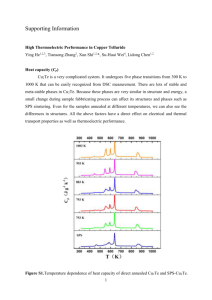
Figure S2.
advertisement

Direct imaging of the near field and dynamics of surface plasmon resonance on gold nanostructures using photoemission electron microscopy Quan Sun1,2, Kosei Ueno1,3, Han Yu1, Atsushi Kubo4, Yasutaka Matsuo1, Hiroaki Misawa1,* 1 Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan Creative Research Institution, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan 3 PRESTO, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi 332-0012, Japan 4 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba 305-8571, Japan 2 *To whom correspondence should be addressed: Prof. Hiroaki Misawa E-mail: misawa@es.hokudai.ac.jp, TEL: +(81)-11-706-9358, FAX: +(81)-11-706-9359. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Contents Figure S1. Demonstration of the measurement of the spatial resolution from one PEEM image. Figure S2. Side view SEM image of the annealed Au nanoparticles. Movie01. (In a separate .mov file) A typical time-resolved movie recorded for the annealed nanoparticle sample. Movie02. (In a separate .mov file) A movie recording the out-of-phase oscillation of the hotspots from two nanoparticle arrays. Figure S1 Figure S1. The spatial resolution of PEEM is usually determined by measuring the distance between the 16% and 84% intensity points of a cross section of small features. As an example here, it is determined to be 14.4 nm measured from one of the hot spots. Figure S2 Figure S2. Side view SEM image (view angle is 75° from the surface normal) of the annealed Au nanoparticles. The shape of the nanoparticles is closer to nanodisk.