(sedimentary) rocks
advertisement
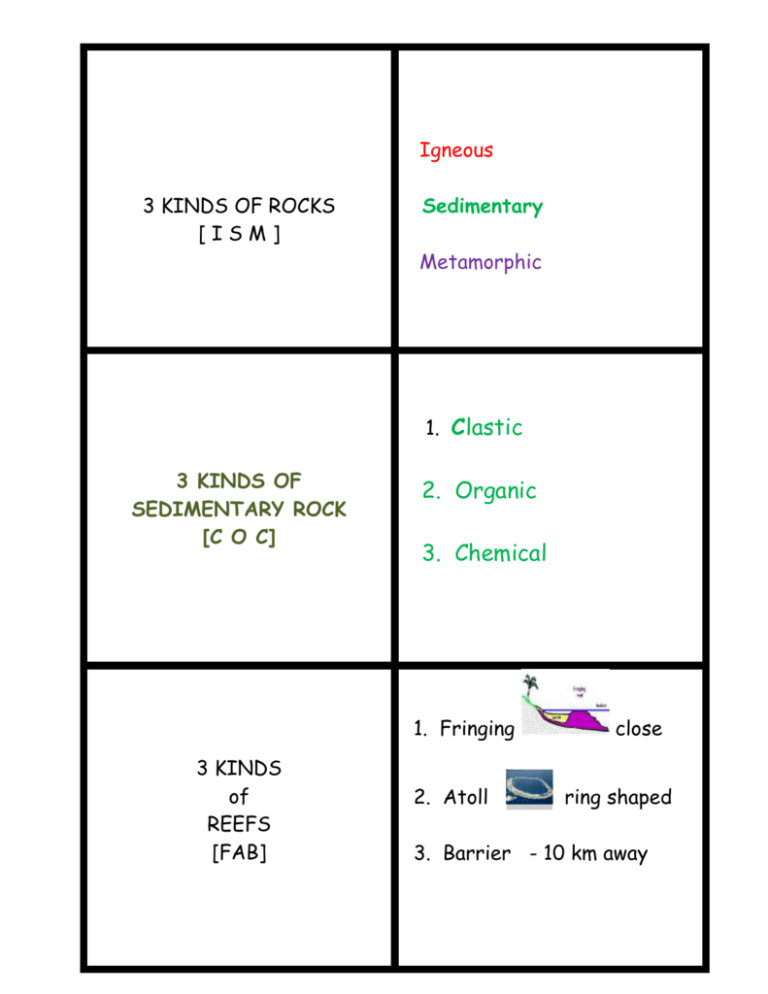
Igneous 3 KINDS OF ROCKS [ISM] Sedimentary Metamorphic 1. Clastic 3 KINDS OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK [C O C] 2. Organic 3. Chemical 1. Fringing 3 KINDS of REEFS [FAB] 2. Atoll close ring shaped 3. Barrier - 10 km away 2 KINDS of INTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS EXTRUSIVE Common INtrusive Common EXtrusive granite basalt CLASTIC 4 Examples of Clastic Rocks Shale tiny clay pcs. Sandstone sand Conglomerates round particles Breccia jagged particles Organic ORGANIC (sedimentary) rocks 3 Steps in Sedimentary Rock Formation 1. Coal 2. Limestone (chalk) 1. Erosion 2. Deposition 3. Compaction & Cementation EROSION DEPOSITION COMPACTION Water, winds, gravity or ice MOVES or CARRIES soil and rock pieces away Sediment SETTLES or is DEPOSITED in a new place Sedimentary rocks are PACKED or PRESSED together [ can see dull layers ] CEMENTATION texture Silica DISOLVED MINERALS CRYSTALIZE AND GLUE, OR CEMENT, PIECES OF SEDIMENT TOGETHER The size, shape, and pattern of a rock’s grain High in silica (lots of it) light colored rock FELSIC Low in silica dark colored rock MAFIC [Mafia bad guy in black] 3 Examples of Chemical rocks Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic Rocks 1. 2. 3. Limestone Gypsum Rock salt Heat, pressure or chemical changes old rocks into new rocks Foliated (bands) orr Non-foliated (NO bands) Examples of FOLIATED Non FOLIATED Slate Schist Gneiss (nice!) marble quartzite Porphritic rock sediment INtrusive has BOTH large and small crystals The small particles of rock or remains of living things that make up sedimentary rock Formed by cooling magma deep IN the earth EXtrusive Formed by cooling lava on the Earth’s surface Coarse grained Large grains; easy to see Fine grained Tiny grains; need magnifying glass to see Metamorphic rock Organic limestone Classified by arrangement / pattern of grain Found on continents (ex. Mountains ) because the Earth’s ancient sea floors has been RAISED above sea level