Landforms of Glacial Erosion Corrie Read pages 102/3 in UG Draw
advertisement

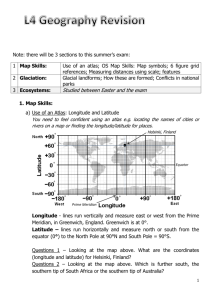
Landforms of Glacial Erosion 1. Corrie Read pages 102/3 in UG a. Draw and label a diagram to show the formation of a corrie (Fig 3 page 102) b. Rearrange the following sentences to explain the formation of a corrie: Frost-shattering and plucking create a steep backwall Snow accumulates in north and east-facing hollows The rock lip and moraine act as a dam A corrie lake fills the rock basin after the ice age. Snow is compacted into ice and moves downhill The scree from freeze-thaw weathering and rocks obtained from plucking are embedded into the ice. A rock lip is left near the front where the rate of erosion decreases They are used in the process of abrasion which deepens the hollow and forms a rock basin The height of the lip is increased by the deposition of moraine As a result of rotational slip movement there is greater pressure from the ice at the base of the headwall and the bottom of the rock basin 2. Aretes and Pyramidal Peaks Draw a clear diagram and add labels, based on the diagram below... Write a paragraph to explain how arêtes and pyramidal peaks are formed. Note named examples: The Matterhorn in the Alps is a pyramidal peak, Striding Edge in the Lake District is a famous arête (google some pictures!)