Section 1 Notes
advertisement
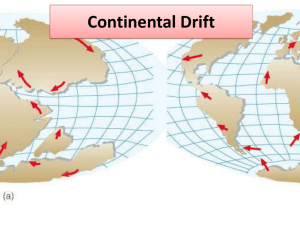
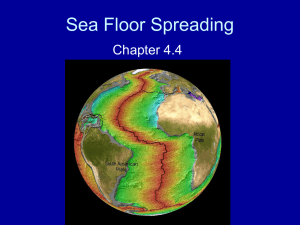
Name: ____________________________ Date: ___________________________ Chapter 10: Plate Tectonics Section 1: Continental Drift Wegener’s Hypothesis Continental drift - the hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form continents, which then drifted to their present location. As people studied continental coastlines on maps, they noticed that the continents looked as though they would fit together like parts of a giant _____________________________________________________. The hypothesis of continental drift was first proposed by German scientist _______________________________________ in 1912. Wegener used several different types of evidence to support his hypothesis. Fossil Evidence Fossils of the same _____________________and______________________ could be found in areas of continents that had once been connected. Evidence from Rock Formations Ages and types of rocks in the ______________________________________ of widely separated areas matched closely. Climactic Evidence Changes in _________________________________________________ suggested the continents had not always been located where they are now. Similar rock formations and fossil evidence supported Wegener’s hypothesis. Missing Mechanisms Despite the evidence that supported his hypothesis, Wegener’s ideas were strongly ___________________________________________. Other scientists of the time rejected the mechanism proposed by Wegener to explain how _______________________________________________________________. Wegener suggested that the continents moved by _______________________________________________________________________ of the ocean floor. This idea was shown to be physically impossible. Wegener spent the rest of his life searching for a _______________________________ for the movement of continents. Name: ____________________________ Date: ___________________________ READING CHECK Why did many scientists reject Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? Mid-Ocean Ridges Mid-ocean ridge a _____________________________________________________ that has a steep, narrow valley at its center Forms as _______________________________________ from the asthenosphere Creates new oceanic ________________________ (sea floor) as tectonic plates move apart The evidence that Wegener needed to support his hypothesis was discovered nearly ____________________________________________ after his death. In 1947, a group of scientists set out to map the ____________________________. While studying the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, scientists noticed __________________________ surprising trends. 1. The sediment that covers the sea floor is ________________ closer to a ridge than it is farther from the ridge. 2. The ocean floor is ______________________________. While rocks on land are as much as __________________________________, none of the oceanic rocks are more than __________________________________________. Rocks _____________________to a mid-ocean ridge are __________________ than rocks farther from the ridge. Rocks _______________________to the ridge are covered with _______________________________________ than rocks farther from the ridge. Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-floor spreading - the process by which new _____________________________________ (sea floor) forms as magma rises to Earth’s surface and solidifies at a mid-ocean ridge Name: ____________________________ Date: ___________________________ In the late 1950s, geologist _________________________________________ proposed that the valley at the center of a mid-ocean ridge was a crack, or ___________________, in Earth’s crust. As the ocean floor moves away from the ridge, molten rock, or magma, _________________________ to fill the crack. Hess suggested that if the _______________________________ is moving, the continents might be moving also. He suggested this might be the mechanism that Wegener was searching for. As the ocean floor spreads apart, magma rises to fill the rift and then cools to form new rock. READING CHECK How does new sea floor form? Paleomagnetism Paleomagnetism - the study of the alignment of ______________________________________ in rock, specifically as it relates to the reversal of Earth’s magnetic poles; also the magnetic properties that rock acquires during formation As magma solidifies to form rock, _________________________________ minerals in the magma align with Earth’s magnetic field. When the rock hardens, the magnetic orientation of the minerals becomes ______________________________. Magnetic Reversals o Scientists have discovered rocks whose magnetic orientations point _________________________of Earth’s current magnetic field. o Rocks with magnetic fields that point ______________________________, or _______________________________________, are classified in the same time interval. Rocks with magnetic fields that point _______________________________, or ________________________________, also fall into specific time intervals. o When scientists placed these periods of normal and reversed polarity in ____________________________________________, they discovered a pattern of alternating normal and reversed polarity in the rocks. Name: ____________________________ Date: ___________________________ o Scientists used this pattern to create the _________________________________________________________________. Magnetic Symmetry o Scientists discovered a ___________________________________________________ on the ocean floor on each side of a mid-ocean ridge. o The pattern on one side of the ridge is a ________________________________ of the pattern on the other side. o When drawn on a map, these patterns ____________________ the geomagnetic reversal time scale. o The symmetry of magnetic patterns and the symmetry of ages of _____________________________ rocks supports Hess’s idea of sea-floor spreading. Magnetic Symmetry o The pattern of magnetic symmetry and age of rock formation indicate that new rock forms at the center of a ridge and then move away from the center in opposite directions. READING CHECK o How are magnetic patterns in sea-floor rock evidence of sea-floor spreading?