Answers for 6.1 homework questions
advertisement

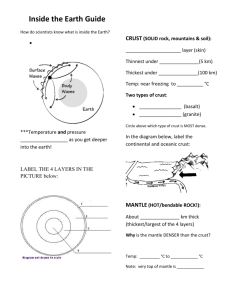
Earth Science CD Section 6.1 Page 168 Review Questions 1-8 1. Scientists learn about the Earth’s interior by studying rocks in its crust. A second way in which scientists learn about the Earth’s interior is by studying seismic waves such as P waves and S waves from Earthquakes as they travel through Earth. 2. The crust is composed of two types of crust: continental: mostly felsic rock (less dense) and oceanic: mostly mafic rock (more dense) it comprises 1% of Earth’s volume and is designated by its type of rock. The mantle is the crust and the top portion of the mantle which is solid, rigid rock. The remaining part of the mantle is not part of the crust and has plasticity. 3. Oceanic crust is very dense, or “heavier” than continental crust . 4. Basalt and Gabbro make up the oceanic crust. The oceanic crust forms when magma seeps through the ocean floor and creates lava flows. 5. Felsic rocks make up the continental crust, such as granite. 6. We know that the outer core is a liquid because P waves bend when they pass through the outer core, and S waves are not able to pass through as they will only pass through liquids. 7. Crust Cool Continental crust made of felsic rock Oceanic crust made of mafic rock Solid rigid rock Mantle Hot Made of solid rock rich in magnesium Core Very Hot Rich in iron 85% and Nickel 15% has plasticity and can flow with convection currents Outer core liquid Inner core solid 8. When you put your hand above a pan of hot water, it warms due to convection currents or hot air that was warmed near the water’s surface and rises. If you touch the hot pan, your hand is burned due to conduction in which a heat transfer occurs by direct contact. Conduction is an easier transfer of heat and more efficient as less is lost to t he environment.