View/Open - Sacramento
advertisement

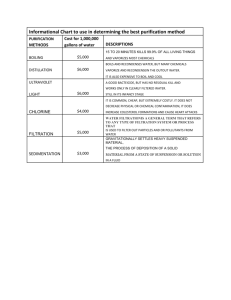
BOILER FEED WATER TREATMENT USING ELECTRODIALYSIS Ankit Patel B.E., Gujarat University, India, 2007 Dhaval Savla B.E., Mumbai University, India, 2006 PROJECT Submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE in ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING at CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, SACRAMENTO SUMMER 2010 BOILER FEED WATER TREATMENT USING ELECTRODIALYSIS A Project by Ankit Patel Dhaval Savla Approved by: __________________________________________________, Committee Chair John Balachandra, Ph.D. ___________________________________________________, Second Reader Fethi Belkhouche, Ph.D. ________________________________ Date ii Student: Ankit Patel Dhaval Savla I certify that these students have met the requirements for format contained in the university format manual and that this project is suitable for shelving in the library and credits to be awarded for the Project. _________________________, Department Chair Suresh Vadhva, Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering iii ________________ Date Abstract of BOILER FEED WATER TREATMENT USING ELECTRODIALYSIS by Ankit Patel Dhaval Savla Water treatment is the most important part of any power plant. Water from natural reservoir is fetched into plant and treated to reduce impurity level, before it is used to generate saturated steam. The saturated steam rotates turbine at high speed so that desired amount of electrical energy is generated. In this whole process water purification is very important. Proper water treatment can increase efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, increase life time of control system vessels. There are various water treatment methods and they are mainly divided into two categories Chemical methods Non-chemical methods (e.g. UV radiation method and Electrodialysis). iv Chemical water purification is concerned with a lot of different methods. These methods require special attention because of the use to harmful chemicals. Special equipments are required to handle them and this will increase the cost of power generated per unit. Nowadays, carbon foot print is a big issue for any industry. More use of chemical increase carbon footprint. So, far Electrodialysis is used to regenerate salts and chemical solutions with specific concentration. It is a modern technique which uses DC power and is capable to purify water up to drinking level. Power requirement for this system is very low compared to other chemical treatment systems. It uses almost no chemicals, so it is environmental safe and reduces the carbon footprint of the power plant. Furthermore, capital costs, operating costs, and maintenance costs are lower than chemical treatment systems. These benefits are very realistic for any industry needing purified water supply. So we are going to focus on Electrodialysis to purify boiler feed water in power plant. _________________________________________________, Committee Chair John C. Balachandra, Ph.D ________________ Date v TABLE OF CONTENTS Page List of Figures………………………………………………………….…………… ix List of Tables………………………………………………………………….......... xi List of Graphs …………………………………………………………………………….. xii Chapter 1. 2. SOURCES OF WATER AND IMPURITIES………………………………... 1 1.1 Effects of impurities ...……………………………………………….... 3 TYPE OF WATER PURIFICATION.....……………………………………. 11 2.1 Filtration……………………………………………………..………… 11 2.2 Sand Filtration .............................................................................…...... 11 2.3 Cross Flow Filtration……..………………………………...………..... 11 2.4 Micro Filtration…..……………………………………………………. 12 2.5 Ultra Filtration…………………….………………………….…........... 12 2.6 Nano Filtration………………………………………………………… 13 2.7 Reverse Osmosis………………………………………………………. 13 2.8 UV Radiation ………………………………………………………… 13 2.9 Distillation……………………………………………………….……. 14 2.10 pH Adjustment………………………………………………………. 14 2.11 Electrodialysis ……………………………………………………….. 15 2.12 Sand Filtration……………………………………………………… 17 2.13 Slow Sand Filter……………………………………………………… 17 vi 2.14 Rapid Sand Filter...…………………………………………………… 19 2.15 Micro Filtration…..…………………………………………………... 