Science Weather Study Guide

Science Weather Study Guide
Review both your notes and the links under each lesson on our wikisite.
Also review any videos or explorations taken in discovery education.
Lesson 1: What is Air page 174
The natural movement of air parallel to Earth’s surface is what scientists call WIND.
First Nations and Metis recognize and respect the power of wind to dry animals hides and skin used to make traditional clothing and blankets.
Recall our Warm Air Rises and Cool Air Sinks Experiment. Review your notes and describe what happened to the balloon when immersed in cold water, compared to warm water?
Lesson 2: Energy from the Sun page 177
Sun hits Earth in different ways because the Earth moves around the sun. Near the equator, sunlight is spread over a small area. At the North Pole sunlight is spread over a large area.
Thermometer- As temperature rises, the liquid heats up and expands, which means it rises in the tube.
Review Discovery Education Temperature EXPLORATION
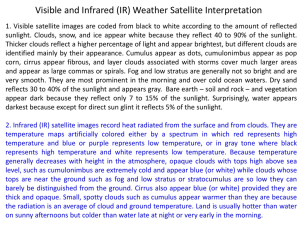
Lesson 3-4: What do Clouds tell us about weather? Page 181
Water is very important for Earth's climate. It evaporates from the oceans and rises into the atmosphere. It then condenses to form different kinds of clouds. Precipitation from clouds falls in the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail.
See CLOUD WATCH on DISCOVERY EDUCATION to review.
Cirrus Clouds- thin and look like curls of hair, cirrus = curl
Cumulus Clouds- look puffy, like a pile of cotton balls and have flat bottoms. Cumulus = heap
Stratus Clouds- flat and form layers low in the sky, when they touch the ground they are called fog. Stratus = “spread out.”
Lesson 5-6: Weather instruments page 184 + 188 More Instruments
Meteorology- the study of weather, a meteorologist studies, predicts or forecasts weather
Thunderstorms-
Floods-
Drought-
Hurricanes-
Tornadoes-
Weather Vane-(wind vane) shows the direction from which the wind is blowing.
Anemometer-measures the speed of the wind, we used a protractor with a golf ball to determine this!
Air pressure- weight of air pushing down on Earth
Barometer- measure air pressure, we used a glass bottle with a balloon and straw attached!
Lesson 7: What helps us predict the weather? Page 195
Radar- a device that uses radio waves to locate objects. The waves bounce off of precipitation and the information is sent back to as a picture to the radio station.
Weather balloons- Environment Canada uses these twice a day; the equipment on the balloon carries measures air temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind.
Lesson 8-9: Can you predict the Weather? Page 202 + Recall YOUR Weather Maps you made on SMART!
Weather Maps summarize weather information in different locations using symbols. H- high pressure
“Happy weather”, L-low pressure “Lousy weather”. Cloud, Rain, Snow, Thunderstorm and Sunshine symbols are used along with the temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
Lesson 10-12: Severe Weather Pages 204-206 + Discovery Education Video
Review the following two quizzes we took on DISCOVERY EDUCATION:
Weather Smart: Forecasting and Weather Instruments QUIZ
1. What is the term for a person who forecasts the weather?
o A) meteorologist o B) geologist o C) ornithologist o D) hydrologist
2. A weathervane tells you how strong the wind is.
o A) false o B) true
3. What can a compass tell you about the weather?
o A) A compass can tell you what direction the wind is blowing. o B) A compass can tell you how hard the wind is blowing. o C) A compass can tell you how high the pressure is o D) A compass can tell you what the temperature is.
4. If the air pressure is high, what kind of weather should you expect?
o A) hot weather o B) clear weather o C) humid weather o D) stormy weather
5. Which weather instrument measures the humidity in the air? o A) barometer o B) hygrometer o C) anemometer o D) thermometer
6. What can meteorologists use radar to help them locate?
o A) wind o B) humidity o C) precipitation o D) thunder
7. Why do meteorologists use maps, graphs, and charts to help them make forecasts?
o A) Maps, graphs, and charts are colorful and fun to look at. o B) Maps, graphs, and charts can be made without using any math o C) Maps, graphs, and charts show a lot of information and are easy to understand o D) Maps, graphs, and charts can be made without making any observations.
8. What is the first thing that a meteorologist considers when making a weather forecast? o A) the clouds o B) the humidity o C) the wind o D) the ocean
9. What pushes a thunderstorm from one town to another town?
o A) humidity o B) tides o C) wind o D) glaciers
10. What word is used to describe something that happens the same way over and over? o A) forecast o B) map o C) satellite o D) cycle
Cloud Watch
1. What type of clouds form high in the sky? o A) cumulus o B) stratus o C) fog o D) cirrus
2. How can clouds help to predict the weather?
o A) Cloud height can indicate daily weather conditions. o B) Cloud sizes can indicate daily weather conditions. o C) Cloud weight can indicate daily weather conditions. o D) Cloud types can indicate daily weather conditions.
3. Clouds are produced when water vapor collects on what?
o A) trees o B) dust particles o C) birds o D) blades of grass
4. When nimbus is added to the names of clouds, such as in cumulonimbus or nimbostratus clouds, it means that those clouds are dropping _____.
o A) humidity o B) evaporation o C) precipitation o D) condensation
5. Most clouds are made of _____.
o A) ash from volcanoes o B) smoke from fires o C) flocks of high-flying birds o D) water that goes into the air
6. What do you call a cloud that is formed on the ground?
o A) fog o B) cirrus o C) stratus o D) cumulus
7. What type of cloud can produce rain, lightning, thunder, hail, and sometimes even tornadoes?
o A) stratocumulus o B) cumulonimbus o C) cirrostratus o D) altostratus
8. Which cloud type usually forecasts calm weather? o A) cirrus o B) stratus o C) cumulus o D) cumulonimbus
9. What is the name of thin clouds that look like curls of hair?
o A) Cirrus o B) Nimbostratus o C) Stratus o D) Cumulus
10. What would the sky look like if it had altocumulus clouds? o A) The clouds would appear like a pile of cotton at about medium height in the sky o B) The clouds would appear flat and low in the sky o C) The sky would appear foggy o D) The clouds would be spread out about medium height in the sky