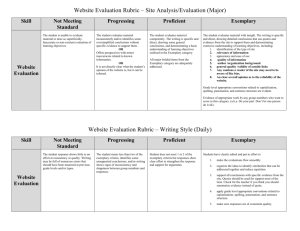
Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary sheet
advertisement

Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary sheet Element Rating Structured learning Learning materials should be well structured to provide the sequence of learning resources and learning activities that will lead to the intended learning outcomes. Date: Comments Exemplary 6 Key Principles for Online Teaching Year/Semester: Satisfactory Unit code and name: Insufficient Theme/school and course: Constructive Alignment All learning outcomes are aligned and directly relate to the teaching and learning activities and assessments. Unit Organisation Unit layout and navigation is convenient, intuitive and designed for learning. Content and Activity Organisation and Presentation A variety of appropriate content is presented logically. Structured Activities Activities are sequenced and linked with clear objectives and expectations in order to provide a route to achieving the learning outcomes Course Fit The unit is co-ordinated into the course. 1 Charles Darwin University, Office of Learning and Teaching, Higher Education Training and Development Team Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary Sheet, Version 3, October 2015 Active learning Learning materials should be designed to encourage learning by active engagement. Learning Activities Activities contain clear guidance for learners to actively work with content in meaningful ways. High order thinking skills Learning activities are sequenced to develop high-order thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation and synthesis. Range of activities and tasks Learning activities and tasks cater for different learning styles and levels of knowledge and skill. Creative use of technology Technology is used to creatively promote active engagement with the unit content. Teacher* presence Teachers need to be actively engaged in the unit, including responding promptly to student queries and actively participating in learning activities such as discussion groups. *The term ‘teacher’ is used as an encompassing term which includes lecturer, trainer, assessor. Pedagogical presence The teacher is actively involved in implementation of the constructive alignment process during the semester. Technical presence The teacher is skilled with the technology and actively supports students in their use of the technology. Managerial Presence The teacher attends to the developmental and administrative tasks associated with the learning environment. 2 Charles Darwin University, Office of Learning and Teaching, Higher Education Training and Development Team Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary Sheet, Version 3, October 2015 Social Presence The teacher promotes a friendly environment and community feelings to support the student cognitive learning processes. Student queries Opportunities for student feedback and queries as well as responsive feedback to such. Collaboration Opportunities should be provided for students to interact with each other, to work and learn collaboratively, and to generate a sense of belonging to a community of learners. Collaborative learning There are opportunities for students to work and learn collaboratively with other students. Community building Communication activities are designed to help build a sense of community among learners. Collaboration management Opportunities for collaboration are guided by the teacher. Feedback Students should be given effective and prompt feedback on their learning progress. This includes prompt return or marked assignments, and self— assessment exercises that allow students to assess their learning 3 Feedback on the Learning experience Students are able to provide feedback about their learning and how it can be improved. Formative assessment Feedback to allow students to assess their progress with learning. Summative assessment Feedback on graded assessment activities (especially formative assessment). Charles Darwin University, Office of Learning and Teaching, Higher Education Training and Development Team Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary Sheet, Version 3, October 2015 Inclusiveness Learning should be designed to allow for diversity in culture, learning styles and abilities, and physical abilities Teaching practices A culturally inclusive, safe learning environment is actively fostered. Indigenous Indigenous students and perspectives are fully included. English Language All students are provided with opportunities to develop their English Language skills International International students and perspectives are fully included User interface design The design of the course is attractive and accessible to all learners. Universal design is better for everybody. Technical design Course content and activities take into account technological aspects of learner access. 4 Charles Darwin University, Office of Learning and Teaching, Higher Education Training and Development Team Exemplary Learnline Unit Summary Sheet, Version 3, October 2015