etc2805-sm-0001-SuppData_S1
advertisement
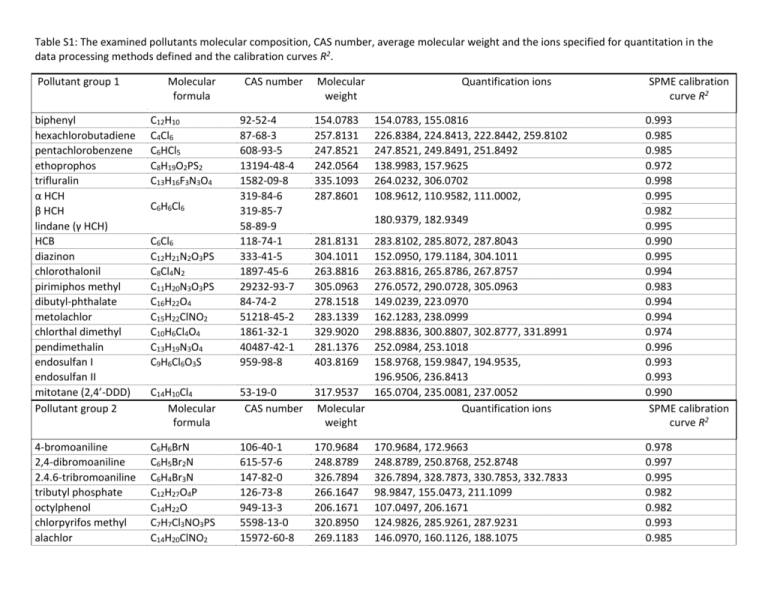
Table S1: The examined pollutants molecular composition, CAS number, average molecular weight and the ions specified for quantitation in the data processing methods defined and the calibration curves R2. Pollutant group 1 Molecular formula biphenyl hexachlorobutadiene pentachlorobenzene ethoprophos trifluralin α HCH β HCH lindane (γ HCH) HCB diazinon chlorothalonil pirimiphos methyl dibutyl-phthalate metolachlor chlorthal dimethyl pendimethalin endosulfan I endosulfan II mitotane (2,4’-DDD) Pollutant group 2 C12H10 C4Cl6 C6HCl5 C8H19O2PS2 C13H16F3N3O4 4-bromoaniline 2,4-dibromoaniline 2.4.6-tribromoaniline tributyl phosphate octylphenol chlorpyrifos methyl alachlor CAS number Molecular weight Quantification ions 92-52-4 87-68-3 608-93-5 13194-48-4 1582-09-8 319-84-6 319-85-7 58-89-9 118-74-1 333-41-5 1897-45-6 29232-93-7 84-74-2 51218-45-2 1861-32-1 40487-42-1 959-98-8 154.0783 257.8131 247.8521 242.0564 335.1093 287.8601 C14H10Cl4 Molecular formula 283.8102, 285.8072, 287.8043 152.0950, 179.1184, 304.1011 263.8816, 265.8786, 267.8757 276.0572, 290.0728, 305.0963 149.0239, 223.0970 162.1283, 238.0999 298.8836, 300.8807, 302.8777, 331.8991 252.0984, 253.1018 158.9768, 159.9847, 194.9535, 196.9506, 236.8413 53-19-0 317.9537 165.0704, 235.0081, 237.0052 CAS number Molecular Quantification ions weight 0.993 0.985 0.985 0.972 0.998 0.995 0.982 0.995 0.990 0.995 0.994 0.983 0.994 0.994 0.974 0.996 0.993 0.993 0.993 0.990 SPME calibration curve R2 C6H6BrN C6H5Br2N C6H4Br3N C12H27O4P C14H22O C7H7Cl3NO3PS C14H20ClNO2 106-40-1 615-57-6 147-82-0 126-73-8 949-13-3 5598-13-0 15972-60-8 170.9684 248.8789 326.7894 266.1647 206.1671 320.8950 269.1183 0.978 0.997 0.995 0.982 0.982 0.993 0.985 C6H6Cl6 C6Cl6 C12H21N2O3PS C8Cl4N2 C11H20N3O3PS C16H22O4 C15H22ClNO2 C10H6Cl4O4 C13H19N3O4 C9H6Cl6O3S 154.0783, 155.0816 226.8384, 224.8413, 222.8442, 259.8102 247.8521, 249.8491, 251.8492 138.9983, 157.9625 264.0232, 306.0702 108.9612, 110.9582, 111.0002, SPME calibration curve R2 180.9379, 182.9349 281.8131 304.1011 263.8816 305.0963 278.1518 283.1339 329.9020 281.1376 403.8169 170.9684, 172.9663 248.8789, 250.8768, 252.8748 326.7894, 328.7873, 330.7853, 332.7833 98.9847, 155.0473, 211.1099 107.0497, 206.1671 124.9826, 285.9261, 287.9231 146.0970, 160.1126, 188.1075 chlorpyrifos chlorfenvinfos transpicoxystrobin tris-(1,3-diClIp) phosphate (TDCIPP) diflufenican triphenyl phosphate naphthalene anthacene phenanthrene C9H11Cl3NO3PS C12H14Cl3O4P C18H16F3NO4 C9H15Cl6O4P C19H11F5N2O2 C18H15O4P C10H8 C14H10 2921-88-2 18708-86-6 117428-22-5 78-43-3 83164-33-4 115-86-6 91-20-3 120-12-7 85-01-8 348.9263 357.9695 367.1031 427.8839 394.0741 326.0708 128.0626 178.0783 196.9202, 198.9173, 257.8948, 313.9574 266.9381, 268.9351, 323.0007 315.9544 145.0653, 173.0603, 335.0769 75.0002, 98.9847, 190.9432, 266.0429, 394.0741 192.9402, 208.9537 326.0708, 327.0742, 233.0368 128.0626, 129.0660 178.0783, 179.0816 0.993 0.993 0.995 0.986 0.978 0.999 0.992 0.995 Table S2: Percentages of DOC-bound test compounds at 5 different CDOC values and in the Baltic Sea sample. DOC-sorbed concentrations at different DOC concentrations naphtalene phenanthrene anthracene trifluralin pentachlorobenzene mitotane pendimethalin chlorothal dimethyl pirimiphos methyl octylphenol hexachlorobenzene dibutyl phthalate diazinon TCDIPP metolachlor ethoprophos triphenyl phosphate biphenyl picoxystrobin 2,4-dibromoaniline hexachlorobutadiene 4-bromoaniline alachlor chlorpyrifos diflufenican chlorothalonil trans-chlorfenvinfos chlorpyrifos methyl 2,4,6-tribromoaniline tributyl phosphate Baltic Sea sample 5 mg L-1 10 mg L-1 50 mg L-1 100 mg L-1 200 mg L-1 5.1 mg L-1 7.7 7.5 14.8 33.0 30.3 37.5 39.8 22.4 45.3 37.6 47.7 36.8 15.0 13.4 11.2 28.4 22.4 4.2 