RNA Transcription and Protein Synthesis via Translation
advertisement

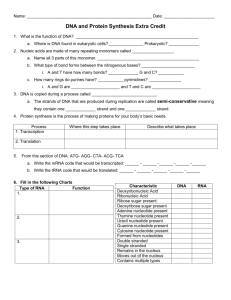
RNA Transcription and Protein Synthesis via Translation Name: ___________________________ Objective: Formulate a model to show how the order of bases in DNA determines the order of bases in mRNA and infer why the structure of DNA enables it to be easily copied. In addition show how proteins are translated from the mRNA Materials: DNA nucleotide templates RNA nucleotide templates scissors Plain paper clear tape colored pencils or markers Assigned order of DNA bases Procedure: 1. Color the DNA template nucleotides and RNA template nucleotides with these colors: deoxyribose – orange adenine - red ribose – brown thymine – green phosphate – black guanine – blue cytosine – yellow 2. Cut out the nucleotides and arrange 6 DNA nucleotides (as a single strand) in the order given to you by your teacher. Tape the nucleotides together. This will only be half of your DNA molecule. Tape this strand onto a blank sheet of paper. 3. Arrange and tape the DNA nucleotides that complement the other half of your DNA molecule (G-C and T-A). Tape this second strand onto the paper halfway unzipped. Put a circle around the DNA strand and label this as the nucleus. 4. Using only the original strand of DNA, begin matching complimentary mRNA nucleotides and tape these together (A-U and G-C). Tape these beside and perpendicular to your DNA strand onto the blank paper. 5. Draw 2 circles (snowman shaped) with your mRNA intersecting the 2 circles. Label these 2 circles as the ribosome. 6. Reading left to right turn each group of 3 bases (codons) into complementary anticodons (G-C and A-U). Using the amino acid code seen below, determine which anticodon translates into which amino acid, there are 4 amino acids produced. 8. At the end of your mRNA strand draw the last anticodon, a tRNA (as a rectangle) and the 4 amino acids produced (as labelled circles) in order. The first amino acid produced will be on the bottom of the linked amino acids, the last one produced will be on the top. These linked amino acids make a protein. Conclusions: 1. What are the 3 components of a DNA molecule? 2. What sugar is in DNA_________________ in RNA _________________? 3. Which base pairs bond together in a DNA molecule? 4. Which base pairs bond together in an RNA molecule? 5. How do DNA strands and RNA differ? (2 ways) 6. How many bases are in a codon________ in an anticodon________; how are these 2 different from each other? 7. What is the process of making mRNA from DNA called; where does it occur? 8. What is the process of assembling a protein (amino acids linked together) called, where does it occur? 9. How many amino acids are linked to a single tRNA? 10.DNA code mRNA sequence Anticodon sequence Amino acids sequence GTA TCC CTT GAC TTC AAA GGG CCC ATG