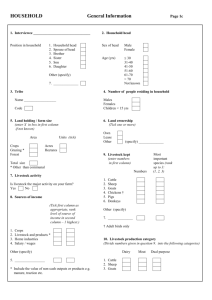
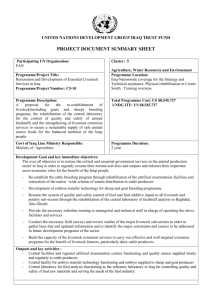
Animal Science Semester Study Guide December 2015 Name
advertisement

Animal Science Semester Study Guide December 2015 Name: ______________________________ Answer the following questions to prepare you for your test. 1. What is the definition of livestock? Animals that are produced on farms and ranches for food and other purposes (ex. Cattle, swine, sheep, horses and goats) 2. What are the functions of animals? Food, Clothing, and By-products 3. What was the first animal to be domesticated? Dog was the first animal. Sheep were the 1st livestock species. 4. Which term describes an animal with one hoof? Perissodactyla 5. What term in the order of classification is the most specific? Species 6. Which term in taxonomy is always capitalized? Genus 7. What is animal ethics? The examination of moral issues to determine right from wrong when dealing with human character and conduct 8. What is the goal of animal rights? To abolish animal use 13. What is the time period for disposing of a dead animal after death? 24-48 hours 14. What is the main objective in handling livestock waste? To prevent surface and ground water pollution 15. Where is the point of balance located on a cow? Shoulder 16. The temperature at which animals will show symptoms of heat stress. Upper critical temperature 17. What is the most effective of the four types of odor control? Masking agent 18. What is the best way to dispose of dead animals? Rendering or disposal plant 19. Bessy the cow escapes from her feedlot and runs in the path of oncoming traffic. A car carrying a family of four hits her. The two children in the car suffer minor injuries and the car is totaled. Who is responsible for the damages? The owner of Bessy the cow 9. What is the goal of animal welfare? The regulation of animal use 10. Which important legislative act regulates slaughter practices, and the fact that all livestock must be slaughtered in a humane manner to prevent needless suffering? Humane Slaughter Act 11. What is the final step in controlling runoff from feedlots? Disposal 12. How many tons of manure are produced each year on livestock farms in the United States? 2 billion tons 20. The following are examples of which type of behavior. - Cows that are in heat, allow themselves to be mounted by others - Bulls, rams, and stallions smell the vagina and urine to detect pheromones Sexual Behavior 21. The following are examples of which type of behavior. - Mothers clean their young by licking them - Mothers fight off intruders - Mothers become aggressive in protecting their young after birth Maternal Behavior 22. The following are examples of which type of behavior. - Distress calls- lambs bleat, calves bawl, pigs squeal - Farm animals respond to calls or whistles of the producer - Bulls bellow deeply to communicate aggressive behavior Communicative Behavior 30. Is PETA an animal rights or an animal welfare organization? Animal Welfare 31. What causes gases and odors to be given off by animal manure? Anaerobic bacteria breaking down organic material 32. What are two types of stimulus? 23. The following are examples of which type of behavior. - Cattle, sheep, goats, and swine defecate while standing or walking, urinate while standing but not walking - Cattle defecate 12-18 times/day, urinate 711 times/day Internal and external 33. What is the scientific name for a horse? Equus caballus 34. Who was the founder of the classification system for naming livestock? Eliminative Linnaeus 24. Hunger, thirst, or the need to scratch an itch is an example of which type of stimulus? Internal Stimulus 35. What is the scientific name for cattle? Bos tarus 36. What is the definition of breed? 25. What type of behavior develops during an animals’ lifetime? Group of animal of a common origin Learned Behavior 37. What is the scientific name for sheep? 26. What is conditioning? Behavior that occurs when the behavior is modified so that the response to one stimulus becomes associated with a different response. 27. What is imprinting? Ovis aries 38. What is the definition of purebred? Animals whose sire and dam are of the same breed Behavior occurs when an animal forms a social attachment to another organism within a specific time period after birth? 39. What is the scientific name for swine? Sus scrofa 40. What is the scientific name for chickens? 28. What class do all farm livestock belong to? Gallus domesticus Mammalia 41. What is the scientific name for goats? Capra hircus 29. What was the first livestock species to be domesticated? Sheep (livestock species) 42. Complete the following flow chart using the order of hierarchy: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Determine if the statements listed below are a characteristic of animal rights or animal welfare. If it is animal welfare place an “A” on the blank. If it is animal rights, place a “B” on the blank. (2 points each) 43. 44. 45. 46. ___B___ Keeping animals in confinement is unethical. __A____ My pet rabbit is kept in a large cage and has plenty of room to run and play. ___B___ Animals should not be used for food, clothing, or entertainment. __A____ Animals used for food, clothing, and entertainment purposes is acceptable as long as they are treated humanely. 47. __A____ I don’t like the idea of animal testing, but if it helps humans, and the animals are taken good care of, it is okay. 48. __B____ Rodeos, horse racing, and circuses are all unethical. Define the following: A. Dilution To weaken by mixing with another element. B. Stimulus Anything in the environment that causes a reaction. C. Animal Husbandry The art of working with animals. M. Liable Legally obligated or responsible. N. Aerobic Must have oxygen for the bacteria to work. O. Confinement To make impure. D. Crossbred Offspring resulting from the crossing of a male of one breed with a female of another breed. E. Contaminate To make impure. F. Taxonomy The science of identifying, classifying, and naming living things. G. Animal Science The study of the biology and management of domestic animals. H. Binomial Nomenclature A two-name system of classification. I. Fertilizer Any organic or inorganic material added to soil or water to provide plant nutrients and to increase the growth, yield, quantity or nutritive value of the plants. J. Trespass To enter onto another’s land without his/her permission. K. Anaerobic Bacteria that work without oxygen. L. Behavior The way an organism interacts with other organisms and their environment.