GALE2
advertisement

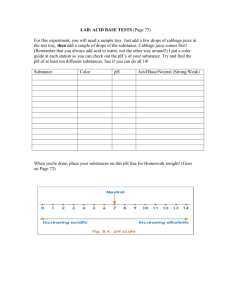
Bio 405 GALE 2 Atoms Part 2 Assessment: Students will be given several substances, which include, sand, dink mix, lemon juice, prepared household ammonia, vinegar, liquid soap, and shampoo, tap water, baking soda (aq), white vinegar, corn syrup (aq). They will also bring in a liquid from home to see the results. They will determine the difference between mixture and solution. They will look at acid, bases, and figure, which substance is which. Learning Goal: Students will be able to show chemical reactions, the difference between solutions and mixtures. They will have a basic understanding of acid and bases. This is a background to feature lessons. Learning Experience: The students will have an opening exercise that will have them explore what they know about compounds, mixtures/solutions and acid and bases. This will also have them show what they want to learn about compounds, mixtures/solutions, acid, and bases. They then will be broken up into groups of two, to work on a lab. They will choose what section they have more interest on (acid/base or mixture/solution) and then they will teach to another group. Instructional Objectives: 1) Students will identify important properties of chemical reactions by filling in a worksheet that goes along with their assigned reading on chemistry. 2) Students will show learn how to identify acids and bases using common household substances as pH indicators as part of a lab activity. Students will demonstrate their proficiency by identifying the pH of an unknown with an accuracy of + or – 1.0. 3) By working with various solutes and investigating their reaction when mixed with water in a classroom lab situation, students will be able to describe the difference between a mixture and a solution. Benchmarks A living cell is composed of a small number of chemical elements mainly carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, and sulfur. Carbon, because of its small size and four available bonding electrons, can join to other carbon atoms in chains and rings to form large and complex molecules Bio 405 This will teach the students what a chemical reaction is and what are some types of reactions are. This activity will teach the student and let them explore what an acid and base is; it will have them experiment with mixtures and solutions. This will all deal with chemical reaction to understand how things are acid or base or how to make a solution. Students will all perform the chemical reaction part, but will be able to choose between the acid and base or the mixture and solutions. Chemical Reaction Directions: Using your book answer the following questions about Chemical reaction 1. What is a chemical reaction? A chemical Reaction occurs when bonds are broken or formed. This will create different substances. 2. What makes chemical reactions to work? The moving of electrons in bonds from compounds to form other compounds 3. How are chemical reactions written out and why is it important to be able to write them out. They are written out by what goes in and what comes out. It shows what happens to the elements or compounds. 4. Why are chemical reactions important to organism? Chemical Reactions occur inside cells. These reactions make it possible for organism to function Acid and Base Students will be given lemon juice, prepared household ammonia, liquid soap, and shampoo, tap water, distilled water, baking soda (aq), white vinegar, corn syrup (aq), and liquid from home. The color indicator we will use is the juice of a red cabbage. Directions: 1. Make predictions of whether it will be an acid, base or neutral. 2. Place one dropper of each solution into separate test tubes to be tested. Make sure to label them. Record the color in the table. 3. Then place one dropper of cabbage juice into each test tube. Record the resulting color in the table. Lab Results Recording Table SOLUTION SUBSTANCE PREDICTION (ACID, BASE, NEUTRAL) COLOR AFTER ADDING ACID/BASE/NEUTRAL? Bio 405 AGENT (Cabbage Juice) Tap Water Pink Acid Distilled Water purple Neutral Baking Soda (Aq) Blue/Green Base White Vinegar Pink Acid Liquid Soap (Aq) Pink Acid Corn Syrup (Aq) Pink Acid Ammonia Blue/Green Base Shampoo Blue/Green Base Lemon Juice Pink Acid 4. Tell whether the solution is acid or base determined by the color. The solutions that show no change of color are neither acids nor bases, and can be generally thought of as having a neutral pH. Solution substances that turn the cabbage juice color indicator pink are acidic. Solution substances that turn the cabbage juice color indicator blue or green are basic. Questions: 1) Were the results different from expected? The answer may very but it gets them thinking about what they thought and what they got. 2) What defines an Acid? The formation of H+ ions when a substance mixed in water. 3) What defines a Base? The formation of OH- ions when a substance mixed in water. 4) Show a chemical equation for an acid and base reaction Bio 405 Base: NaOH + H2O -> Na+ + OH- + H2O Acid: HCl + H2O -> H+ + Cl- + H2O Mixtures and Solutions Students will be given sugar, sand, and dink mix. Directions: follow the steps and the questions 1) Mixing the sugar and sand, what is seen? They mix and you can see the difference. 2) Are they mixable? Yes, they mix pretty well. 3) What can be done to split them up? Mixing the mixture in water. The sugar will dissolve and the sand will not. 4) Mixing the sugar, and drink mix, what happens? They mix and you can see the difference 5) What is the difference between this and the sugar and sand? They look about the same but the colors. They both mix together well. 6) What happens when they are put in water and mixed? They do not come apart they both dissolved. 7) Explain the difference between the two mixings. You can see the two elements before they were both mixed in water. 8) Define Mixture. A combination of substances in which the individual components retain its own properties 9) Define Solution. A mixture in which one or more substances are distributed evenly in and other substance. 10) What is the difference between mixture and solution? A mixture can be separated, where as a solution cannot be separated. Bio 405 Name: Date: Period: Chemical Reactions with Acid and Base and Mixtures and Solutions Chemical Reaction Directions: Using your book answer the following questions about Chemical reaction 1. What is a chemical reaction? 2. What makes chemical reactions to work? 3. How are chemical reactions written out and why is it important to be able to write them out. 4. Why are chemical reactions important to organism? Acid and Base Directions: 1. Make predictions of whether it will be an acid, base or neutral. 2. Place one dropper of each solution into separate test tubes to be tested. Make sure to label them. Record the color in the table. 3. Then place one dropper of cabbage juice into each test tube. Record the resulting color in the table. Bio 405 Lab Results Recording Table Name____________ SOLUTION SUBSTANCE PREDICTION (ACID, BASE, NEUTRAL) Date _______________ COLOR AFTER ADDING AGENT ACID/BASE/NEUTRAL? (Cabbage Juice) Tap Water Distilled Water Baking Soda (Aq) White Vinegar Liquid Soap (Aq) Corn Syrup (Aq) Ammonia Shampoo Lemon Juice 4. Tell whether the solution is acid or base determined by the color. The solutions that show no change of color are neither acids nor bases, and can be generally thought of as having a neutral pH. Solution substances that turn the cabbage juice color indicator pink are acidic. Solution substances that turn the cabbage juice color indicator blue or green are basic. Bio 405 Questions: 1. Were the results different from expected. 2. What defines an Acid? 3. What defines a Base? 4. Show a chemical equation for an acid and base reaction Mixtures and Solutions Directions: follow the steps and the questions 1. Mixing the sugar and sand, what is seen? 2. Are they mixable? 3. What can be done to split them up? 4. Mixing the sugar, and drink mix, what happens? 5. What is the difference between this and the sugar and sand? 6. What happens when they are put in water and mixed? 7. Explain the difference between the two mixings 8. Define Mixture. 9. Define Solution 10. What is the difference between mixture and solution?