DisQues.Muscle.HighAltPhysio.Solutions.2010
advertisement

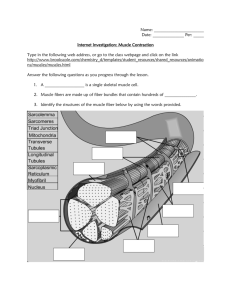
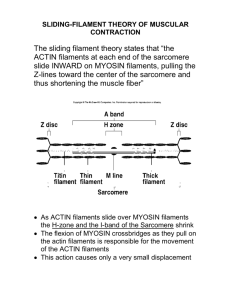
EEOB 410 Discussion Questions Week 8 1. Label the diagram below: see lecture 2. Circle the correct answer: Skeletal muscle fibers contain one/many nucle(us/i). 3. Explain the following phenomenon regarding high altitude physiology: ”On arrival at 14,000 feet, they will increase ventilation by ~ 65%. Three days later their ventilation will increase by ~ 400%.” at altitude: increase ventilation to get more oxygen (up to 65%); increasing ventilation also increases blood pH body sensitive to that ph change; natural inhibition that prevents increasing ventilation any further Over time, body overcomes inhibition 4. Below is a graph showing quantity of oxygen in the blood of a person dwelling at sea level (sea-level dweller). What might you expect to see in a graph of the same for a person who has spent their life at high altitude? Draw your prediction on the graph below. see lecture 5. List 4 mechanisms that animals employ to cope with life at high altitude. - increase in pulmonary ventilation-most all animals breathe faster at high elevation-immediate response increase in number of RBC increased vascularity of peripheral tissues increased ability of tissues to use O2 despite low PO2-- more mitochondria 6. What is erythropoitin (EPO)? Explain how this compound can be exploited by endurance athletes. EPO: increase RBC production – athletes can use for more efficient delivery of O2 to target tissues 7. What is hypoxia? List the acute affects of hypoxia. def: body is deprived of adequate oxygen 1. mental fatigue 2. drowsiness 3. lassitude 4. muscle fatigue 8. Define pulmonary edema. What would you expect the pH to be of a patient with pulmonary edema? What is the cause of edema? def: abnormal buildup of fluid in the arid sacs (alveoli) pH: high cause = pressure in capillaries forces fluid into lungs 9. At each end of a muscle fiber, the sarcolemma fuses with a ___________, which collect into bundles and insert into _____________. tendon fiber; bones 10. Explain the etiology of the “khumbu cough,” a dry cough experienced at high altitude. cough developes because water vapor pressure is very low at altitude; air dries the trachea, causing a cough 11. What does the acronym HACE stand for? What causes HACE? high altitude cerbral edema; same cause as pulmonary edema—pressure forces fluid into brain (lungs in pulm.) 12. Identify the following in the figure below: A band, I band, Z line, H zone, nucleus. see lecture 13. What are the roles of titin and nebulin in muscle fiber structure? structural proteins that help align actin and myosin titin: elastic and gives muscle ability to spring back when stretched. nebulin: inelastic…runs length of thin filament, stabilizes it. 14. Fill in the blanks for the 3 posulates of the sliding theory of muscle contraction: a. b. c. during contraction, ________ shorten during contraction, ________ filaments slide past ________ filaments cross-bridges form between ________ and ________, providing the force that draws filaments past one another sarcomeres; actin, myosin; actin, myosin (or other way around) 15. ________ is a divalent ion important in muscle physiology. Ca++ 16. Actin is composed of: ______________________, of which ____________ has a strong affinity for calcium. F-actin filaments, tropomyosin, troponin (I, T, C); troponin C 17. What evidence suggests that the active site on actin is covered by the tropomyosin-troponin complex? - actin sans troponin-tropomyosin binds immediately and strongly to heads of myosin molecules - add trop/t-mysin complex; binding between actin and myosin inhibited 18. Outline the interaction of ATP and Ca++ in muscle contraction: 1. myosin head binds ATP before contraction 2. Ca++ enters cell; actin head exposed (mechanism unknown) 3. energized myosin tilts (cleaves ATP to ADP), pulls actin along 4. new ATP attaches to site, causing detachment from actin 5. if Ca++ present, cycle re-initiates 19. Explain isometric and isotonic contraction. isometric – contraction where muscle maintains length isotonic – contraction where muscle shortens