GeoPhysical: Student Objective Sheet Name: Date:
advertisement

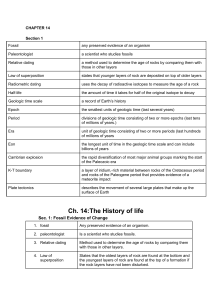
GeoPhysical: Student Objective Sheet Name:_____________________________________________________ Date:____________________ Standards: Unit: 6- Earth History 3.1 Key Vocabulary: Absolute age, relative age, extinction, fossils, geologic time, isotopes, Pangaea, radiometric dating/radioactive dating, index fossil, trace fossil, superposition, crosscutting, unconformity, uniformitarianism, geologic time scale Student Knowledge: Student Skills: That the Earth is very old, has changed in the past and continues to change That there are several methods for determining the age of rocks That there have been a number of extinction events in the Earth’s past and that a number of hypothesis exist to explain those events How to read and obtain information from the geologic time scale What ages of life forms existed through geologic time (e.g., the age of reptiles in the Mesozoic Era) Describe how the Earth has changed and then identify the mechanisms of change (weathering, erosion, deposition, plate tectonics) Compare and contrast methods used to determine age of rocks (or organic material) and Earth structures (layers of rocks) Given a diagram, be able to interpret the geologic sequence of events that have taken place in an area. (e.g., sedimentary layers deposited in layers before an igneous intrusion cuts across them. Research the past geologic history of an area (e.g., formation of the Grand Canyon , the Grand Valley) Explain how the age of the earth is determined (moon rock and other solar system data, as well as info from rocks on earth) READING GUIDE: Unit 6 – Earth History Due Date: Assignment: Chapter 23.6 pp.732-738 MES Ch 17 - 19 Questions: 1. What is the difference between relative age and absolute age? Give an example of each 3 pts 2. Define the law of superposition and draw a simple diagram to illustrate it. 2 pts 3. What is an index fossil and how is it used to date the earth? 2pts 4. What is radioactive Dating and how is it used to date the earth? 2pts 5. What is the Geologic time scale? Draw a simple sketch showing the eras and periods – 15 pts 6. In geology, if a rock layer has been undisturbed it is horizontal and in layers (for sedimentary rock). If movement and forces in the earth uplift and move these rock layers they change. The change or break in the geologic rock record is called an unconformity. There are three types. – Name them, describe them , and sketch them in the boxes below 6 pts 7. What is cross-cutting relationships? Sketch, label, and explain what knowing this relationship can tell us about rocks. GeoPhysical: Student Objective Sheet Name:_____________________________________________________ Date:____________________ Challenge Questions: If you clearly understand the concepts of this unit, you should be able to answer the following. 1. Use the diagram to answer the following Explain what happened at each number 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which is the oldest? Which is the youngest? Which layers show evidence of erosion? How do you know? 2. Use the graph to answer the following: a). What is the half-life in years of the substance represented? b) If a bone specimen is 23,000 years old, according to the data, How many half-lives would have passed? 3. Which substance would be best for determining the age of dinosaur remains from the Triassic geologic period? Explain why