Hepatomegaly - Physiology for Medical Students
advertisement

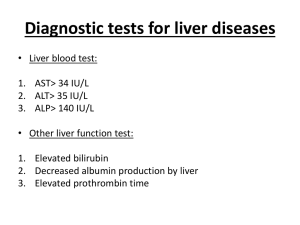
Hepatomegaly Hepatomegaly is enlargement of the liver. The liver edge is normally palpable in children and thin adults and some patients may have a palpable right lobe of the liver. It is smooth, uniform, non-tender and descends to meet the palpating fingers on inspiration. The best way to assess size is by percussion - a normal-sized liver can appear enlarged if displaced downwards by lung disorders. An enlarged liver expands down and across towards the left iliac fossa (LIF). To avoid missing a really big liver, always begin liver palpation in the LIF and work towards the right upper quadrant. Presentation Associated symptoms may be few or rather vague - eg, loss of appetite, weight loss and lethargy. There may be symptoms relating to liver dysfunction - eg, jaundice, bruising, gynaecomastia, spider naevi, ascites; or related to the underlying cause - eg, xanthelasma suggests autoimmune liver disease. Measure the hepatomegaly by percussing the upper and lower borders (will rule out causes such as emphysema which can push the liver down giving a false impression of hepatomegaly). On palpation Smooth hepatomegaly suggests: hepatitis, chronic heart failure, sarcoid, early alcoholic cirrhosis, tricuspid incompetence with a pulsatile liver. Craggy hepatomegaly suggests: primary hepatoma or secondary tumours. NB: a small liver is typical in late cirrhosis and nodular cirrhosis typically produces a small shrunken liver not a large craggy one. Ask particularly about alcohol consumption, sexual activity, IV drug abuse, blood transfusions and recent travel. Aetiology Venous congestion failure Viral hepatitis (acute and chronic). Infectious mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Cytomegalovirus (CMV). Malaria. Helminthic infection. Pyogenic abscess. Amoebic abscess. Biliary disease Autoimmune Autoimmune liver disease. Extra-hepatic obstruction. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. Tumours and infiltrative diseases Secondaries (metastatic carcinoma). Primary hepatic tumour - eg hepatocellular carcinoma. Granulomatous hepatitis. Amyloidosis. Sarcoidosis. Metabolic Haemochromatosis. Wilson's disease. Glycogen storage diseases. Porphyria. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. DM-associated fatty liver. Haematological disorders Sickle cell disease. Haemolytic anaemia. Myeloma. Leukaemia or lymphoma. Toxic/drug-related Alcoholic liver disease: acute alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic fatty liver. Drug-induced hepatitis - eg, statins, macrolides, amiodarone, paracetamol (indicates significant damage). Hepatomegaly in neonates and children Infections: TORCH* infections, hepatitis viruses and EBV and malaria. Metabolic: galactosaemia, lipid storage disorders - eg, Gaucher's disease. Neoplastic: leukaemia, lymphoma and hepatoblastoma. Haematological: sickle cell anaemia and thalassaemia. Cardiovascular: congestive cardiac failure and tricuspid regurgitation. Miscellaneous: schistosomiasis, toxins, sepsis, polycystic kidneys and liver. Drugs: for example, antituberculous medications. Hepatomegaly With normal bilirubin: consider hepatoblastoma, metabolic diseases. With raised conjugated bilirubin: o With splenomegaly: TORCH infections, sepsis and disorders of carbohydrate metabolism - eg, galactosaemia. o Without splenomegaly: liver tumour, choledochal cyst, biliary atresia, neonatal hepatitis. With raised unconjugated bilirubin: CCF, toxins, haemolytic anaemias. *TORCH is an acronym for TOxoplasmosis, Rubella, CMV and Herpes simplex. Some use the 'O' to stand for 'Other infections': ie hepatitis B, syphilis and varicella zoster. What to do if a patient has hepatomegaly If unwell, may need urgent admission. Full history - include recent travel, tattoos, IV drug abuse, medications including herbal remedies, alcohol intake and sexual history. Full examination - look for stigmata of chronic liver disease, delirium tremens, lymphadenopathy, and presence of splenomegaly; digital rectal examination may be necessary. If the patient does not need urgent admission then request some basic investigations - eg, LFTs, liver ultrasound scan, hepatitis screen. Further tests can be decided according to the results of these tests. Consider referral to a specialist (CT scan or liver biopsy may be needed). Further reading & references Hepatomegaly, Medline Plus 1. French's Index of Differential Diagnosis, 13th ed, (1997) Butterworth Heinemann; ISBN 0-7506-1434-X 2. Professional guide to Signs and Symptoms, 3rd ed. Springhouse Corp. 2001 3. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 15th Ed. Eds: Braunwald, E et al. McGrawHill, USA, 2001 4. Kumar P, Clarke M; Clinical Medicine, 6th Ed, (2005). WB Saunders: London 5. Lissauer T, Clayden G; Illustrated textbook of Paediatrics, 1997, Mosby Original Author: Dr Gurvinder Rull Last Checked: 10/12/2012 Current Version: Dr Gurvinder Peer Reviewer: Dr Helen Rull Huins Document ID: 785 Version: 23 © EMIS Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but make no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other health care professional for diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. For details see our