16-Individualized Intervention Summary notes
advertisement

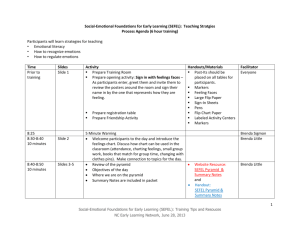
Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Positive Behavior and Intervention Support (Tier 3) Objectives: Define challenging behavior Explore challenging behavior as communication & identify its forms & functions Examine and practice a six-step process of Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Review resources to learn more about developing individualized intensive intervention Social- Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL) Pyramid Model: Tier 3 - Individualized Positive Behavior Support- Children with persistent challenges Tier 2 - Social Skills Curricula-Children at Risk Tier 1 – High Quality Early Education-All Children Notes: Continuum of Problem Behavior: 5-7% - Students with severe/chronic problem behavior 10-12% - Students at-risk for problem behaviors 80-90% - Students with mild or no problem behaviors Notes: Challenging Behavior: Behaviors that are not responsive to the use of developmentally appropriate guidance procedures Any repeated pattern of behavior that interferes with learning or engagement in pro-social interactions with peers & adults Prolonged tantrums, physical & verbal aggression, disruptive vocal & motor behavior, property destruction, self-injury, noncompliance, & withdrawal Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 1 Another Definition of Challenging Behavior: Any behavior that: Interferes with children’s learning and development Isolates the child from peers Causes harm to the child, other children, or adults Causes damage to the physical environment Puts a child at risk for later behavior problems or school failures Notes: Why Challenging Behavior? Communicates message when child does not have language Is used instead of language by child who has limited social skills Is effective in gaining access to something or someone or avoiding something or someone Notes: Dimensions of Communication: Form: the behavior used to communicate Function: the reason or purpose of the behavior Notes: Functions of Challenging Behavior: Escape/avoid Obtain Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 2 Forms of Communication: Words Sentences Eye gaze Pulling adult Crying Biting Tantrums Notes: Functions of Communication: Request object, activity, or person Escape demands, activity, or person Request help Request social interaction Comment Request sensory stimulation Escape sensory stimulation Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support: An approach for changing a child’s behavior An approach for developing an understanding of why the child has challenging behavior & teaching the child new skills to replace the challenging behavior A holistic approach that considers all of the factors that impact a child, family, & the child’s behavior Based on humanistic values & research Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 3 Research on Positive Behavior and Intervention Support: Effective for individuals with disabilities, ages 2-50 Effective for diverse groups of individuals with challenges Only comprehensive, evidence-based approach to address problem behavior Effective in a variety of natural environments Notes: Old Way: General intervention for all behavior problems Intervention is reactive Focus on behavior reduction Quick Fix New Way: Intervention matched to purpose of the behavior Intervention is proactive Focus on teaching new skills Long-term intervention Notes: Intensive Individualized Intervention: An evidence-based process of assessment and intervention for establishing desirable, competent behavior while reducing challenging behavior Notes: Universal Classroom Practices: If High-quality Classroom Practices are implemented: May not need individualized interventions If needed, may not be so intensive or effortful Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 4 Five “SUPER” Classroom Practices: Use 5:1 ration of positive to negative/neutral attention Use predictable and comprehensible schedules and routines Use routines within routines Teach behavioral expectations directly Teach peer-related social skills Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 1- Behavior Support team Step 2- Person-Centered Planning Step 3- Functional Behavior Assessment Step 4- Hypothesis Development Step 5- Behavior Support Plan Development Step 6- Monitor Outcomes Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 1- Behavior Support team Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 2- Person-Centered Planning Notes: Person Centered Planning Features: Builds a collaborative team Builds on strengths of the child Builds on interests of the child Supports visions and dreams of the child Prioritizes long and short term goals Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 3- Functional Behavior Assessment Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 5 Conducting a Functional Assessment: Observe the child in target routines & settings Collect data on child behavior, look for situations that predict challenging behavior & are linked with appropriate behavior Interview persons most familiar with the child Review records Notes: Observation: A system or plan for looking at behavior - J. Billman & J. Sherman , 2003 Notes: ABCs: Antecedent Behavior Consequence Notes: Setting Event: An event that occurs at another time that increases the likelihood the child will have challenging behavior Serves to “set the child up” to have challenging behavior Notes: Context Cards: Describes the setting Describes interpersonal context Describes problem Behavior Looks at the social reaction Notes: Conducting Interviews: Interview family & other significant adults, child care providers, special educators, specialized therapists, & service providers Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 6 Critical Questions to ask: What is the behavior? How often does it occur? Intensity? Duration? What are the setting events? What are the predictors or triggers? What happens after the behavior? What is the use of the behavior trying to communicate? What strategies have been used in the past? What are the reinforcers? Notes: Reviewing Records: Screenings Evaluations Portfolios Other written documentation Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 4- Hypothesis Development Notes: Developing a Hypothesis Description of the challenging behavior Trigger/predictor of the challenging behavior Function/purpose of the behavior Maintaining consequences Notes: Tim: Tim is riding a trike on the playground’s bike path. He sees Charlie move to the sandbox where Tim had just finished building a roadway. Tim leaps off his trike & tackles Charlie. Tim hits Charlie. An adult comes over to intervene. The adult comforts Charlie & scolds Tim. Tim goes to the sandbox & continues construction on his roadway. Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 7 Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 5- Behavior Support Plan Development Notes: Behavior Support Plan: Behavior Hypothesis statement Prevention Strategies Replacement/Teach Skills Consequence/Reinforce Strategies Notes: Prevention Strategies Questions: How can the environment be changed to reduce the likelihood of the challenging behavior occurring? What strategies would naturally fit into the routines/structure of the classroom and family? Notes: Specific Prevention Strategies: Provide choices Intersperse non-preferred tasks with preferred ones Use visual supports and schedules Embed interests into activity Enhance predictability with schedules Alter physical arrangement of room Remove triggers of challenging behaviors Notes: Replacement/Teach Skills: Effective as the challenging behavior Serves the same function or close to it Easy for the child to do Relevant to the child’s unique situation and abilities Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 8 Replacement/Teach Skills: Teach communication skills Peer related social skills Self-monitoring Tolerate delay of reinforcement Teach independence with visual schedules Notes: Consequence/Reinforce Strategies: Reinforce desirable behavior Remove reinforcement for challenging behavior Redirect the child to use the replacement behavior and then reinforce Notes: Positive Behavior and Intervention Support Process: Step 6- Monitor Outcomes Notes: Data Collection: Data collection method identified (what, when, how and who) Data collection needs to be easy and accurate Measure what it is intended to measure Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 9 Direct Measurement: Event recording Duration Frequency Count Notes: Indirect Measurement: Incident reports Rating scales Notes: Use of Data for Decision Making: If progress is good, then keep going. If progress is unsatisfactory: 1. Be certain that your data are accurate 2. Check fidelity --- be certain that procedures are being implemented as intended 3. Check strength of reinforcers 4. Re-check functional assessment – including functions of challenging behavior Notes: Social-Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (SEFEL): Individualized Intervention NC Early Learning Network Summer Institute 2013 10