B4 Revision questions - Blackpool Aspire Academy
advertisement

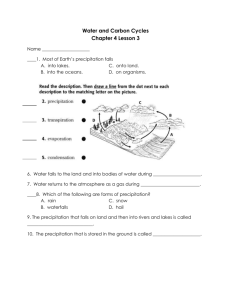
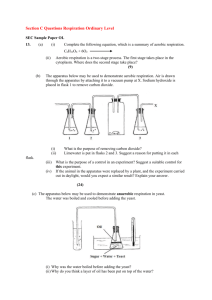
B4 – The Processes of Life Revision questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. What is the name of the chemical reaction which produces energy in cells? What is photosynthesis? Why do all organisms rely on photosynthesis? What is respiration and how is it different to photosynthesis? What type of molecule is an enzyme? (i.e., fat, carbohydrate, protein?) What do enzymes do? Where are the instructions for making enzymes kept in the cell? What is an ‘active site’? What is the ‘lock and key model’? How does temperature affect the shape of the active site, and how does this affect the working of the enzyme? What does it mean to ‘denature’ and enzyme? Why does increasing temperature increase the rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction? Other than temperature, what other factor can denature an enzyme? Write out the word and balanced symbol equation for photosynthesis. What role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis? Where is chlorophyll found? What does light energy do in the photosynthesis reaction? Glucose is used to make new molecules in the cell. Name two of these molecules. Sometimes glucose is stored by the plant. What is the storage polymer of glucose called? Draw and label a typical plant cell to show chloroplasts, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, vacuole and cell wall. Describe the role in photosynthesis fulfilled by each of these structures: a. Chloroplasts b. Cell membrane c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm Which mineral, taken up by the roots, is needed to make protein? What is diffusion? Give an example of diffusion that occurs in photosynthesis. What is osmosis? Give an example of osmosis in plants. What is active transport? Give an example of active transport in plants. Name three factors that can limit the rate of photosynthesis. What is a quadrat? What is a transect and how is this used in fieldwork to investigate the effect of light on plants in a woodland? Other than movement, give two examples of how energy released by respiration is used in living organisms. What does ‘synthesis of polymers’ mean, and give an example of this happening in plants. 33. Which two molecules are used by plants to make an amino acid? What is a polymer of amino acids called? 34. Write out the word and balanced symbol equation for respiration. 35. What is the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration? 36. What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and some bacteria? 37. What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in plant cells and yeast? 38. Which is the more efficient process for releasing energy from glucose; aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration? 39. Draw the structure of an animal cell, a bacterial cell and a yeast cell. List the key differences between these types of cells. 40. What role do mitochondria play in aerobic respiration (in animals, plants and yeast)? 41. What role does the cell membrane play in respiration? 42. Why is the nucleus (or circular DNA in bacteria) important in respiration? 43. What role does the cytoplasm play in anaerobic respiration. 44. What is biogas and how is the knowledge of anaerobic respiration important in its production? 45. How is the knowledge of anaerobic respiration used in the production of bread and alcohol?