Rock-Cycle-Study
advertisement

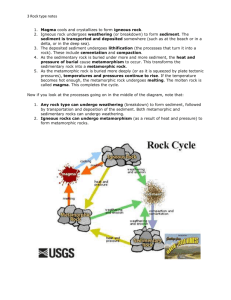
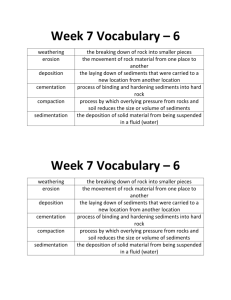
Name: __________________________________________________________________ Date: ___________ Hour: __________ Rock Cycle Study Guide VOCABULARY SECTION Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer from the options below. Write the letter of the answer on the line in front of the question. No word will be used twice, but not all words will be used. a. erosion b. metamorphic rock d. radiation e. conduction h. deposition f. igneous rock i. community k. convecction c. population g. strata j. sedimentary rock l. weathering m. magma _____ 1. The process in which sediment is laid down _____ 2. All of the species of living organisms that live and interact in an area _____ 3. The type of rock that forms from the compaction and cementation of sediment _____ 4. The transfer of thermal energy by movement in liquids and gases _____ 5. The process in which sediment moves from one place to another _____ 6. The texture of metamorphic rock in which grains are arranged in bands _____ 7. The type of rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies _____ 8. Layers in sedimentary rock _____ 9. The transfer of thermal energy by waves _____ 10. The type of rock formed due to heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK SECTION Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer from the options below. Write the letter of the answer on the line in front of the question. No word will be used twice, but not all words will be used. _____ 1. Which of the following substances cools and hardens to create igneous rock? a. sediment b. magma c. muffins d. sand _____ 2. How are igneous rocks classified? a. composition and how they form b. texture and how they form c. texture and composition d. how they form and their minerals _____ 3. What two categories is the composition of igneous rock broken into? a. foliated and nonfoliated b. felsic and mafic c. clastic and chemical d. fine-grained and coarse-grained _____ 4. Which of the following accurately describes the texture of intrusive igneous rocks? a. fine-grained b. clastic c. coarse-grained d. organic _____ 5. Which of the following accurately describes the texture of extrusive igneous rocks? a. fine-grained b. clastic c. coarse-grained d. organic _____ 6. What is the color and density of a mafic igneous rock? a. dark colored, more dense b. light colored, less dense c. dark colored, less dense d. light colored, more dense _____ 7. What is the color and density of a felsic igneous rock? a. dark colored, more dense b. light colored, less dense c. dark colored, less dense d. light colored, more dense ____ 8. How and where do extrusive igneous rocks cool? a. slowly, inside Earth’s crust b. slowly, outside Earth’s crust c. quickly, inside Earth’s crust d. quickly, outside Earth’s crust ____ 9. How and where do intrusive igneous rocks cool? a. slowly, inside Earth’s crust b. slowly, outside Earth’s crust c. quickly, inside Earth’s crust d. quickly, outside Earth’s crust SEDIMENTARY ROCK SECTION Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer from the options below. Write the letter of the answer on the line in front of the question. No word will be used twice, but not all words will be used. _____ 10. The movement of sediment is called ______________________. a. cementation b. weathering c. deposition e. compaction f. erosion e. compaction f. erosion e. compaction f. erosion e. compaction f. erosion e. compaction f. erosion _____ 11. The laying down of sediment is called ____________________. a. cementation b. weathering c. deposition _____ 12. The breaking down of existing rock is called ____________________. a. cementation b. weathering c. deposition _____ 13. The binding of sediment is called ____________________. a. cementation b. weathering c. deposition _____ 14. The pressing together of sediment is called ____________________. a. cementation b. weathering c. deposition _____ 15. Which of the following shows the correct order of events that creates a sedimentary rock? (Think of your flow chart) a. weathering, erosion, cementation, compaction, deposition b. cementation, compaction, deposition, erosion, weathering c. weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation d. cementation, deposition, weathering, erosion, compaction _____ 16. How are sedimentary rocks classified? a. how they form b. texture c. composition d. their minerals _____ 17. What is the most noticeable feature of sedimentary rocks? a. stripes b. chunks c. strata d. there are no noticeable features _____ 18. What type of sedimentary rock forms from minerals crystallizing out of a solution? a. clastic b. chemical c. organic d. felsic ____ 19. Which type of sedimentary rock often contains fossils? a. clastic b. chemical c. organic d. felsic ____ 20. Which type of sedimentary rock is made of large pieces of minerals compacted together? a. clastic b. chemical c. organic d. felsic METAMORPHIC ROCK SECTION Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer from the options below. Write the letter of the answer on the line in front of the question. No word will be used twice, but not all words will be used. _____ 21. What creates metamorphic rock? a. cementation b. heat and/or pressure c. sediment d. cooling _____ 22. How are metamorphic rocks classified? a. composition b. texture c. texture and composition d. how they form _____ 23. Which of the following describes the texture of metamorphic rocks in which mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands? a. fine-grained b. nonfoliated c. coarse-grained d. foliated _____ 24. What type of metamorphism occurs when hot magma directly touches and changes a rock? a. contact b. regional c. foliated d. nonfoliated _____ 25. What type of metamorphism occurs deep within Earth’s crust due to pressure from many layers of rock? a. contact b. regional c. foliated d. nonfoliated ____ 26. Which of the following describes the texture of metamorphic rocks in which mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands? a. fine-grained b. nonfoliated c. coarse-grained d. foliated ROCK CYCLE SECTION Directions: Look at the rock cycle below. For each number missing on the diagram, determine which answer best completes the diagram. Write the letter of your answer on the line in front of the number. 6 _____ 6. Which item below fits in #6 to complete the rock cycle diagram accurately? a. magma b. igneous rock c. cementation d. heat and pressure _____ 7. Which item below fits in #7 to complete the rock cycle diagram accurately? a. magma b. sedimentary rock c. compaction d. heat and pressure _____ 8. Which item below fits in #8 to complete the rock cycle diagram accurately? a. melting 10 8 b. metamorphic rock c. sediment d. cooling _____ 9. Which item below fits in #9 to complete the rock cycle diagram accurately? 7 a. sedimentation b. weathering and erosion c. deposition, compaction and cementation 9 _____ 10. Which item below fits in #10 to complete the rock cycle diagram accurately? a. sedimentation b. weathering and erosion c. deposition, compaction and cementation CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE SECTION Directions: Completely respond to all three bullet points IN A PARAGRAPH. Constructed Response Prompt: Compare and contrast the formation of rock types. Describe how each rock type forms. (1 point) Describe at least one way that the formation of rocks are similar. (1 point) Describe at least one way that the formation of rocks are different. (1 point)