Rock notes - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

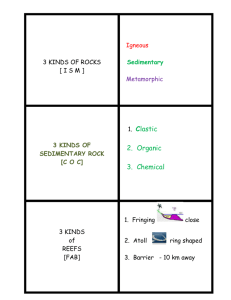
Rocks What is a rock? Naturally occurring, solid. How many minerals do you need in a rock? Most rocks have a variety of minerals but obsidian and coal have none. How do geologists categorize rocks? In various ways but one important way is the way they form. Sedimentary through erosion, deposition, and cementation. Pressure pushes loose sediment together into a rock. Igneous molten material cools on or in Earth. Metamorhic rocks are heated and pressured additionally. Igneous rocks can be intrusive (formed in the earth) or extrusive (formed on the earth) Which has more visible crystals? Intrusive because it has more time to get with its friends and form a group. Extrusive is like a fire drill. Everyone is just going out of the building and there is not time to find friends. Metamorphic rocks can be foliated or non foliated. Foliated (neat folded laundry) has visible lines that show how the rock was pressed down GNEISS OR SLATE. Non foliated just looks normal with no parallel lines QUARTZITE OR MARBLE. Know how each rock can become the other rock. What is a sedimentary rock and how do they form? Sedimentary rocks form by the weathering and erosion of preexisting rocks or from the deposition of organic material. When preexisting rocks are exposed at the surface they are subjected to chemical and mechanical weathering, which breaks them down into small pieces called sediment. The sediment is then transported by ice, water, or wind to another location where it is deposited, commonly in horizontal layers or strata. Compaction occurs as more and more sediment is deposited. In many cases, dissolved minerals recrystallize and cement the sediments together as well. When compaction and cementation change the sediment into rock, lithification occurs. There are three major types of sedimentary rock—clastic, chemical, and organic. A clast is a piece of rock or the hard part of an organism, such as a shell or bone. Thus, when clasts are compacted or cemented together, they form clastic sedimentary rock. Chemical sedimentary rock forms when dissolved minerals or organic materials recrystallized out of a water solution. One example of a chemical sedimentary rock is chemical limestone, which forms at the bottom of the ocean. Another is rock gypsum, which forms as water evaporates from shallow lakes. Organic sedimentary rock forms from the depositing of large amounts of organic material, as occurs in areas such as swamps.