Comparing Properties Reading
advertisement
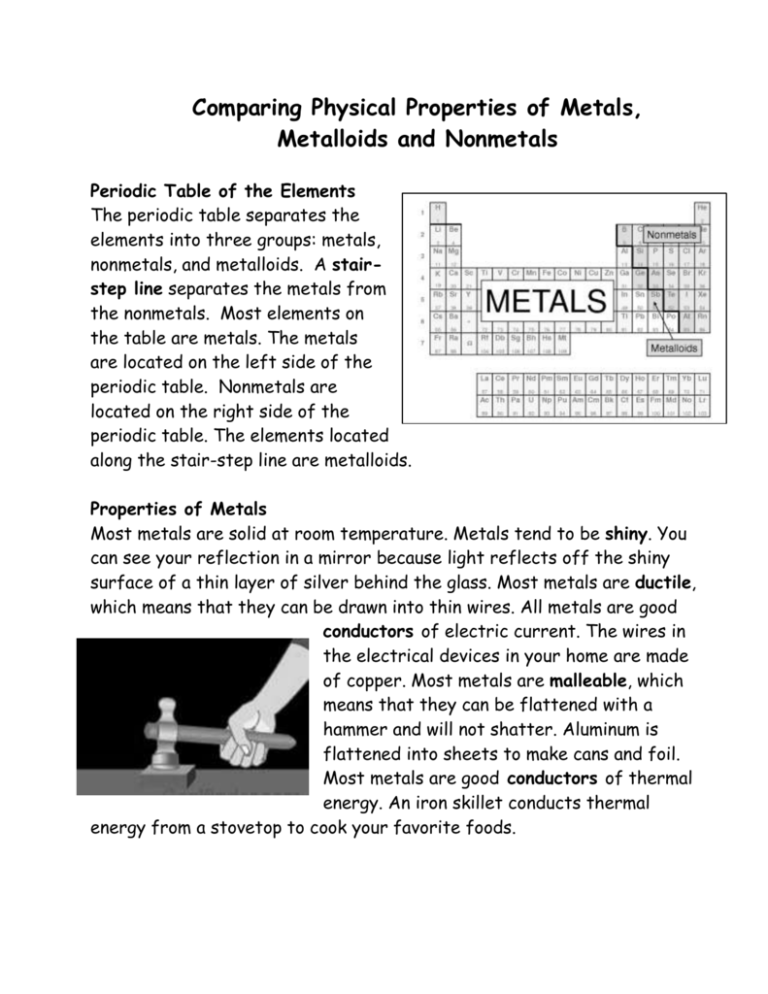
Comparing Physical Properties of Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals Periodic Table of the Elements The periodic table separates the elements into three groups: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. A stairstep line separates the metals from the nonmetals. Most elements on the table are metals. The metals are located on the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table. The elements located along the stair-step line are metalloids. Properties of Metals Most metals are solid at room temperature. Metals tend to be shiny. You can see your reflection in a mirror because light reflects off the shiny surface of a thin layer of silver behind the glass. Most metals are ductile, which means that they can be drawn into thin wires. All metals are good conductors of electric current. The wires in the electrical devices in your home are made of copper. Most metals are malleable, which means that they can be flattened with a hammer and will not shatter. Aluminum is flattened into sheets to make cans and foil. Most metals are good conductors of thermal energy. An iron skillet conducts thermal energy from a stovetop to cook your favorite foods. 32 Ge Germaniun m 84 Po Polonium Properties of Nonmetals Nonmetals are very different from metals. There are only 17 nonmetals and more than half of the nonmetals are gases at room temperature. Many properties of nonmetals are the opposite of the properties of metals. Nonmetals are NOT malleable or ductile. In fact, solid nonmetals, such as carbon in the graphite of a pencil lead, are brittle and will break or shatter when hit with a hammer. Sulfur, like most nonmetals, is dull or not shiny. Nonmetals are poor conductors of thermal energy and electric current so they are known as insulators. If the gap in a spark plug is too wide, the nonmetals nitrogen and oxygen in the air will stop the spark and a car’s engine will not run. Properties of Metalloids Metalloids have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. Some metalloids are also called semiconductors. This means that they can carry an electrical charge under certain conditions. This property of metalloids makes them useful in calculators and computers. Tellurium is one of the metalloids. It is shiny, but it is brittle and can easily be smashed into a powder. Boron, another metalloid, is almost as hard as diamond, but it is also very brittle. At high temperatures, it is a good conductor of electric current. Exceptions The periodic table is useful when classifying elements as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids, but watch out for a few exceptions. Metals are all solids except for Mercury (Hg) which is liquid at room temperature. Hydrogen (H) is on the left side of the periodic table, but it is a nonmetal. Aluminum (Al) touches the stair-step line, but it is actually a metal.








