Beer-Lambert Law: Spectrophotometry Study Guide
advertisement

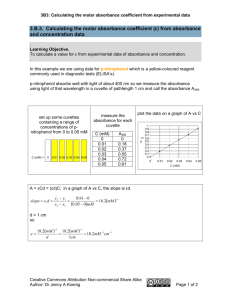
Royal Society of Chemistry ‘Study Guide’ - G Currell -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Spectrophotometric measurement of concentration: Beer-Lambert Law The absorbance, A, (sometimes known as optical density, OD), of light passing through a solution is given by the Beer-Lambert law as: A = ε×b×C where ε (Greek letter, epsilon) is the molar absorptivity of the solute with units of M-1 cm-1 (or (mol L-1)-1 cm-1 or mol-1 dm3 cm-1) b is the path length of the light through the solution in units of cm. C is the concentration of the solution in mol L-1 (or mol dm-3 or M) This straight line relationship works well for dilute solutions (low values of C), but it is important to remember that, at higher concentrations, the equation can cease to be valid and the relationship between A and C becomes non-linear. In a simple spectrophotometric experiment to measure the concentration of a solution of potassium permanganate: 1. the spectrophotometer is zeroed to give A = 0 when C = 0, by using a 'blank' solution (this can occur automatically in a double-beam instrument), 2. the absorbances, A, are measured for a series of standard concentrations, C, of potassium permanganate at a wavelength of 522 nm, 3. a 'best-fit' line of regression in a graph of the measured values of A against C, gives a calibration line for the particular measurement, 4. the absorbance, Ao, of the solution being tested is measured and the equivalent value of concentration, Co, is calculated from the calibration line. The absorbance, Ao, of the solution being tested is measured three times, giving replicate values, Ao = 0.763, 0.741, 0.749. The calibration values of absorbances, A, of the six standard concentrations, C, are given in the table below: C (mg L-1) 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 A 0 0.267 0.583 0.824 1.120 1.313 1.499 Molar mass of potassium permanganate, KMnO4, Mm = 158 g mol-1. Answer the following questions: Question 1 Use the experimental data to calculate a 'best-estimate' for the concentration, Co, of the test solution. Calculate a 'best-estimate' for the molar absorptivity, ε, of potassium permanganate at this wavelength, assuming that the path length of the cell used to hold the solution is 10 mm. You will need to consider the applicability of Beer's law for this particular set of experimental data. Question 2 (advanced) Calculate the 95% confidence interval for your value of, Co.