MCQ`s With KEY MEDICINE
advertisement

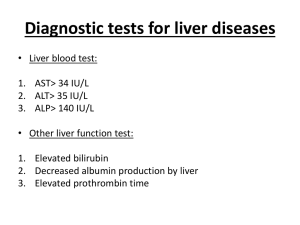
Surgery Paper MCQ’s along with KEY The Bold Option is KEY 1: A 37 y/o female presented with pain in the epigastrium. She pointed her fingers at the pain site.She also complaints of heart burning and post prandial discomfort. You perform H. Pylori antibody test and it is positive. What is your Diagnosis? a. Dyspepsia b. Gastritis c. Peptic ulcer disease. d. All of the above e. None of the above 2: A patient presents with pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen with Jaundice and ascites. He has itching, indigestion and a history of weight loss. The gall bladder is palpable on examination, what type of jaundice is this? a. Hemolytic (Prehepatic) b. Hepatic c. Obstructive (Post Hepatic) d. Unknown etiology. e. All of the above 3: A CT scan is performed, there is a mass in the Head of the Pancreas. It is most probably: a. Carcinoma head of the pancreas. b. pancreatic pseudocyst c. Chronic pancreatitis d. Benign Tumor. 4: This condition is caused by: a. Fatty Meals b. Smoking. c. Environmental factors d. Starvation/ Strict dieting e. None of the above 5: A patient presented with cramping abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and fever. You suspect: a. Amoebic dysentery (Ameobiasis) b. Diarrhea secondary to food poisoning c. Viral Diarrhea secondary to Rota Virus. d. All of the above e. None of the above 6: The above patient should be treated with: a. Metronidazole TDS for 5-7 days b. ORS only c. Ciprofloxacin TDS for 3 days d. IV fluids and elcetrolytes. e. All of the above 7: The above condition can cause: a. Amoebic Liver Abscess b. Dehydration c. Blood loss d. All of the above e. None of the above 8: If Amoebic liver Abscess is diagnosed, it is treated with: a. Albendazole 200 mg BD for 3 days, KEY: a b. Metronidazole 800mg TDS for 7-10 Days c. Tinadozole 400 mg TDS d. All of the above e. None of the above 9: Cirrhosis of the liver is related to: a. Alcohol use b. Drugs c. Defective regeneration process d. Viral Hepatitis e. All of the above. 10: Bile is produced by: a. The gall bladder b. The liver c. The pancreas d. RBCs e. None of the above 11: What does the liver do to the bilirubin produced by RBC breakdown: a. Absorbs b. Congugates c. Breaks down. d. All of the above e. None of the above 12: A patient has a fatty liver on Ultrasound scan. It is called: a. Hepatic Steatosis b. Hepatic Fibrosis c. Hepatic Cirrhosis d. Hepatomegaly e. All of the above 13: Fatty liver is the precursor for Cirrhosis of the liver: a. True b. False c. May be d. All of the above e. None of the above 14: The function of bile in digestion is related to: a. Fat digestion by Emulsification b. Absorption of glucose c. Breakdown of proteins d. All of the above e. None of the above 15: A 45y/o Fat, Fertile, Female presented with pain in the RUQ that occurs after a Fatty meal. Your suspected Diagnosis is: a. Cholecystitis secondary to gall stones b. Cholangitis c. Obstructive jaundice d. Dyspepsia e. Peptic Ulcer disease 16: Fever with chills, jaundice and pain in the RUQ is called: a. Charcot`s Triad b. Murphy`s sign c. Courviser`s law d. All of the above e. None of the above 17: It occurs in: a. Cholingitis b. Cholelithisis (gall stones) c. Cholangiocarcinoma d. All of the above e. None of the above 18: You suspect PBC (primary biliary cirrhosis) in a patient who presents with generalized pruritis (Itching)and jaundice. What drug will you prescribe? a. Ursodeoxycolic acid b. Vitamin supplememtation c. Antiallergics for itching d. DIgestive enzymes. e. None of the above 19: A young female patient has been on Oral contraceptive pills i.e OCP`s. She felt her RUQ was painful. A CT scan was done and a liver mass was detected. Most probable diagnosis is: a. Benign liver tumor b. Malignant Tumor c. Metastatic liver Tumor d. Hepatocellular Carcinoma e. None of the above 20: A patient has Ascites and portal hypertension secondary to Liver pathology. She is chronically ill, has melena and hematemesis. Looks drowsy and pale.Has multiple bruises on her skin and a flapping tremor of her hands. There is moderate splenomegaly and decreased dullness over the liver on examination. The most probable bleeding site is: a. Esophageal varices. b. Intra Hepatic lesion c. Skin lesions d. Intravascular hemolysis. e. All of the above 21: A patient has hepatic failure. The best indicator of liver function is: a. increased liver enzymes b. increased Prothrombin time c. decreased bilirubin d. Encephalopathy e. None of the above 22: Liver manufactures which of the following a. Clotting factors b. Bile c. Albumin d. Urea from Ammonia e. All of the above 23: Renal failure secondary to Liver pathology is called: a. Renal failure b. Hepatic failure c. Hepato-Renal Syndrome d. Hepatic encephalopathy e. All of the above 24: A patient presented with severe epigastralgia (pain epigastrium) . Serum Amalyase and LDH levels are high. RBS is 220mg/dl. The patients seems to be in distress and dehydrated. Your diagnosis is: a. Acute Cholecystitis b. Acute Pancreatitis c. Peptic Ulcer disease. d. Peptic Pain. e. None of the above 25: A patient was admitted to the ward with mild jaundice. Liver function tests were normal. On U/S no abnormality was detected in the biliary tract. However unconjugated Bilirubinema was detected. You diagnosed Gilbert`s syndrome which is a congenital disease. What will you tell the patient about it: a. It is curable. b. It is a fatal disease, c. Your liver can not conjugate bilirubin. d. All of the above e. None of the above 26: A 33 y/o female presented with fever, malaise and cough for the past 3 months. She also has a red rash i.eerythema nodosum on her legs. Chest X-Ray shows bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Whats your diagnosis? a. Pulmonary tuberculosis. b. Sarcoidosis. c. Pneumonia. d. Bronchial Asthma. e. Pulmonary Embolism. 