Alcohols_Selbstlern
advertisement

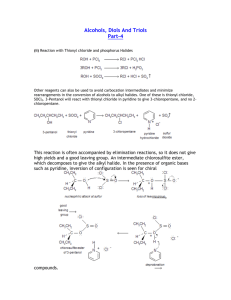
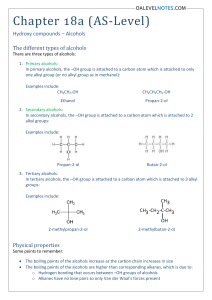
Alcohols The most important example is ethanol sum formula C2H6O better: C2H5OH Lewis formula skeletal formula group formula CH3CH2OH structural formula Formation of Ethanol 1. By fermentation: 2. Technical: C6H12O6 -------------------> ...... CO2 + ......... C2H5OH by the addition of water to ethene Usage of ethanol Drinks, spot removers, for disinfection, as a solvent (in perfumes; in the industry), methylated spirit; ethanol as a fuel: Problem: big cultivation areas are necessary. in Brazil 1/4 of all cars. Further alcohols Beside ethanol there are some more alcohols. Alcohols belong to a compound class whose best known representative is ethanol. The other alcohols also contain the typical OH-group which is bound to a hydrocarbon framework (an organic rest). H H H C C O H H H Ethyl residue Hydroxy group O R H R: general organic residue Organic residues which are derived from alkanes are designated alkyl residues. Nomenclature of alcohols: Name of the suitable alkane + suffix "ol" Properties of related alcohols Methanol Alcohol Ethanol 1-Propanol 1-Butanol Skeletalformula Lewisformula -------- becomes smaller / bigger -----------> The alkyl residue The solubility in water (hydrophily) --------- increases / decreases ------------> The solubility in heptane (lipophily) --------- increases / decreases ---------------> The boiling point: ------------ becomes higher / lower ------------------------------------> Which alcohol has the higher boiling point? OH Bp. 83°Coder Bp. 138°C OH OH OH Bp. 97°C or HO OH Bp. 290°C Isomeric alcohols with the example of the isomeres of butanol Lewis formula Name General designation Butanol primary Alcohol R The C-atom which carries the OH is primary (one Alkyl residue is bound to H it) OH OH 2-Methyl-propanol OH 2-Butanol OH 2-Methyl-2propanol tert. Butanol General 3-dimensional designation OH H " " secondary Alcohol 2 alkyl residues on the OH-carrying C-Atom (secondary C) R1 tertiary alcohol 3 alkyl residues on the OH-carrying C-Atom (tertiary C) R1 R2 R2 OH H OH R3 Examples of known alcohols Methanol a colourless liquid; tastes almost like ethanol; Boiling point (B.p.): 65°C 20 to 50 ml are deadly; 5 to 10 ml lead to loss of sight and brain damage. Formation: with the "dry distillation" of wood (old name: "wood alcohol"); moreover, by the improper accomplishment of the distillation and use of inapt basic material; technically: CO + 2 H2----> CH3OH Use: Solvent and raw material for the chemical industry; as a fuel (only in the project phase) Propanol, Butanol and Pentanol originate as undesirable by-products of the alcoholic fermentation and are included in small quantities in all alcoholic beverages. They are more toxic than ethanol and amplify the hangover effect (after too plentiful consumption of alcohol) substantially . Isopropanol (2-Propanol) B.p. 82°C Skeletal formula: important solvent: Many glasses- and screen-cleaners are practically pure 2-propanol which is sold terribly expensively. It loosens glue very well, however without loosening plastics which is the case with acetone. Ethylene glycol (1,2-Ethandiol) a bivalent alcohol Skeletal formula: a toxic, sweetly tasting liquid (from Greek glycos = sweet; the more OH-groups, the sweeter); B.p. 198°C Use: as a raw material for the plastic production as an antifreeze in the car (engine cooling, windshield wiper); a 1:1 mixture from ethylene glycol and water freezes only at -40°C. Glycerol (1,2,3-Propantriol) B.p. 290°C a trivalent alcohol Skeletal formula: a sweetly tasting, viscous liquid; completely indissolvable in pentane ; very well water-soluble; takes up if even air humidity (is hygroscopic - water attracting); can form several H-bonds - thereby it becomes viscous; Use: to hold creams, toothpastes and stamp colours damp Component of fats (see later); for the production of nitroglycerine (correct name: Glycerol trinitrate): Nitrogycerine is a colourless oily liquid. Dynamite is N. soaked up in porous kieselguhr. With sudden heating or with vibration or impact a violent explosion occurs: 4 C3H5(NO3)3 --------> … CO2 + … H2O + ….N2 + O2