Chapter 3, Section 1 Notes * Volcanoes & Plate Tectonics

Chapter 3, Section 1 Notes – Volcanoes & Plate Tectonics
I.
Volcanoes & Plate Boundaries a.
Volcanoes can be found on land or underwater i.
Underwater volcanoes can be difficult to observe and map ii.
Often found along plate boundaries
1.
diverging or converging plates cause crust to fracture and allow magma to reach the surface b.
often occur in belts that cross continents and oceans i.
Ring of Fire – rims Pacific Ocean c.
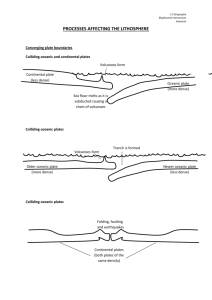
diverging plate boundaries i.
volcanoes form along mid-ocean ridges (water) or rift valleys (on land) ii.
lava pours out of the rift valley (center of the ridge) iii.
as lava cools and hardens, new mountains are formed d.
converging plate boundaries i.
two oceanic plates or oceanic and continental plates ii.
oceanic plate sinks beneath a trench iii.
rock above the plate melts to form magma iv.
eruptions to the surface – lava e.
volcano formation i.
magma is less dense than the plates ii.
magma rises toward the surface and breaks through crust forming volcanoes iii.
when two oceanic plates collide, island arcs are formed from the resulting string of volcanoes f.
Hot Spot Volcanoes i.
Plates move over hot spots in Earth’s mantle ii.
Over long periods of time, forms string of islands (ex.
Hawaii) iii.
Can occur on or in the middle of plate boundaries