22 2.16 Membrane Filters for Water Purification ……….…………………… 23 2.17 Classification of Membrane………………………………………….. 24 2.18 Classification Based on Separation Mechanism ……..……………… 25 2.19 Porous/ Non Porous Membranes….………………………………… 25 2.20 Ion Exchange Membrane…………….…..…………………………… 26 3. 2.21 Classification Based on Morphology……..……………………....... 26 2.22 Composite Membranes……………………………………………… 26 2.23 Classification Based on Geometry……..…………………………….. 27 2.24 Membrane Cleaning ……….………….………………………….….. 28 2.25 Forward Flushing……………..……………………………………… 28 2.26 Backward Flushing ……………...…………………………………... 29 2.27 Air Flush…………………………...………………………………… 30 2.28 Chemical Cleaning ………………………………………………….. 31 2.29 General Membrane Equation ………………………………………... 34 2.30 pH adjustment ………..……………………………………………… 35 2.31 Flocculation …………………………………………………………. 35 2.32 Active Carbon Filtration …………………………………………… 36 ELECTRODIALYSIS.…………………………………………………….. 37 3.1 Electrodialysis Principle..……………………………………………. 38 3.2 Elements of Electrodialysis .……………………………….................. 41 vii 3.3 Power Consumption………………………………………………….. 43 3.4 Advantages of Electrodialysis …………………………………........... 47 3.5 Issues with Electrodialysis …………………………………………… 48 3.6 Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR).……………………………………… 50 3.7 Advantages of EDR...…………………………….…………………… 52 3.8 Cost Consideration.…………………………………………………… 53 4. MATLAB CODE FOR SIMULATION……………..……………………… 57 5. CONCLUSION ……………………………………………..………………. 63 6. Bibliography ………………………………………………………….. 64 viii LIST OF FIGURES Page 1. Figure 1 Corrosion Due to Presence of Oxygen………………………………. 4 2. Figure 2 Reduced Flow Channel Due to Deposits…………………………….. 4 3. Figure 3 Destruction After Boiler Explosion………………………………….. 5 4. Figure 4 Construction of Slow Sand Filter……………………………………. 18 5. Figure 5 Basic Block Diagram of Rapid Sand Filter………………………….. 19 6. Figure 6 Actual Experimental Setup (a) General View………………………. 20 7. Figure 7 Actual Experimental Setup Front View……………………………... 21 8. Figure 8 Cross Flow Microfiltration Technique………………………………. 22 9. Figure 9 Schematic Representation of Isotropic Porous Membranes, (a) 25 Macropores>50nm; (b) Mesopores >50nm ; (c) Micropores <2nm…………… 10. Figure 10 Schematic Drawing of Asymmetric Membrane …………………… 27 11. Figure 11 Schematic Drawing of Composite Membrane …………………….. 27 12. Figure 12 Forward Flush Cleaning Technique………………………………… 28 13. Figure 13 Backward Flush Cleaning Technique………………………………. 29 14. Figure 14 Air Flush Cleaning Technique……………………………………… 30 15. Figure 15 Membrane Cleaning Effect of Short Term Experiment ……………. 32 16. Figure 16 Membrane Cleaning Effect of Long Term Experiment…………….. 33 17. Figure 17 Typical Electrodialysis Cell ……………………………………….. 38 18. Figure 18 Ion Separation During Electrodialysis. (CM - Cation Exchange 39 Membrane, D - Diluate Chamber, e1, e2 - Electrode Chambers, AM - Anion Exchange Membrane, K - Concentrate Chamber ……………………………... ix 19. Figure 19 Close Look Into Electrodialysis Process………………………......... 40 20. Figure 20 Electro dialyzer made by Zhejiang Feiying Environmental 42 Technology Engineering Co. LTD ……………………………………………. 21. Figure 21 Change In Polarity And Product Outlate in EDR ………………….. 50 22. Figure 22 Self Cleaning During Electrodialysis Reversal…………………….. 51 x LIST OF TABLES Page 1. Table 1 Water Impurities, Issues and Solution ………………………………. 6 2. Table 2 Classification of Membrane Separation Processes for Water Purification…………………………………………………………………… 16 3. Table 3 Volume of Water Filtered In a 24 Hour Period by Filters of Varying Size Surface Area……...……………………………………………………… 18 4. Table 4 Working Condition For Electrodialyzer Made by Zhejiang Feiying Environmental Technology Engineering Co., LTD…………………………... 42 5. Table 5 Allowed Impurities In Boiler Water………………………………….. 46 6. Table 6 Comparison Between RO & ED by Boris Pilate……………………... 47 7. Table 7 Water Content Difference Before and After Electrodialysis 54 Treatment…………………………………………………………………........ 8. Table 8 Costing for Electrodialysis Plant Established by Howard R Green Company……………………………………………………………………… xi 55 LIST OF GRAPHS 1. Graph 1 Experimental Result to Decide Limit for Dissolved Solids in Water... xii 2