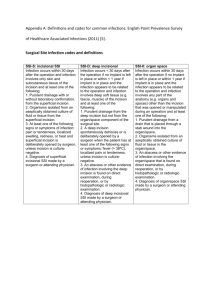
Panel 1: A list of previously identified risk factors for spinal SSI
advertisement

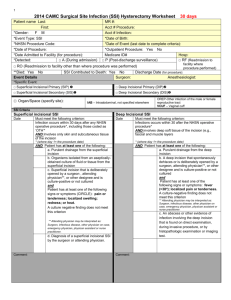
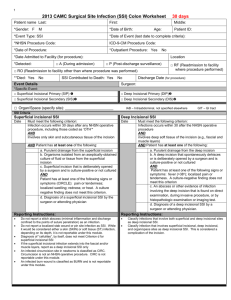
Panel 1: A list of previously identified risk factors for spinal SSI. Patient characteristics Surgical characteristics -Age26, 28, 29 -Presence of dural tear during surgery or use of glue21 -Month of surgery22 -Type of skin preperation23, 32 -Antibiotic prophylaxis28 -Instrumentation involved28, 29, 32 - Anatomical location 27, 29, 30, 32, 37 -Type of procedure30, 35 -Surgical approach6, 32, 41 -Duration of procedure23, 24, 32, 41 -Anaesthesiology variables32 -Transfusion38 -Hemoglobin level after sugery34 -Packed Red blood cells usage after surgery34 -Diabetes Mellitus25-31, 37, 39, 41, 43 -Alcohol abuse/ use26 -Obesity/ BMI6, 27, 32, 35, 38, 40, 41 -Weight loss39 -Smoking37, 39 -Urinary incontinence6 -Neurological deficit36 -Comorbidities23 -ASA risk class21, 32, 39 -Previous spinal infection/ SSI26, 35, 41 -Previous spinal surgery24, 37 -Functional status39 -Malignancy33, 39 -Serum albumin level24 -Radiation therapy before surgery43 Panel 2: Criteria for defining a surgical site infection (SSI) according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention42 Superficial incisional SSI A. Infection occurs within 30 days after the operation and B. Infection involves only skin or subcutaneous tissue of the incision and at least one of the following: C1. Purulent drainage, with or without laboratory confirmation, from the superficial incision. C2. Organisms isolated from an aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue from the superficial incision. C3. At least one of the following signs or symptoms of infection: pain or tenderness, localized swelling, redness, or heat and superficial incision is deliberately opened by surgeon, unless incision is culture-negative. C4. Diagnosis of superficial incisional SSI by the surgeon or attending physician. Deep incisional SSI A. Infection occurs within 30 days after the operation if no implant is left in place or within one year if implant is in place and the infection appears to be related to the operation and B. Infection involves deep soft tissues (e.g., fascial and muscle layers) of the incision and at least one of the following: C1. Purulent drainage from the deep incision but not from the organ/space component of the surgical site. C2. A deep incision spontaneously dehisces or is deliberately opened by a surgeon when the patient has at least one of the following signs or symptoms: fever (>38° C), localized pain, or tenderness, unless site is culture negative. C3. An abscess or other evidence of infection involving the deep incision is found on direct examination, during reoperation, or by histopathologic or radiologic examination. C4. Diagnosis of a deep incisional SSI by a surgeon or attending physician Panel 3: Applied and reported definitions of two frequently investigated risk factors. Study Apisarnthanarak et al.21 Boston et al.23 Chen et al.25 Chen et al.24 Demura et al.43 Fang et al.26 Friedman et al.27 Kanafani et al.28 Kuo et al.29 Lee et al.30 Liao et al.31 Maragakis et al.32 Pull ter Gunne et al.41 Pull ter Gunne et al.35 Pull ter Gunne et al.35 Schimmel et al.37 Schwarzkopf et al.38 Veeravagu et al.39 Obesity* Diabetes Mellitus† Males BMI >27,8, Females BMI >27.3 BMI ≥30 BMI ≥30 as noted in medical record BMI ≥30 BMI ≥30 BMI ≥30 - NR NR Diagnosed and treated by primary care physician NR NR NR NR NR Fasting blood sugar > 150mg/dl NR Use of medication or symptoms of DM including a preoperative plasma glucose concentration over 200 mg/dl NR NR NR NR NR NR No or diet controlled, Oral agents, Insulin Abbreviations and Symbols. NR: Not reported, -: Not evaluated in this study, *: as defined by the CDC: BMI: ≥30,49 †:as defined by the NIH: Any of the following test results, confirmed by retesting on a different day: 1-A blood glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or higher after an 8-hour fast. This test is called the fasting blood glucose test.2-A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher 2 hours after drinking a beverage containing 75 grams of glucose dissolved in water. This test is called the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). 3-A random (taken at any time of day) blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher, along with the presence of diabetes symptoms.48