here
advertisement

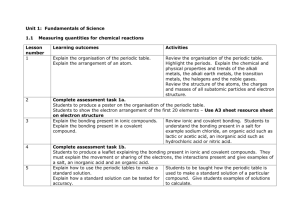
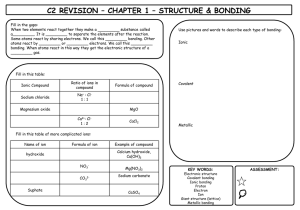
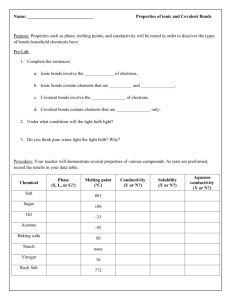
Waseley Hills High School BTEC Level 1/2 First Award in Principles of Applied Science Unit 2: Chemistry and Our Earth Name: Start Date: Interim deadline: Deadline Date: Related Unit content: Learning aim A: Investigate chemical reactivity and bonding (Part 2) Bonding and structure: a. formulae of molecules b. covalent bonding (hydrogen, chlorine, carbon dioxide, methane, water, oxygen) c. ionic bonding (sodium chloride, magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride) d. properties of simple covalent, giant covalent and ionic materials. Assignment A Chemical Bonding & Structure Scenario You work for a chemical company as a quality control laboratory technician. It is important to understand how chemical substances are bonded together, in order for you to carry out laboratory tests on products as they are produced and determine what uses they could have. As part of an induction day for new recruits, you will need to present material showing how substances are formed through ionic or covalent bonding, and how their properties are related to their bonding and structure. Task 1: Why things don’t fall apart On the induction day, a simple experiment will be used as a teamwork and ‘icebreaking’ exercise. You need to try the experiment first to get a standard set of results to be used when checking the experiments conducted by people on the induction day. 1. a) Carry out the practical experiment ‘Investigating the properties of substances’. b) Write up the practical by recording the results appropriately in the observations table, make relevant conclusions and comparisons between the different properties of the substances tested and answer the questions on the worksheet (2.A P2) 2. a) In order to prepare the new recruits for their work, you need to produce a written report called ‘Bonding, structure and applications of chemical substances’. Include in your report detailed notes and fully labelled diagrams about the following: (i) the chemical formulae and ‘dot-and-cross’ diagrams of ammonia, carbon dioxide, chlorine, hydrogen, magnesium chloride, magnesium oxide, methane, nitrogen, oxygen, sodium chloride, sodium oxide, water. (2.A P3) (ii) an account of how the following chemical substances are formed from their atoms, mentioning the type of chemical bonds formed in each case: sodium chloride, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, magnesium chloride, methane, water. (2.A M3) RESOURCES (iii) how the observed properties of the substances investigated in the practical (see part 1a) can be explained in terms of the type of chemical bonding and the chemical structure present. (2.A M2) (iv) the applications and uses of sodium chloride and silicon dioxide, stating how their applications link to their properties and how the type of chemical bonding and their chemical structure are also related to their properties.(2.A D2) (v) a concluding statement about the properties of ionic and covalent substances. (2.A M2) and their applications (2.A D2) The grading criteria that this assignment relates to: P2 Compare properties of ionic and covalent substances P3 Draw dot-and-cross diagrams of simple ionic and covalent substances M2 Explain the properties of ionic and covalent substances M3 Describe the formation of ionic and covalent substances D2 Relate applications of compounds to their properties and to their bonding and structure If you have not achieved the Level 2 criteria, your work will be assessed to determine if the following Level 1 criteria have been met. Criterion To achieve the criteria you must show that you are able to: Unit reference Describe properties of ionic and covalent substances 2 1A.2 Classify substances as ionic or covalent 2 1A.3 Evidence you must produce for this task; Level 2A.P2 2A.P3 2A.M3 Part 2A.M2 Part 2A.M2 Part 2A.D2 Part 2A.D2 Description Table 4- Practical and observation sheet Questions on worksheet task 2a questions Dot and cross diagram for Ammonia Dot and cross diagram for Carbon dioxide Dot and cross diagram for Chlorine Dot and cross diagram for Hydrogen Dot and cross diagram for Magnesium chloride Dot and cross diagram for Magnesium oxide Dot and cross diagram for Methane Dot and cross diagram for Nitrogen Dot and cross diagram for Oxygen Dot and cross diagram for Sodium chloride Dot and cross diagram for Sodium oxide Dot and cross diagram for Water Report on how Sodium chloride is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Hydrogen is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Oxygen is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Nitrogen is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Magnesium chloride is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Methane is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report on how Water is formed and the type of bonding it contains. Report explaining the properties of ionic substances Report explaining the properties of simple covalent substances Report explaining the properties of giant covalent substances Concluding statement on the properties of ionic and covalent substances Table 5- completed Description of the uses of sodium chloride related to its properties Description of the uses of silicon dioxide related to its properties Checklist Learner Assessment Submission and Declaration This sheet must be completed by the learner and provided for work submitted for assessment. Learner name: Date issued: Assessor name: Completion date: Submitted on: Qualification: BTEC Level 1/2 First Award in Principles of Applied Science Assessment reference and title: Unit 2: Chemistry and Our Earth, Assignment A (part 2) Task ref. Evidence submitted Page numbers or description Learner declaration I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own. I have clearly referenced any sources used in the work. I understand that false declaration is a form of malpractice. Learner signature: ________________________________Date:_______________ Summary assessor’s feedback Signed: Dated: Internal verifier’s comment Signed: Dated: