. Notice how it covers southern United States. Robert La Salle’s Route for France. Down the Mississippi Valley Champlain’s route for France. This is a map of Northeastern United States. He settled Quebec. John Cabot’s route for England. He explored eastern Canada and Newfoundland. 5|Page USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 Africa The empires of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai dominated West Africa, one after another, from 300 to 1600. The Empire of Ghana was the first empire in West Africa. It was rich in gold and traded gold for salt and cloth. Muslims conquered Ghana around 1200 and built the Empire of Mali. Mali had a powerful leader named and Musa who used his army to increase Mali’s wealth. The Empire of Mali was replaced by the Songhai Empire. Trade and farming were important to the Songhai Empire. The Songhai Empire remained powerful until about 1600. Each empire used its location as a center of trade for West Africa and became powerful by controlling trade in the area. Ghana, Mali, and Songhai were located in the western region of Africa, south of the Sahara Desert, near the Niger River. _______ 6|Page _______ _______ USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson Ghana •First West African Empire •Rich in Gold Mali •Muslims conquered Ghana in 1200 •Leader named Musa Songhai 2012-13 •Stayed until 1600 •Trade & Farming were important *** To help you remember Ghana-Mali-Songhai, just think of your ABCs. They are in ABC order *** Portuguese sailors began to explore the West African coast in the 1400s. The Portuguese were interested in the gold trade as well as the buying and selling of enslaved Africans. Portuguese made voyages of discovery along West Africa. The Portuguese carried goods from Europe to the West African empires, trading metals, cloth, and other manufactured (manmade) goods for gold. Ghana, Mali, and Songhai became powerful by controlling trade between Europe and West Africa. **African people and African goods played an important role in arousing European interest in world resources. ***African people and African goods played an important role in arousing European interest in world resources. African goods encouraged explorers to look for more in the world around them. 7|Page USI.4 European Exploration Study Guide Tara Johnson 2012-13 Lets Sum up the unit: There were several reasons why they wanted to explore the New World: 1) Economic Reasons: they wanted to find gold, natural resources, and to trade 2) Religious Reasons: they wanted to spread Christianity 3) Competition: they wanted to own more land than anyone else and believed their culture was best But, there were problems... 1) they had poor maps and navigational tools 2) there was little food and many became sick or died from starvation or disease 3) they were afraid of what was over in the New World, since no one had been before 4) they did not have appropriate supplies Some explorers achieved great things from exploring the New World: 1) they exchanged goods and ideas 2) they were able to improve navigational tools and ships 3) they claimed new territories Sometimes there was cooperation between the Explorers and the Native Americans: 1) Technologies-- they shared knowledge about transporting weapons and farm tools 2) They traded with one another 3) Native Americans taught the Explorers a great deal about crops But at other times, there was conflict: 1) Who owned the land? 2) They competed for trade 3) There were many differences between European and Native American cultures 4) Disease was brought over by the Explorers 5) They spoke different languages, so communication was very difficult 8|Page