Additional country gender inequality information (based on
advertisement

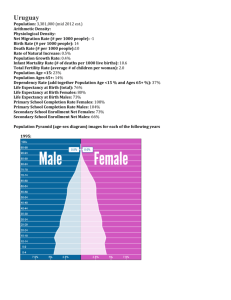
COUNTRY GENDER EQUALITY PROFILE The Profile is to be based on the national and various agency annual statistical reports, last census, sociological studies, mass-media. International websites may be used also. Indicate information for the latest year available. IT IS IMPORTANT TO SHOW THE SOURCE AND YEAR OF THE DATA FOR EACH INDICATOR A GOOD PRACTICE IS TO PRESENT THE INDICATORS FOR THE LAST 5 YEARS IN DYNAMIC, WHERE PRACTICABLE («GROWS, FALLS, STABLE», where changes are significant, indicate coefficient of growth or reduction for 5 years) Country: Kyrgyz Republic Population: 5.3 mln Type of governance: Parliament (Democratic Republic, Federal Republic, Parliament Democracy, Presidential etc.) Date of Constitution: 1993. Is gender equality (equality between men and women) specifically guaranteed in the Constitution? YES ∨ NO Is equality guaranteed in the Constitution? YES ∨ NO Highlights Several bullet points giving the gender equality priorities in the country. Such priorities will have been identified by a range of stakeholders and should be easily accessible. Keep it brief. National framework Legislation – specific gender equality (GE) legislation, plus any other where GE is guaranteed - yes Women’s legal position in relation to inheritance, land tenure, housing rights, family law and labour law. - no Strategy – specific GE strategy or any other where GE is mentioned. - no National Action Plan on 1325 International Commitments List international human rights instruments to which the country is a party o CEDAW – Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (1979) ∨ o CEDAW Optional Protocol (2000) o CERD – Convention on the Elimination of all forms of Racial Discrimination (1996) ∨ o CRD Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989)∨ ILO C100 – Equal Remuneration Convention (1951) ∨ o ILO C111 – Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention (1958)∨ 1 o ILO C156 – Workers with Family Responsibilities Convention (1981) o ILO C183 – Maternity Protection Convention (2000)∨ National action on international human rights commitments, eg. CEDAW report (date of last report) 2011 R. Otunbayeva speech in Washington Membership of Council of Europe International Cooperation List all donor organisations, and if possible, with the level of their financial commitment and name their gender equality priorities or programme focus. List specific major donor funded gender equality projects carried out in conjunction with national government that have taken place in last five years. Gender Inequality Indices1 Gender Inequality Index (calculated since 2010) Gender Inequality Index (GII) rank Gender Inequality Index (GII) value Maternal mortality (per 100 thousand live births) 51. 3 Adolescent fertility (number of births by women of 15-19 years age per 1000 women) 81. 7 Seats in national parliament (% female) 23. 9 Population with at least secondary education (% ages 25 and older) Female Male Labour force participation rate (%) Female Male 51.6 47.1 70.7 48.4 Reproductive health Contraceptive prevalence rate, any method (% of married women ages 15-49) At least one antenatal visit (%) Births attended by skilled health personnel (%) Total fertility rate 98.3 3.1 30.3 Human Development Index (calculated since 1990, education and income indicators changed in 2010) Human Development Index (HDI) rank Human Development Index (HDI) value Life Expectancy at Birth (years) Mean years of schooling (average number of schooling years in age of 25 and older) Expected years of schooling (number of oncoming schooling years for a schoolable child) 69.3 Gender-Related Development Index (calculated until 2010, provide latest data available showing the year) Gender-related Development Index (GDI) Life Expectancy at Birth (years) Adult Literacy rate (% ages 15 and above) Rank Female Males Female 73.5 65.3 Value Male 1Certain indicators in the gender inequality indices may repeat. However, we have left the tables as they are presented in the world statistical sources for completion convenience 2 GNI by PPP in US dollars Gross School Enrolment Ratio (%) Estimated Earned Income (PPP US$): Female Female Males Males Gender Empowerment Index (calculated until 2010, provide latest data available showing the year) Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM) Рейтинг страны Значение Seats in Parliament held by women (% of total) Female legislators, senior officials and managers (% of total) 23.9 39.9 Female professional and technical workers (% of total) Ratio of estimated female to male earned income Gender Gap Index of World Economic Forum (calculated since 2005) Economic participation Female labour force participation over male value Wage equality between women and men for similar work Estimated female earned income over male value Female legislators, senior officials and managers over male value Educational attainment Female professional and technical workers over male value Political empowerment Women with seats in parliament over male value Women at ministerial level over male value Number of years with a female head of state or government (last 50 years) Female literacy rate over male value Female net primary level enrolment over male value Female net secondary level enrolment over male value Female gross tertiary level enrolment over male value Health and survival Female healthy life expectance over male value Sex ratio at birth Demographic parameters Population growth rate Number of women - 2 773 332 persons, men – 2 703 688 Rural population rate, women – 1 791 776, men – 1 824 127 Total birth rate – 3.1, mortality rate – 11.9, marriage rate - 9.2, divorce rate – 1.5 Natural increase rate Migration gain rate Average age at the first marriage, women – 23.5, men – 26.9 Number of early marriages for women (in age below 18 years) – 9197, men – 799 Bastardy rate – 30.9 Average age at the birth of the first child Infant mortality rate (below 1 year) – 3 337 Child mortality rate (below 5 year) – 3 809 Mortality rates by the main death causes by gender (circulatory diseases, malignant neoplasms, respiratory diseases, alimentary system diseases, malignant tumours, infections, external causes (murders, suicide, poisoning, injuries, MVA etc.) – 36 174 Social disease morbidity by gender (tuberculosis, AIDS, sexually transmitted disease etc.) – any indicators available – 11.1 3 Abortions per 100 births Abortions per 1000 women – 14.3 An opportunity for a free abortion, the cost of abortion Average household size Rate of households with children of age below 18 years Rate of large families with number of children of 3 and