final exam - Chemistry at Winthrop University
advertisement

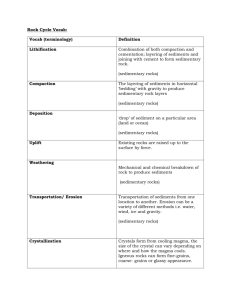
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM – ONLY WRITE ON THE ANSWER SHEET! Multiple Choice Questions (50 points) – for each question, please choose the best answer and circle your answer on the answer sheet (do not write on this exam). One point each. 1. Identify the FALSE statement. William Smith’s observations a) were made around 1800 in fresh exposures of sedimentary bedrock in the English countryside. b) recognized that groups of fossil species (fossil assemblages) occurred in limited intervals of strata. c) noted that a fossil species could disappear, then reappear in much younger strata. d) led to the principal of fossil succession. e) recognized that fossil species progressed from older at the bottom to younger at the top of sedimentary strata. 2. Which of the following statements is FALSE? The principle of a) superposition says that in a sequence of sedimentary beds, the youngest is on top. b) original continuity says that sedimentary layers began as continuous expanses of sediment. c) inclusions says that rock containing inclusions is older than the inclusions. d) cross-cutting relations says that the feature doing the cutting is younger than the feature it cuts. e) original horizontality says that sedimentary layers started out flat. 3. The two most common gases of Earth’s atmosphere and their percentages are a) carbon dioxide (CO2), 21%, and oxygen (O2), 78%. b) water (H2O), 21%, and oxygen (O2), 78%. c) oxygen (O2), 21%, and carbon dioxide (CO2), 78%. d) nitrogen (N2), 21%, and oxygen (O2), 78%. e) nitrogen (N2), 78%, and oxygen (O2), 21%. 4. Large oil fields contain such great quantities of oil because they’ve developed from the largest dinosaurs. a) True; b) False 5. Macroscopic organic material (leaves, stems, trunks) of swampy areas undergoes heat and pressure in an oxygen-poor environment over a geologically long time. The result is a) oil shale. b) kerogen. c) tar sands. d) petroleum. e) coal. 6. Boundaries between Earth’s layers a) are unreachable to humans, so they must be studied by indirect methods. b) are defined by abrupt changes in earthquake-wave velocities. c) are places where there’s abrupt change in the density of rock. d) divide the Earth into three major layers (crust, mantle, and core) and several sublayers. e) All the possible answers are correct. 7. A rock is a solid organic substance in which atoms are arranged either in an orderly pattern (crystalline) or as irregularly shaped grains; a mineral is an aggregate (mixture) of rocks. a) True; b) False 8. Identify the FALSE statement: a) Metamorphic rocks form when preexisting rocks undergo changes in response to heat and pressure. b) Hot molten rock that cools and hardens produces igneous rocks. c) Sedimentary rocks form when preexisting rock grains are cemented together. d) Sedimentary rocks form when minerals precipitate out of a water solution. e) Magma is the term for very hot rock that is molten; when it cools and hardens, it’s called lava. 9. Identify the FALSE statement: The categories of materials that constitute Earth include a) glasses; solids in which atoms are not in any orderly pattern. b) volatiles; materials that easily become gases at ordinary Earth surface temperatures. c) organic chemicals; all carbon-containing compounds, including oil, protein, carbon dioxide, and calcium carbonate. d) alloys; mixtures of more than one type of metal atom. e) melts; solid materials that have melted due to heat. 10. A cross-section cut through the Earth would reveal a very thin atmosphere surrounding a thin crust of low-density rock, all shifting around slowly on an internal sea of semi-liquid rock (magma.) a) True; b) False 11. Earthquakes are generated when rock moves along faults. a) True; b) False 12. Iron a) is forming today in the Great Lakes region as banded iron formations (BIFs). b) is mined from bauxite deposits. c) was the first of the common metals (iron, aluminum, and copper) to be smelted for use by humankind. d) constitutes up to 85 percent of some ore deposits. e) All the possible answers are correct. 13. The inner core is so hot, it’s liquid, and therefore some seismic waves can’t travel through it. a) True; b) False 14. Which of the following statements is FALSE? Mass movement a) simply explained, means things have a tendency to move downward because of gravity. b) was the basic cause of the tragedies of Yungay, Peru, and Armero, Colombia. c) is more likely to happen under wet conditions than under dry conditions. d) happens when the slope of a hill gets steeper than the angle of repose. e) can’t happen underwater because the buoyancy force of water is too great. 