HL Topic 11.2 Muscles
advertisement

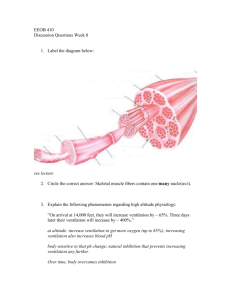
1. B [1] 2. C [1] 3. D [1] 4. B [1] 5. B [1] 6. C [1] 7. (a) (b) Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and correctly labelled. Z lines; actin filaments; myosin filaments with heads; light bands and dark bands; 3 max Ca2+ ions released when a nerve impulse arrives at the muscle; Ca2+ ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum; binding sites for myosin heads are exposed; this allows cross-bridges between myosin and actin to form; 2 max [5] 8. (a) (i) (ii) biceps and triceps correctly labelled; (biceps = muscle on right, triceps = muscle on left) Both needed for mark. 1 (cartilage is hard but flexible) able to absorb mechanical shocks / allows bones to pivot or move smoothly 1 IB Questionbank Biology 1 (b) ATP binds to myosin heads; ATP binding causes cross bridges to break/heads detach from binding site; ATP broken down/hydrolysed to ADP + Pi, causing myosin heads to change angle/become “cocked”; myosin heads attach to binding sites on actin filament further along sarcomere; ADP + Pi released and myosin heads push actin filament along/power stroke occurs; Allow ONE mark if there is a general understanding of the role of ATP in the sliding of filaments but without specific details. 3 max [5] 9. (a) (b) I. II. III. thick filament / myosin; Z line; A/dark band; vital capacity may increase slightly/appears to be unaffected by training; Do not award the mark for increase that is unqualified. 3 1 [4] 10. (a) (b) moderate-intensity exercise stimulates development (in size) of slow muscle fibres whilst high-intensity exercise stimulates development (in size) of fast muscle fibres; both decrease heart rate at rest; 2 benefits: more red blood cells after transfusion so more transport of oxygen by hemoglobin; enhances endurance; OWTTE risks: foreign blood could cause rejection / own blood banks to avoid rejection/ disease transmission; excess of red blood cells causes clots; bigger volume of blood increases blood pressure; unethical/unfair advantage to athlete results in banning/disqualification; To award [4 max] at least one risk and one benefit must be addressed. 4 max [6] 11. (a) I. II. Z line; actin (filaments); IB Questionbank Biology 2 2 (b) (i) (ii) slow muscle fibre (tonic) fast muscle fibre (twitch) contract slowly contract rapidly; resist fatigue fatigue easily; high myoglobin low myoglobin; aerobic metabolism anaerobic metabolism; very good blood supply moderate blood supply; high stamina low stamina; more mitrochondria less mitrochondria; Award [1] per correct row. 2 max warm up involves gentle exercise before exercise; warm muscles/joints are less likely to be strained/more supple; increases blood flow/oxygen to muscles; but there is limited scientific proof; some people do not suffer ill effects from not warming up; 3 max [7] 12. (a) (b) Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and correctly labelled. light and dark bands; Z line; (thin) actin filaments shown with no gap between these and Z line; (thick) myosin filaments shown with heads; 3 max binds oxygen when level is high; releases oxygen when level is low; acts as an oxygen store; allows muscles to continue with aerobic respiration for longer; 2 max [5] 13. (a) Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and correctly labelled. Sarcomere — clearly indicated between Z lines; Z lines; actin filaments attached to Z line; myosin filaments with heads; (two) light bands; dark band; IB Questionbank Biology 4 max 3 (b) (c) calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum; they expose the myosin binding sites (on actin) / cause movement of blocking molecules/troponin; cross-bridges form between actin and myosin molecules; ATP provides energy; for actin filaments to slide over the myosin filaments / for myosin to push actin; ATP provides energy to release myosin from binding site; action can be repeated further along the molecule; 5 max the resting potential of cell is negative inside compared with outside; stimulation causes depolarization/reversal of charge on each side; due to Na+ channels opening / Na+ flowing into the cell; which causes an action potential; K+ channels open / K+ flows out of the cell; sodium potassium pump restores resting potential; transmitted between neurons across a synapse; neurotransmitter released into synaptic cleft; diffuse across cleft to postsynaptic membrane; where they bind to receptors; influx of Na+ into cell; which may initiate action potential; 9 max (Plus up to [2] for quality) [20] 14. (a) (b) (c) positive/direct correlation / as mitochondrial concentration increases so does HAD activity 1 fur seal has greater mitochondrial concentration / vice versa; fur seal has greater HAD activity / vice versa; lowest value of HAD for fur seal equal to/slightly above highest sea lion value/ no overlap of data points; 2 max swimming muscle has a greater mitochondrial concentration than non-swimming muscle; the range in HAD activity is similar in both / non-swimming has slightly larger range; mitochondrial concentration overlaps in the middle range of values / low mitochondrial concentration only in non-swimming muscle / highest mitochondrial concentration only in swimming muscle; 2 IB Questionbank Biology 4 (d) more mitochondria means more aerobic respiration; more mitochondria in swimming muscles; products of fatty acid oxidation could be used in respiration (so hypothesis could be supported); increase in HAD activity would mean an increase in fatty acid oxidation; little/no increase in HAD activity in swimming muscles (so hypothesis not supported); during diving low oxygen/hypoxic conditions so high HAD activity/ mitochondrial concentration allows aerobic metabolism to continue; 3 max [8] IB Questionbank Biology 5