Chapter 1
advertisement

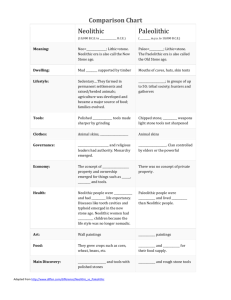
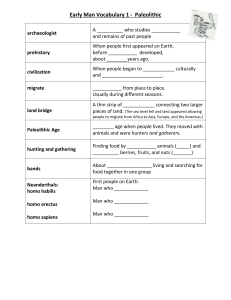
Chapter Glossary Ch. 1 Glossary agricultural revolution (ancient) The change from food gathering to food production that occurred between ca. 8000 and 2000 B.C.E. Also known as the Neolithic Revolution. australopithecines The several extinct species of humanlike primates that existed during the Pleistocene era (genus Australopithecus). bipedalism The ability to walk upright on two legs, characteristic of hominids. culture Socially transmitted patterns of action and expression. Material culture refers to physical objects, such as dwellings, clothing, tools, and crafts. Culture also includes arts, beliefs, knowledge, and technology. evolution The biological theory that, over time, changes occurring in plants and animals, mainly as a result of natural selection and genetic mutation, result in new species. foragers People who support themselves by hunting wild animals and gathering wild edible plants and insects. Great Ice Age Geological era that occurred between ca. 2 million and 11,000 years ago. As a result of climate shifts, large numbers of new species evolved during this period, also called the Pleistocene epoch. (See also Holocene.) history The study of past events and changes in the development, transmission, and transformation of cultural practices. Holocene The geological era since the end of the Great Ice Age about 11,000 years ago. Holy Roman Empire Loose federation of mostly German states and principalities, headed by an emperor elected by the princes. It lasted from 962 to 1806. hominid The biological family that includes humans and humanlike primates. Homo erectus An extinct human species. It evolved in Africa about 2 million years ago. Homo habilis The first human species (now extinct). It evolved in Africa about 2.5 million years ago. Homo sapiens The current human species. It evolved in Africa about 200,000 years ago. It includes archaic forms such as Neanderthals (now extinct) and all modern humans. megaliths Structures and complexes of very large stones constructed for ceremonial and religious purposes in Neolithic times. Neolithic The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution(s). It follows the Paleolithic period. Paleolithic The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period. Stone Age The historical period characterized by the production of tools from stone and other nonmetallic substances. It was followed in some places by the Bronze Age and more generally by the Iron Age.