15. Which statement about the hydrologic cycle is FALSE? a) It includes the exchange of water among oceans, land, and atmosphere. b) Water that infiltrates the ground exits from the hydrologic cycle. c) Processes that do not involve liquid or gasseous (vapor) of H20 can also be part of the hydrologic cycle. d) Precipitation can fall directly into a stream, accumulate in a standing body, become sheetwash, or infiltrate the soil. e) It includes water that is released into the air by plants during photosynthesis. 16. Black smokers are undersea springs of hot water rich in mineral precipitate. a) True; b) False 17. Which of the following would increase the risk of having a landslide? a) allowing water to infiltrate the slope b) removing weight at the top of the slope c) adding support to the toe of the slope d) recontouring the slope to reduce its slope angle e) planting vegetation that has deep roots 18. Because the majority of Earth’s crust is oceanic, the oldest crustal rocks will likely be igneous rocks of the sea floor. a) True; b) False 19. Streams come down out of steep areas onto much flatter land, lose velocity, and drop material in wedge-shaped structures called a) point banks. b) alluvial fans. c) levees. d) sandbars. e) deltas. 20. Stars are evenly distributed throughout the Universe. a) True; b) False 21. Which of these was NOT a line of evidence for the original proposal of the supercontinent Pangaea? a) closely matching coastlines of several continents, if arranged together b) radiometric age-dating of similar types of rocks on several continents c) the types and distributions of fossils in similar rocks on several continents d) traces of past glaciations on now far-separated and, in some cases, subtropical or equatorial lands e) inferred similarities of past climates made from rocks on continents with now very different climates 22. Earthquakes are the best geologic marker for the three types of plate boundaries. a) True; b) False 23. Why were the apparent histories of polar wander later discarded as nearly meaningless? a) The Earth’s magnetic field has sometimes had multiple north and south magnetic poles at the same time. b) The records of apparent past polar wander are affected by the passage of seismic waves. c) No single reference point or area could be relied upon as having remained in the same place on the planet’s surface. d) Inundation of rocks by flooding or rising groundwater can erase the paleomagnetic record. e) Glaciers have lasting effects upon the paleomagnetic records of rocks over which they pass. 24. A hot spot track is formed by the periodic eruption of material from a mantle hot spot through a plate that is migrating over the Earth’s surface. a) True; b) False 25. Who was Alfred Wegener? a) a pioneer of paleomagnetism b) a desert explorer c) the first geoscientist to provide geologic observations supporting a vastly different past arrangement of the continents d) one of several men in the 1960s who developed the basic theory of plate tectonics e) All the possible answers are correct. 26. The Moho lies below the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. a) True; b) False 27. Which of the following key methods for identifying both plate boundaries and the relative motions of plates did not exist in the early 1960s? a) isotopic age-dating that has verified the distribution of sediment and sea-floor igneous rock ages b) global positioning system (GPS) data c) a method for accurately determining the locations at which earthquakes occurred d) the ability to accurately determine both paleomagnetic declination and inclination e) All the possible answers are correct. 28. For which of the following reasons is the methane within natural gas not a mineral? a) It’s naturally occurring. b) There may have been biological processes involved in its formation. c) It has a specific composition. d) It is formed by geologic processes. e) It lacks a crystalline structure. 29. Which is NOT a physical property commonly used in the lab or field to identify minerals? a) color b) streak c) luster d) diffraction e) specific gravity 30. Ore minerals are often sulfides and oxides of metallic elements. a) True; b) False 31. Minerals generally can be destroyed by heating, dissolution or other chemical reaction. a) True; b) False 32. Silicates a) have the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron as their structural unit. b) are a major component of continental crust. c) are classified on the basis of how the tetrahedrons join and share oxygen atoms. d) are a huge category of minerals and include the common minerals quartz and feldspar. e) All the possible answers are correct. 