18.1 4.8 6.4 6.6 4.8 19.4 23.6 18.6 21.4 13.2 5.9 43.5 11.3 12.7 30.7 44.7 40.6 47.0 48.7 28.4 61.8 64.6 65.6 66.6 67.0 25.8 33.9 36.8 47.7 7.0 44.7 8.3 8.4 8.8 9.3 50.8 54.6 45.4 39.2 27.2 11.5 72.7 31.7 29.7 51.1 39.8 42.6 55.2 58.5 30.2 76.7 92.2 78.1 73.4 67.5 41.5 38.1 42.8 74.5 9.5 90.6 18.7 34.3 17.9 18.2 68.9 82.1 54.6 80.0 52.3 21.6 80.5 56.0 41.8 78.9 54.7 45.9 59.6 60.2 30.5 82.4 94.3 80.7 79.7 74.5 61.0 41.7 48.7 80.3 15.8 92.1 29.8 36.4 24.6 26.3 80.4 88.8 63.7 87.5 93.9 36.7 89.7 91.6 60.6 93.3 51.4 46.3 59.5 62.7 38.2 89.4 95.8 93.5 84.7 78.5 65.8 49.7 53.2 87.0 19.5 94.2 47.5 46.0 27.3 29.1 84.4 91.7 67.7 89.5 94.0 63.6 92.5 N.S. N.S. N.S. N.S. 9.0 7.8 10.0 10.9 13.5 18.1 3.0 20.8 15.2 12.6 12.0 N.D. 24.9 5.6 18.2 6.8 10.9 26.8 20.7 48.9 45.4 32.7 37.6 17.2 10.7 71.4 No big changes in percentages sorbed (within ± 3 %) to DOC compared to 5 mg L-1 Large decrease in percentages sorbed to DOC compared to 5 mg L-1 Large increase in percentages sorbed to DOC compared to 5 mg L-1 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1: The autosampler sequence schedule with the PrepAhead function. The 10 subsequent runs are represented by horizontal bars labeled by numbers with different sections. For each run the equilibration times were set to 30 min (first section of the bar), the extraction times for FS-PDMS fibers were 2 min (second section). Than the bars are split up into two subsections, the upper section represents the fiber desorption times (1.5 min) while the lower section depicts the GC run and GC oven cooldown times (9.8 and 2 minutes respectively). With the PrepAhead function engaged it is possible to overlap different processes to minimize the full analysis cycle times to the GC run times Figure S2: Calibration curves for biphenyl (a), diazinon (b), 2,4-dibromoaniline (c) and triphenyl phosphate (d). Exact aqueous concentration on the x-axis (ng mL-1) and the peak area on the y-axis. Figure S3: Comparison of total ion chromatograms (TIC) of the GC-MS analysis of SPME samples with (bashed line) and without (solid line) added DOC. Differences of peak areas correspond to a signal decrease of the spiked compounds due to the addition of DOC Figure S4: Extracted ion chromatograms from samples without (dashed line) and with (black line) added fulvic acid Figure S5: Log KDOC versus log KOW data for compounds that have been found in the literature (a) including pyrene and accordingly, the experimentally determined (b) solely for fulvic acids. Figure S6: Percentages of the amounts of test compounds sorbed to DOC at CDOC of 5 – 200 mg L-1. The bars from left to right correspond to CDOC of 5, 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg L-1. Figure S7: The measured log KDOC values for different DOC concentrations. The bars from left to right correspond to CDOC of 5, 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg L-1. Figure S8: Differences of the measured log KDOC values relative to the log KDOC average values over the 10 – 100 mg L-1 CDOC range. The bars from left to right correspond to CDOC of 5, 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg L-1. Figure S9: Percentages sorbed to DOC at CDOC range of 5 – 200 mg L-1 for test compounds where the sorbed amounts to DOC did not reach 10% at more than 3 DOC concentrations. The bars from left to right correspond to CDOC of 5, 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg L-1. Endo-I and endo-II stand for endosulfan-I and –II. Figure S10: The measured log KDOC values at CDOC range of 5 – 200 mg L-1 for test compounds where the sorbed amounts to DOC did not reach 10% at more than 3 DOC concentrations. The bars from left to right correspond to CDOC of 5, 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg L-1. Endo-I and endo-II stand for endosulfan-I and –II.