Mitosis and meiosis notes
advertisement
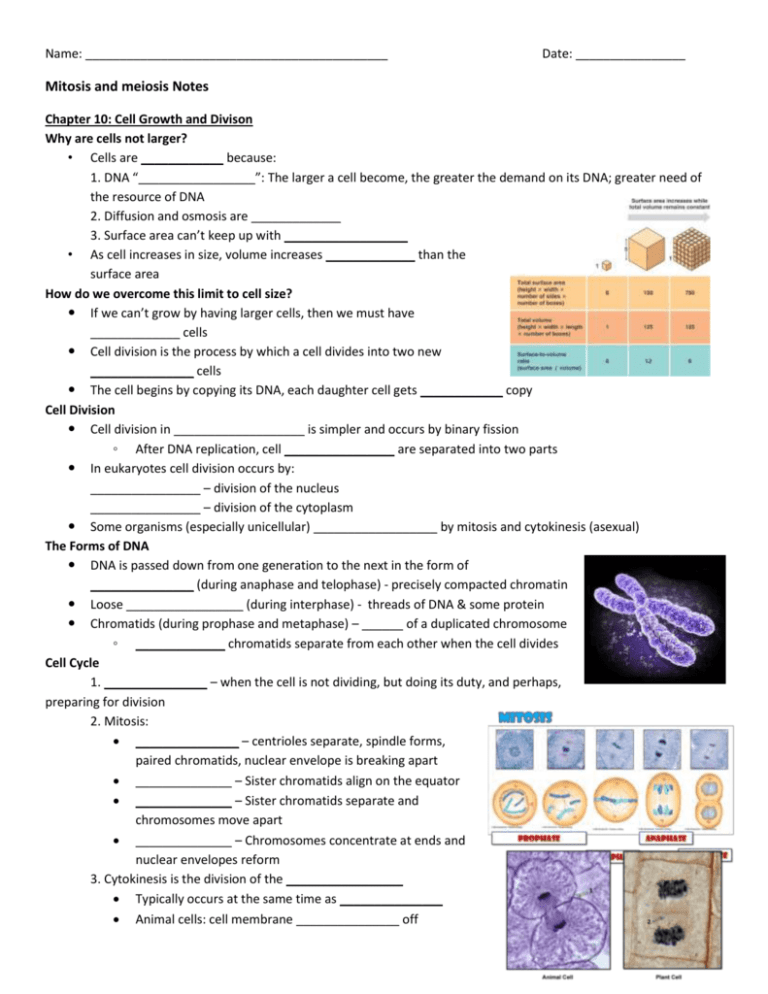
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ________________ Mitosis and meiosis Notes Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Divison Why are cells not larger? • Cells are ____________ because: 1. DNA “_________________”: The larger a cell become, the greater the demand on its DNA; greater need of the resource of DNA 2. Diffusion and osmosis are _____________ 3. Surface area can’t keep up with __________________ • As cell increases in size, volume increases _____________ than the surface area How do we overcome this limit to cell size? If we can’t grow by having larger cells, then we must have _____________ cells Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two new _______________ cells The cell begins by copying its DNA, each daughter cell gets ____________ copy Cell Division Cell division in ___________________ is simpler and occurs by binary fission ◦ After DNA replication, cell ________________ are separated into two parts In eukaryotes cell division occurs by: ________________ – division of the nucleus ________________ – division of the cytoplasm Some organisms (especially unicellular) __________________ by mitosis and cytokinesis (asexual) The Forms of DNA DNA is passed down from one generation to the next in the form of _______________ (during anaphase and telophase) - precisely compacted chromatin Loose _________________ (during interphase) - threads of DNA & some protein Chromatids (during prophase and metaphase) – ______ of a duplicated chromosome ◦ _____________ chromatids separate from each other when the cell divides Cell Cycle 1. _______________ – when the cell is not dividing, but doing its duty, and perhaps, preparing for division 2. Mitosis: _______________ – centrioles separate, spindle forms, paired chromatids, nuclear envelope is breaking apart ______________ – Sister chromatids align on the equator ______________ – Sister chromatids separate and chromosomes move apart ______________ – Chromosomes concentrate at ends and nuclear envelopes reform 3. Cytokinesis is the division of the _________________ Typically occurs at the same time as _______________ Animal cells: cell membrane _______________ off Plant cells: ______________________ forms midway, gradually developing into a separating membrane Cell Division Control Cell growth and cell division are ____________________ controlled ◦ Cells will grow into open space, but when cells ______________ other cells they respond by not growing ◦ Controls for cell growth (cell division) can be turned _______________________ ◦ Similar effect occurs if you _________________ yourself _______________ – proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle Many other proteins involved in regulating the cell cycle including internal and external regulators Cancer – _________________ cell division. Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells Causes of cancer: 1. ____________________ (smoking, UV radiation, viruses…) 2. ________________ (many have a defect in gene p53 which stops the cell cycle until all chromosomes have been properly replicated Cancer Treatments There is no ___________ for cancer, and there probably never will be However, there are a number of current and future cancer _________________ ◦ Radiation therapy- ionizing radiation designed to kill cancer cells; _________________ cancer and healthy cells ◦ Chemotherapy- ____________ that destroy cancer cells; traditionally affect all rapidly dividing cells ◦ _______________- cut out the cancer cells; is not possible for all cancers ◦ Other treatments- angiogenesis inhibitors, targeted therapies, __________________, electroporation, nanoparticles ◦ ____________________________ Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics DNA and Sexual Reproduction Why do many organisms combine _________ from two parents to make offspring? How does a sperm and egg (gametes) _________________ to form 1 cell with appropriate amount of DNA? ◦ If two normal human cells combined to form the new embryo, how much DNA would the embryo have? ◦ How would you overcome this problem? Chromosome Number Humans have _____________ of 23 chromosomes (46 total) ◦ 1 ________ comes from the female, the other from the male parent ◦ The sets are called ________________ chromosomes which code for the same trait but are different A cell that has both sets of homologous chromosomes is called _____________ (2 sets) A cell (gametes) that only contain 1 set of chromosomes is called ____________ (1 set) Meiosis Meiosis is a process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in _________ through the separation of homologous in a diploid cell ◦ Has two distinct sections: ________________________________ ◦ At the end of Meiosis II, 1 diploid cell has become ____________________ cells Meiosis I Prior to Meiosis I each chromosome is _______________ (like mitosis) ◦ Meiosis I is similar to _______________ ◦ Difference is that in prophase I each chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome to form a ______________ ◦ As a result, ________________ occurs which results in exchanging portions of their chromatids Meiosis II After Meiosis I, the two cells enter a _________________ meiotic division (no replication beforehand) ◦ Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II/ Cytokinesis ◦ Cell now only have _________ the standard DNA (chromosomes) – haploid ◦ Each of the 4 cells created are ____________ (genetically different) For males the cell created become sperm, in females an egg (both are ________________)