module specification form
advertisement
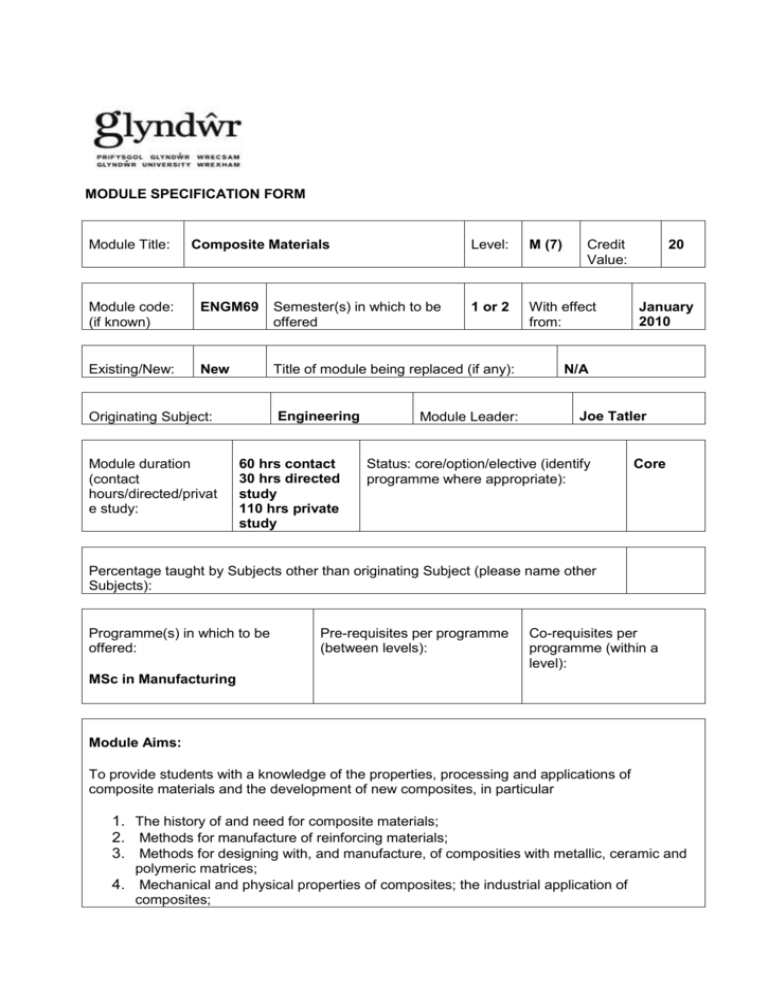
MODULE SPECIFICATION FORM Module Title: Composite Materials Level: M (7) 1 or 2 With effect from: Module code: (if known) ENGM69 Semester(s) in which to be offered Existing/New: New Title of module being replaced (if any): Engineering Originating Subject: Module duration (contact hours/directed/privat e study: 60 hrs contact 30 hrs directed study 110 hrs private study Module Leader: 20 Credit Value: January 2010 N/A Joe Tatler Status: core/option/elective (identify programme where appropriate): Core Percentage taught by Subjects other than originating Subject (please name other Subjects): Programme(s) in which to be offered: Pre-requisites per programme (between levels): Co-requisites per programme (within a level): MSc in Manufacturing Module Aims: To provide students with a knowledge of the properties, processing and applications of composite materials and the development of new composites, in particular 1. The history of and need for composite materials; 2. Methods for manufacture of reinforcing materials; 3. Methods for designing with, and manufacture, of composities with metallic, ceramic and polymeric matrices; 4. Mechanical and physical properties of composites; the industrial application of composites; 5. Appropriation of a composite material for a particular engineering application and development of composites. Expected Learning Outcomes Knowledge and Understanding: On completion of this module, the student should be able to: 1. Design composite materials with specific properties; 2. Interrelate design considerations with both manufacturing processes and ultimate performance; 3.Justify the use of a composite material for a particular application and new development of composites; 4. Critically assess the significance of aspects of composite development in a wider materials context; 5. Apply methods for determining mechanical properties of composites to other suitable materials. Transferable/Key Skills and other attributes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Communication ICT Technologies Time management and organisation Interpersonal skills Problem solving Information handling including numeracy Assessment: Assessment One: An individually prepared critique of the use of composite materials in complex structure situations. Assessment Two: A written examination which assesses the capability of knowledge and application of the principles, concepts and limitations of various composite materials. Assessment Learning Outcomes to be met Type of assessment Weighting Assessment 1 1,3,4,5 In course assessment 50% Assessment 2 2,3,4,5 Written examination 50% Duration (if exam) Word count or equivalent if appropriate 2000 words 2 hours Learning and Teaching Strategies: The module will be delivered through detailed presentations combined with interactive sessions to enhance students’ learning. The learning experience will be further supported by tutorials and self study work. Syllabus outline: Introduction: The history, classification, definitions and scope of composite materials. Polymer Matrix Composites: Fibres, matrices and interfacial/interphasial effects. Mechanics of reinforcement for long and short fibre systems. Structure/property relationships with respect to strength, modulus, fatigue, toughness, thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, etc. Methods and effects of manufacture and fabrication on properties and design. Mechanical and non-destructive testing of composite systems and typical applications. Metal Matrix Composites (MMC): Sources and properties of metal whiskers. Uses of metal matrix composites. Fabrication techniques - solid state, liquid state, in situ fabrication. Mechanical and chemical bonding. Discontinuous reinforcement in MMC. Strength, stiffness, transverse, compressive, electrical and thermal properties. Applications and problems of high temperature use. Ceramic Matrix Composites: Fabrication, properties, interface problems, toughness. High temperature, corrosive, biomedical, friction related applications. New developments in composite materials and potential applications, including the practical applications in the area of renewable energy. Bibliography:Essential Reading: Callister,W, (2002), Materials Science and Engineering: John Wiley and Sons. Harper ,CA, (2002): ,Handbook of Plastics, Elastomers and Composites ( 4th Ed) ; Mcgraw Hill. Mitton,G,(2002):Theory of Composites: Cambridge University Press. Recommended Reading: Sholte J, ( 2005), Nanotechnology industry trends and applications. Wiley. Swanson SP, (1997), Introduction to Design and Analysis with advanced Composite materials: Prentice Hall. Journal of Materials: Design and Applications IMechE Journal of Nanoengineering and Nanosystems IMechE Journal of Advanced Materials. Wiley