Mr. Ryan Pioneer Valley High School Earth Science Name: Period
advertisement
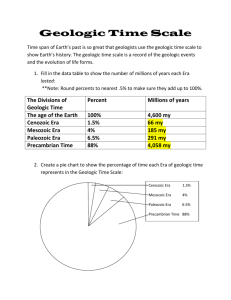
Mr. Ryan Pioneer Valley High School Earth Science Name: ______________________________________ Period: _________ Unit 2: Our Planet Earth Day HW Assignments 1 Tue Unit 2 Vocab #1: 2 Wed Unit 2 Vocab #2: Planetismals Radioactive Decay Particles Energy Differentiation Silica Dense Core Mantle Crust Density Outgassing Gas Molecules Helium Water Vapor Elements Atmosphere Hydrogen Solar Wind Carbon Dioxide 3 Thu Unit 2 Vocab #3 4 Fri The Moon Earths Satellite “worksheet” & Moon Journal 5 Mon 6 Tue Reading Page #’s 688-690 690 28-29 672-674 Ozone Ultraviolet Radiation Photosynthesis Cynobacteria Byproduct Oxygen Chemical Composition Nitrogen Condensed Dissolved Precipitates Unit 3 Vocab #4: 719- 30 In Class Activity Intro (road map) to Unit # 2, SQ3R Earths Formation of: 1) Earth 2) Earths ATM 3) Earth’s Oceans Do “Formation of Earth” RQ: 5-6, SQ3R SQ3R Earth Interior Earth’s Interior RQ: 34, Structure of Earth’s Interior “notes & diagrams”, Center of the Earth “worksheet”, Subsurface Changes “worksheet” Earths Fiery Interior “worksheet”, Density, Video: Density & Buoyancy, Density Problems “worksheet”, Quiz Differentiation lab Axis Rotation The Coriolis Effect Revolution Perihelion Aphelion Ellipse Solstice Equinox Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere Unit 2 Vocab #5: Moon Solar Eclipse Waxing Gibbous Waning Crescent New Moon Satellite Lunar Eclipse Waning Gibbous Waxing Crescent Full Moon 7 Wed Unit 2 Vocab # 6: 8 Thur Unit 2 Vocab # 7: Composition Inner Core Mantle Asthenosphere Oceanic Crust Geologic Time Geologic Eons Geologic Era’s Mesozoic Era Precambrian Time Geologic Column & Moon Journal 667-669 674 Structural Outer Core Moho Lithosphere Continental Crust Geologic Periods Geologic Epoch’s Cenozoic Era Paleozoic Era 211-214 214 Movements of Earth “notes’, Movements of Earth RQ: 1-2, Movements of Earth “notes”, RG: The Seasons, Solstice-vs-Equinox “notes”, Earths 4Seasons ‘notes & diagram”, Video: Earths seasons “BN” Earth’s Moon “reading” Moon Journal, Earth, Sun, Moon System ‘worksheet”, 10 Homework 5 0 Absent 9 Fri Unit 2 Vocab # 8: 10 Mon Unit 2 Vocab # 9: 11 Mon Unit 2 Study Guide & Moon Journal 12 Mon Review for Unit 2 Test & Moon Journal Geologic Time “reading”, Geologic Time RQ: 1-4 Geologic Time Chart “worksheet”, Mesozoic Era “bar graph” Oblate Spheroid Magnetosphere Magnetic Field Mass Magnetic Field Reversals Isaac Newton Galileo Gallia Universal Gravitation Inertia Weight & Moon Journal 54-55 Latitude Longitude Prime Meridian Parallel Meridian Topography Contour Lines Coordinates Topographic Maps International Date Line & Moon Journal 63-65 76 Earth a Unique Planet “reading’ Earth a Unique Planet “worksheet” SQ3R “Finding Locations on Earth”, Latitude and Longitude “diagrams w/notes & worksheet” Topographic Maps “reading’, Topographic Map of Desolation Watershed Unit 2 Review Unit # 2 Test, 13 Moon Journal Mon Key Terms: Planetismals Radioactive Decay Particles Energy Differentiation Silica Dense Core Mantle Crust Density Elements Outgassing Atmosphere Gas Molecules Hydrogen Helium Solar Wind Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide Ozone Ultraviolet Radiation Photosynthesis Cynobacteria Byproduct Oxygen Chemical Composition Nitrogen Condensed Dissolved Precipitates Axis Rotation Coriolis Effect Revolution Perihelion Aphelion Ellipse Solstice Equinox Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere Moon Satellite Solar Eclipse Lunar Eclipse Waxing Gibbous Waning Gibbous Waning Crescent Waxing Crescent New Moon Full Moon Composition Structural Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Moho Asthenosphere Lithosphere Oceanic Crust Continental Crust Geologic Time Geologic Periods Geologic Eons Geologic Epoch’s Geologic Era’s Cenozoic Era Mesozoic Era Paleozoic Era Precambrian Time Geologic Column Oblate Spheroid Magnetosphere Magnetic Field Mass Magnetic Field Reversals Isaac Newton Galileo Gallia Universal Gravitation Inertia Weight Latitude Longitude Prime Meridian Parallel Meridian Topography Contour Lines Coordinates Topographic Maps International Date Line California State Content Standards: Earth's Place in the Universe 1.e) Students know the Sun is a typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion of hydrogen to form helium. 1.f Students know the evidence for the dramatic effects that asteroid impacts have had in shaping the surface of planets and their moons and in mass extinctions of life on Earth. Energy in the Earth System 4.a) Students know the relative amount of incoming solar energy compared with Earth's internal energy and the energy used by society. 5.a) Students know how differential heating of Earth results in circulation patterns in the atmosphere and oceans that globally distribute the heat. Biogeochemical Cycles 7.c) Students know the movement of matter among reservoirs is driven by Earth's internal and external sources of energy. Structure and Composition of the Atmosphere 8.b) Students know how the composition of Earth's atmosphere has evolved over geologic time and know the effect of outgassing, the variations of carbon dioxide concentration, and the origin of atmospheric oxygen.