Unit 1 Revision: Cloze Exercise 4.
advertisement
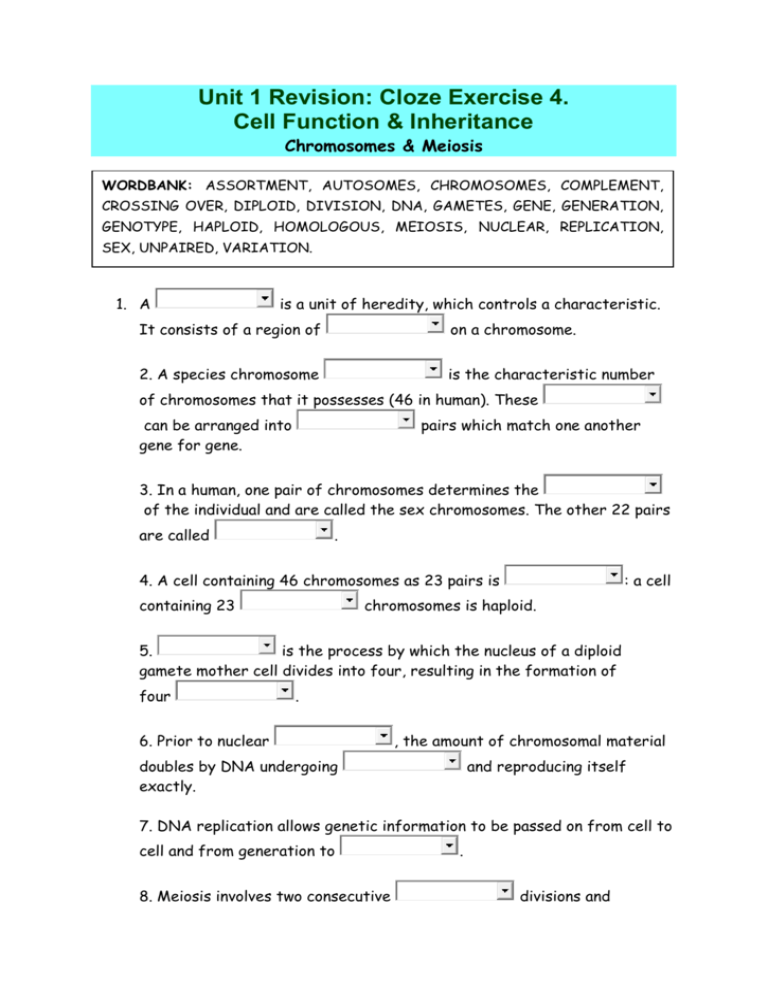
Unit 1 Revision: Cloze Exercise 4. Cell Function & Inheritance Chromosomes & Meiosis WORDBANK: ASSORTMENT, AUTOSOMES, CHROMOSOMES, COMPLEMENT, CROSSING OVER, DIPLOID, DIVISION, DNA, GAMETES, GENE, GENERATION, GENOTYPE, HAPLOID, HOMOLOGOUS, MEIOSIS, NUCLEAR, REPLICATION, SEX, UNPAIRED, VARIATION. 1. A is a unit of heredity, which controls a characteristic. It consists of a region of on a chromosome. 2. A species chromosome is the characteristic number of chromosomes that it possesses (46 in human). These can be arranged into gene for gene. pairs which match one another 3. In a human, one pair of chromosomes determines the of the individual and are called the sex chromosomes. The other 22 pairs are called . 4. A cell containing 46 chromosomes as 23 pairs is containing 23 : a cell chromosomes is haploid. 5. is the process by which the nucleus of a diploid gamete mother cell divides into four, resulting in the formation of four . 6. Prior to nuclear , the amount of chromosomal material doubles by DNA undergoing exactly. and reproducing itself 7. DNA replication allows genetic information to be passed on from cell to cell and from generation to 8. Meiosis involves two consecutive . divisions and produces reproduction. gametes in preparation for sexual 9. During meiosis, new combinations of existing alleles arise by independent chromosomes. and between homologous 10. The meeting of two haploid gametes at fertilisation allows mixing of part of one person's with that of another. By producing diploid individual who are genetically different from their parents, this process produces species. amongst the members of the human ANSWERS: Unit 1 Revision: Cloze Exercise 4. Cell Function & Inheritance Chromosomes & Meiosis 1. A gene is a unit of heredity, which controls a characteristic. It consists of a region of DNA on a chromosome. 2. A species chromosome complement is the characteristic number of chromosomes that it possesses (46 in human). These chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs which match one another gene for gene. 3. In a human, one pair of chromosomes determines the sex of the individual and are called the sex chromosomes. The other 22 pairs are called autosomes. 4. A cell containing 46 chromosomes as 23 pairs is diploid: a cell containing 23 unpaired chromosomes is haploid. 5. Meiosis is the process by which the nucleus of a diploid gamete mother cell divides into four, resulting in the formation of four gametes. 6. Prior to nuclear division, the amount of chromosomal material doubles by DNA undergoing replication and reproducing itself exactly. 7. DNA replication allows genetic information to be passed on from cell to cell and from generation to generation. 8. Meiosis involves two consecutive nuclear divisions and produces haploid gametes in preparation for sexual reproduction. 9. During meiosis, new combinations of existing alleles arise by independent assortment and crossing over between homologous chromosomes. 10. The meeting of two haploid gametes at fertilisation allows mixing of part of one person's genotype with that of another. By producing diploid individual who are genetically different from their parents, this process produces variation amongst the members of the human species.