above, 5 and above Rate of incomplete families Number of immigrants and emigrants for a year period by gender and age, marital status, settlement (urban – rural) Socio-economic status parameters Income and welfare GDP value – USD 5 bln., GDP per capita (in the national currency, dollars, growth rate) – KGS 60 610 Consumer price index – 4 647 soms Average monthly nominal and actual (with account of price index) wage (in the national currency, dollars, growth rate) women – 5 271 soms, men – 8 282 soms Minimum wage (in the national currency, dollars) Income of self-employed population in agriculture (in the national currency, dollars) Average monthly nominal and actual (with account of price index) income (in the national currency, dollars, growth rate) Level of subsistence minimum (if any) – 3502.62 soms Ratio between the minimum wage and minimum subsistence level for the working-age population Population without access to minimum subsistence level in thousands of persons by gender, % of the total population Differentiation coefficient (10% high income persons to 10% low income persons) Structure of the poor by gender and basic age groups (children, youth, employable, unemployable) Food products consumption per capita by the main types (kg) (by gender and age groups) Durables supply per household (or per capita) by the basic types Total accommodation area per capita, sq. m. Average number of rooms in various types of households Accommodation quality (availability of water supply, sewage, heating) Number of cars per 1000 persons Women and men land access (% owners) Land availability (limits in ha) Female land owners rate Economical participation, employment and unemployment Female company owners rate Main employment branches in % (agriculture, industry, commerce and services, state funded social and cultural branch, administration) Main “female” and “male” branches Working-age population rate, including that by gender Economically active population (by gender) Economically inactive population, involved in housework (by gender) Female and male rates in informal economy The number and the rate of the employed below working age (by gender) 4 Male and female unemployment level (registered, as defined by the ILO) Male and female retirement age Numbers of the retired, by gender, number of persons not receiving pension, by gender Working retirees rate, by gender Family and work balance 2-3 indicators of the time budgets (hours spent by females and males for the housework and children rearing during workdays and weekends, females and males leisure time duration) Rate of children attending preschool facilities Unsatisfied demand for preschool facilities (number of children in the waiting queue for kindergarten etc) Preschool facility fee size, preschool facility fee compensation from the state Availability, duration and pay for: maternity leave, child care leave for mother, father, parents Availability of part-time employment, distant work mode, flexible work schedule and their popularity among females and males Availability of programs to establish friendly work climate for parents and workers with family responsibilities Social security, medical services, education % GDP for the health care, education, social support (in dynamic for the last 5 years) Temporary disability allowance size Unemployment benefit size Average level of state pension benefit for males and females (in the national currency, dollars, growth rate) Taking child rearing into account in length of service for retirement eligibility Child benefits by types and size (in the national currency, dollars), compared to child minimum subsistence level Availability of modern obstetric centres Any indicators of medical services for women (gynecology, obstetrics) and children (pediatrics) Number of students by type of education and gender (secondary education (school), secondary professional, tertiary, high) (or number of graduates) Rate of persons with certain level of education by gender (by census) Rate of children not going to school Gender-based violence Number of bullet points on stats on gender-based violence, including: Domestic (in the home) gender-based violence Trafficking Number of refuges Legislation and enforcement infrastructure (training for police, lawyers and judges, refuges and other supports for victims of GBV, including support to NGOs providing services and advocacy, public information campaigns etc.) Labour migration information Number of labour migrants (females and males), emigrating during a year Rate of households with a worker “in the field” (with a labour migrant) Funds transferred by the migrants to the Motherland (in the national currency, dollars, % GDP) 5 Budget revenues from migrants (in the country of residence, in the country of work) Rate of money transfers from migrants in the total income of a household Average number of household members dependent on money transfers from migrant Types of work chosen by emigrating females and males (professional composition as registered, actual occupations) Countries where females and males go How often, for what time Rate of returning migrants, rate of migrants not returning over one year, over 3 years Do they form alternative families in the country of work? Cases (information) of having a child abroad Is migration available for the poorest or it requires funds (what size)? What are the abroad earnings spent for? Percentage of the earnings sent home Challenges existing in the country of work What provisions/amendments of the migration law in own country and the country of work are liked/disliked Estimation of illegal migration level Additional country gender inequality information (based on qualitative and quantitative sociological studies) USEFUL WEBSITES BESIDE NATIONAL STATISTICS AGENCIES: Human development indices (including gender equality and gender empowerment measure, gender inequality index) http://hdr.undp.org/en/reports/ World Economic Forum and gender gap index http://www.weforum.org/issues/global-gender-gap (http://www.weforum.org/pdf/gendergap/report2010.pdf www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GenderGap_Report_2011.pdf) World Bank gender statistics http://data.worldbank.org/ UN gender statistics http://www.un.org/ru/databases/#stats Statistical data of Economic Commission for Europe. Comparison of Europe, Northern America and Central Asia Millennium Development Goals accomplishment indicators Official data, definitions, methodology and indicator sources to determine the Goals accomplishment progress UN data UN system statistical resources Population Information System (POPINS) International, regional and national information about population from various UN sources 6