33. Color and cleavage are two very useful physical properties used to identify quartz. a) True; b) False 34. Bowen’s reaction series a) shows the sequence in which different silicate minerals form during the progressive cooling of a mafic melt. b) has a discontinuous track in which each step yields a different class of silicate mineral. c) has a continuous track in which there’s a progressive change from calcium-rich to sodium-rich plagioclase. d) was established by laboratory experiments in which mafic melt was quenched in mercury. e) All the possible answers are correct. 35. Identify the FALSE statement: Hot solid rock in the Earth a) may experience decompression melting as it rises to shallow depths. b) may melt if volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide are added. c) may melt if heat is transferred to it from hot mantle rock rising up into the crust. d) maintains uniform composition as it melts and becomes magma. e) may be even hotter than surface lava because of the pressure of overlying rock. 36. Identify the FALSE statement: Mafic minerals a) freeze at a higher temperature than silicic minerals do. b) are those rich in iron and magnesium. c) would be at the top of Bowen’s reaction series, crystallizing first out of the melt. d) form rhyolite and granite. e) form black or dark-gray rocks. 37. Granite a) is a phaneritic rock. b) is felsic in composition. c) logically could be found in a batholith. d) is the coarse-grained equivalent of rhyolite. e) All the possible answers are correct. 38. Mt. St. Helens erupted in 1980, sending out gas and pyroclastics. Geologists have found evidence of many eruptions of St. Helens, dating back 37,000 years. The mountain is huge and is composed of layers of lava and pyroclastics. Which of the following is most likely true? a) When lava flows, it will be basalt. b) It will not erupt again. c) It’s a stratovolcano (or composite cone). d) It’s on a transform-plate boundary. e) It’s a cinder cone. 39. Lava of low viscosity a) could logically build a shield cone. b) indicates an area that has little potential for explosive eruptions. c) is logically basalt. d) has low silica content. e) All the possible answers are correct. 40. Which of the following features indicates the top of a sedimentary bed, or bed-surface, marker? a) scour marks b) fossil footprints c) graded bedding d) mud cracks e) All the possible answers are correct. 41. Formation of a clastic sedimentary rock involves five stages. Which of the following describes lithification? a) disintegration of bedrock into separate particles b) compaction and cementation of loose particles to form solid rock c) separation of rock or regolith from its substrate d) process by which particles settle out of transport medium e) the movement of sedimentary particles by water, wind, or ice 42. Choose the proper listing of detritus terms, going from smallest to largest. a) sand, silt, pebbles b) mud, silt, sand c) silt, mud, sand d) sand, cobbles, pebbles e) mud, sand, silt 43. Foliation occurs along bedding planes. a) True; b) False 44. What is the protolith of marble? a) quartz sandstone b) chert c) phyllite d) gypsum e) limestone 45. Identify the TRUE statement: Quartzite a) is basically a solid mass of interlocking quartz crystals. b) breaks around the separate grains of quartz that make it up. c) is always either white or gray. d) always shows strong compositional banding. e) All the possible answers are correct. 46. Most major earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur a) in similar locations. b) along all three types of plate boundaries. c) within the continental lithosphere. d) along convergent plate boundaries. e) along divergent and convergent plates. 47. Which of the following earthquake phenomena has killed the fewest number of humans? a) ground shaking b) landslides and avalanches c) tsunami d) fire 48. The first half-life period of potassium-40 is 1.3 billion years; the second half-life period of potassium-40 is half of this, and the number of years is cut in half for each succeeding half-life period. a) True; b) False 49. The boundary surface between two stratigraphic formations is called a key bed. a) True; b) False 50. A disconformity is a type of unconformity in which sedimentary rocks overlie either igneous or metamorphic rocks. a) True; b) False