27. A 7 year old child presents with cough and shortness of breath which is episodic. On chest Auscultation bilateral diffuse wheezing can be heard. He has pets in the house and had atopic (allergic) eczema in early childhood. Your diagnosis? a. Allergy b. Bronchial Asthma c. Acute Bronchitis d. Bronchopneumonia e. Laryngotracheobronchitis (Viral croup) 28. A lady had a road traffic accident. Her chest was hit by the steering wheel of her car. She has chest pain. You suspect fracture of which of the following bones: a. Anterior Ribs b. Sternum. c. Scapulae. d. Clavicle. e. None of the above 29. A 72 y/o Male presented with cough, fever with chills, right sided chest pain that increases with inspiration. He has increased sputum production. On chest X-Ray there is right sided consolidation in the lower lobe. Your diagnosis is: a. Pulmonary embolism b. Pneumonia c. Pneumothorax d. Pulmonary tuberculosis. e. All of the above 30. Carcinoma of the lungs can be prevented by which of the following measures: a. Reducing air pollution b. Quitting cigarette smoking. c. Early screening for lung cancers. d. Wearing facial masks in dusty environment. e. All of the above 31. A 17 year old male has a history of weight loss, nocturnal fever with sweating, cough and right sided chest pain on inspiration for the past 1 month. Chest X-Ray has a blunted costophrenic angle on the right lower lung field. You suspect: a. Bronchopneumonia. b. Pleural effusion secondary to Pulmonary T.B. c. Carcinoma of the lungs. d. Aspiration Pneumonitis. e. Acute Bronchitis. 32. A young female presented with sudden onset of severe left sided chest pain that increases with respiration. She has tachypnea and diaphoresis (sweating) Auscultation reveals absent breath sounds and percussion reveals hyper-resonant sounds on the right side. What is the diagnosis? a. Bronchial obstruction. b. Tension pneumothorax. c. Anxiety neurosis. d. Emphysema e. Bronchopneumonia. 33. A HIV positive patient presented with cough not responding to cough syrups. An opportunistic infection is suspected. Your diagnosis is: a. Bronchopneumonia. b. Lobar pneumonia. c. Aspiration pneumonitis. d. Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia 34. A 72 y/o male who started smoking at the age of 22 years develops sudden onset of chest pain and dyspnea. He has had recurrent respiratory tract infections in the recent past. He has miosis, ptosis and anyhdrosis on the left side of his face. What is this condition called: a. Cushing`s Syndrome. b. SIADH. c. Kallman`s syndrome. d. Down`s syndrome. e. Horner`s syndrome. 35. Your Diagnosis is: a. Bronchogenic Carcinoma. b. Mesothelioma. c. Metastatic Lung Cancer. d. All of the above e. None of the above 36. Which afferent nerve fibers are involved: a. Parasympathetic b. Sympathetic c. Cranial Nerves d. Dermatomes e. Peripheral Nerves 37. A patient is put on Anti-Tubercular therapy (ATT) for pulmonary TB. Which drug causes hepatotoxicity? a. Isoniazid b. Rifampicin c. Ethambutol d. Pyrazinamide e. All of the above. 38. Which of the above drugs is toxic to the retina (eye)? a. Isoniazid b. Rifampicin c. Ethambutol d. Pyrazinamide e. None of the above 39. The patient comes to you after a week and says that her tears, contact lenses and underwear are stained orange in color. Which drug caused it? a. INH b. Rifampicin c. Ethambutol d. Pyrazinamide. e. Streptomycin 40. The patient feels better after 2 months therapy. What should you do? a. Stop all the drugs b. Stop PZA and continue the other three for another four months, c. Give Rifampicin only for 6 more months d. Reassure and send him home with out any drugs e. INH alone should be continued for atleast 6 more months. 41. Bronchial asthma being a chronic disease is: a. Curable b. Can be managed. c. Contagious d. Communicable e. None of the above 42. A 23 y/o lady returned from Hajj where she had been taking oral contraceptive pills (OCP`s) to avoid menstruation. She developed swelling in her calf muscles and had dyspnea and chest pain. She is unconscious now with a low blood pressure. Lung fields are clear on auscultation and a chest Roentgenogram (X-Ray). She has a loud P2 at the left sternal border. There is jugular venous distention. Your diagnosis? a. Acute pulmonary thrombo-embolism b. Right sided heart failure. c. Pulmonary edema d. Heat Exhaustion or Heat Stroke e. All of the above 43. T0his condition occurred because of: a. A hypercoaguable state due to OCP`s b. A hyperdynamic circulation c. Due to over exertion d. Physical stress of the journey. e. None of the above 44. Right sided heart failure secondary to a pathology is the lungs is called: a. Corpulmonale b. Congestive heart failure c. Pericadritis d. Pulmonary edema e. All of the above 45. A patient had an opiod overdose. He is an Intravenous drug abuser and injects morphine. He has euphoria and has pin point. His respiratory rate is expected to be pupils: a. Normal (Eupnea) b. Fast (Tachypnea) c. Slow (depressed) Bradypnea d. Apnea (Absent breathing) e. All of the above