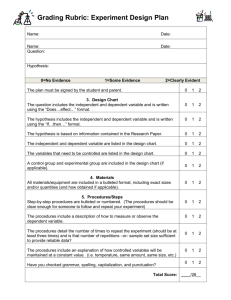
Scientific Method Worksheet

Hypothesis
Before you claim your hypothesis is a fact, it must be verified by other scientist. They must repeat your experiment several times to prove it. If so, it may become a theory.
The Scientific Method
The way to solving a problem in a scientific way.
Theory
An explanation of something based on scientific knowledge that is the result of many observations and experiments. It is not someone's guess or opinion. If data collected from several experiments over a period of time all support the hypothesis, it finally can be called a theory. Theories can change as new knowledge is gained from additional experiments.
Name: ___________________
6 Basic Steps
Research: You must gather information about the problem that will help you make a good hypothesis and design a good experiment
Hypothesis-
An educated guess. A prediction that can be tested. It is written as an If/then statement:
Experiments will have 2 groups:
Experimental groups- the groups that receive the test (independent variables)
Example: If the temperature of water rises above 70 degrees, then water fleas will not mate.
Control group- the group you compare the results of the experimental groups too. This group does not receive the test (independent variable)
Variable
s are factors that change in an experiment. There are 2 types of variables:
Independent variable (aka: manipulated) -
The factor you are testing. The one and only variable the person purposely changes or manipulates in the experiment. Usually expressed after the word “If” in the hypothesis.
Dependent variable (aka: responding)What you measure and write down as data. Should be charted or graphed. This variable changes as a result of the independent variable. Usually expressed after the word “then” in the hypothesis.
Conclusion - state whether your hypothesis was correct, use your data to explain why you came up with your decision.
It is very important that you only allow ONE variable to change during an experiment. Otherwise, you would not be able to determine which variable caused the results of the experiement.
Example: Picking out the parts of an experiment
The Experiment: Maverick believes that Miracle Grow does not make plants grow taller. He takes two identical pots, puts
½ cup of dirt into each one, puts 3 pea plant seeds into each one, and tops each off with ½ cup more dirt. He waters the plants the same amount at the same time each day. The only difference is that one plant is watered with regular water, while the other is watered with water that has Miracle Grow in it. He then measures how tall the plants grow.
Data collection / Analysis:
Very careful recording is important for valid results. Use charts or tables to organize data.
Record measurements as well as observations and things you want to remember about what happened. Complete calculations. Then use your data to prove or disprove your hypothesis.
Types of Data: Qualitative & Quantitative
Qualitative: describes with words. Ex: color or shape
Quantitative: describes with numbers Ex:
50 mi/hr or 67meters
Constants - Factors that remain the same throughout the entire experiment. (both in the experimental and control groups)
Identify the following parts of the experiment:
Hypothesis-Miracle Grow does not make plants grow taller.
Independent variable- Type of water (regular or miracle grow)
Dependent variable- Height (growth) of the plants
Constants- 1 cup of dirt, 3 pea plants, same amount of water, and watered the same time
Law
A scientific law is a statement about how things work in nature that seems to be true
all the time. They do not change like theories can. Laws tell you what will happen under certain conditions but do not necessarily explain why it happened.
1.
Hypothesis
2.
Independent variable
3.
Dependent variable
4.
Theory
5.
Law
6.
Constant
7.
Control Group
8.
Conclusion
A.
A statement about whether your hypothesis was right, based on your data.
B.
Factors that remains the same throughout the experiment.
C.
A statement about how things work in nature that seems to be true all the time.
D.
A prediction that can be tested.
E.
The factor you are testing. Usually changed by the person.
F.
An explanation of something based on scientific knowledge that is the result of many observations and experiments
G.
The group in the experiment that does not receive the test (independent variable)
H.
The variable that changes as a result of the independent variable. It is what you measure and write down as data
Read the experiment and identify the parts of the experiment:
A shopping mall wanted to determine whether the more expensive “Tough Stuff” floor wax was better than the cheaper
“Steel Seal” floor wax at protecting its floor tiles against scratches. One liter of each type of floor wax was applied to each of the 5 test sections of the main hall of the mall. The test sections were all the same size and were covered with the same kind of tiles. Five (5) other test sections received no wax. After 3 weeks, the number of scratches in each of the test sections were counted.
Question:
Independent variable:
Dependent variable:
Constants:
Which part of the Scientific Method? Write (Q)uestion, (H)ypothesis,
(E)xperiment, (C)onclusion
______ A scientist measures the amount of acid necessary to dissolve acertain amount of magnesium.
______ If my car will not start, then it is because I am out of gas.
______ Why are the plants in the front yard growing more than the plants in the back yard?
______ After looking at the data, it is proven that adding alt to ice water allows the ice water to get colder than just water alone
Use numbers 1-6 to put the following in the correct order of the scientific method:
_____a) Counted snails on each side of the box
_____b) Looked up snail behavior in a book and on the internet
_____c) Snails prefer dark areas to light areas
_____d) Released snails in a box with one side light and the other dark.
_____e) Based on data, snails will choose a dark area over light area
_____f) Noticed snails are often found in dark areas.
Sammy observed that the dandelions growing in the lawn grow very short. The Dandelions in the tall grass are tall.
Write a reasonable hypothesis for the above observation:
Gary believes he can improve his brain power by drinking “Jolt Cola.” In order to test this hypothesis, he recruits several friends to help him with the experiment. The friends drank one 12 oz. can with each meal every day for three weeks. Gary created a test and gave it to his friends before they started drinking the beverages as well as after three weeks.
Data is below:
Friend Before
Garry
Larry
Terry
Barry
64%
78%
82%
72%
After
80%
78%
84%
70%
Identify the following:
Hypothesis:
Independent variable
Dependent variable:
Constants:
Based on the data provided, do the Jolt colas work? Why?
How do Theory and Law differ?