Elements, Mixtures & Compounds 1
advertisement

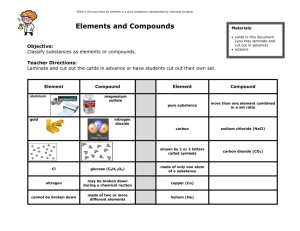
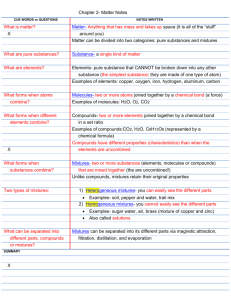
1 Elements, Mixtures, & Compounds 1. Define elements, compounds, and mixtures? Elements: A pure substance that can’t be further divided by physical or chemical means. Mixtures: Made up of two or more elements just physically combined. Compounds: Made up of two or more elements chemically combined and can be chemically separated. 2. What is the difference between mixtures and compounds? Mixtures: Physically combined Not a fixed ratio of combining elements Constituent elements keep their properties Easily separated Eg: Salt & Water Compounds: Chemically combined Combined in a fixed ratio Properties will be different of elements Can’t be easily separated Eg: CO2 3. What is the difference between an element and a compound? Elements are pure substances while compounds are made up of two or more elements chemically substances. 4. Discuss the methods of formation of compounds with an example. Combination: When elements and compounds burn and combine with oxygen. Decomposition: When complex compounds are heated to break them down into simpler compounds. 5. Discuss some common properties of mixtures. It has the properties of its constituent substances. It can be easily separated by physical means and they are not mixed in any fixed proportion. 6. What are different types of mixtures? Explain with examples. Solid-Solid Mixtures: When a solid is mixed with a solid. Zinc+Aluminum= Alloy Liquid-Liquid Mixtures: When two different liquids combine and form a new mixture. Ethanol+Water=Drinks Solid-Liquid Mixtures 2 When a solid is combined with a liquid. Water + Tang Liquid-Gas Mixtures: When a gas is mixed with a liquid. Flavoured Liquid + Carbon Dioxide = Drinks Gas-Gas Mixtures When two different gases combines. Air= Oxygen + Carbon Dioxide etc 7. What is the link between solubility and temperature of a compound? If the temperature increases the solubility increases and if the temperature decreases the solubility decreases. 8. Which element is the most abundant in air? Nitrogen, 78%. 9. Which two elements are the most abundant in the Earth’s crust? Nitrogen and Oxygen. 10. Which element is combined with oxygen to form sand? Oxygen is combined with silicon. 11. What is the use of oxygen for humans and plants? 12. What two elements make water? Two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. 13. What is the chemical formula for water? H2O 14. What do common properties of some elements allow them to be classified into? Metals and Non-metals. 15. How are metals different from non-metals? Give two examples of each. Metals are shiny and malleable while non-metals are dull and brittle. 16. What is the melting point of mercury? 38.9oC. 17. On what basis are elements arranged in the periodic table? According to their increasing atomic number. 3 18. What have the scientists organized to study the properties of elements systematically? 19. Who was the first person to compile a true table of elements, and how many elements did he arrange on the periodic table? Dmitri Mendeleev. 20. What is a chemical symbol? Give examples. The names of chemical represented by a symbol. 21. What are the categories of elements in the periodic table? Give examples. On the left side are metals and on the right are non-metals and in between are metalloids. 22. Why are water and carbon dioxide not found in the Periodic Table? Because they are not elements they are compounds. 23. What are metalloids? Give examples Which contain properties of both non metals and metals. 24. Are the properties of a compound same of its constituent elements? No, they are usually different. 25. What are some characteristics of a compound? Constituents are in fixed proportions. Methods are: Combination and Decomposition. Compounds are different from its constituent elements. 26. When does decomposition of a compound occurs? When complex compounds are heated to break them into simpler compounds. 27. What is the air mixture of? Elements. For eg: Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, and Nitrogen. 28. What substances make a mixture? Two or more different substances. 29. What is an alloy? Give examples. 30. Fill in the blanks. 1. Nitrogen makes 78% of the air whereas oxygen makes up 21%. 4 2. Water can be separated into its constituent elements hydrogen and oxygen by passing an electric current through it. Therefore water is not an element. 3. is one that is liquid at room temperature. 4. The table organizes elements broadly into 5. The sun is a giant ball of and and gases. 6. the names of elements ate represented by 7. Elements that are arranged in the same horizontal row belong to the same 8. is a highly reactive solid at room temperature 9. Compound is formed by a chemical reaction. 10. One common example of combination is 11. Milk is a mixture of such as and 12. When a mixture is formed, no occurs. 13. Element is the basic building block of matter. 1Q. Complete the following table. Elements Properties Uses Aluminum Shiny, strong, light weight Making utensils Copper Make pipes, used in homes Reddish Brown, Strong, Malleable Iron Good conductor, ductile, strong Make cutlery Iodine Black, poisonous Medicines Sulphur Yellow, Soluble Rubber tires Carbon (Diamond) Hard, can be polished Diamond drills can cut through hard metals Carbon (Graphite) 2Q. Black, Light Weight Complete the following table. Mixtures Iron & Gold Sulphur & Iron Carbon & Salt Zinc Sulphide 3Q. Make rackets Complete the following table. Separation Method 5 4Q. Elements Symbol Atomic Number Hydrogen H 1 Boron B 5 Lithium L 3 Neon Ne 10 Helium He 2 Argon Ag 18 Nitrogen N 7 Magnesium Mg 12 Fluorine F 9 Potassium K 19 Carbon C 6 Silicon Si 14 Calcium Ca 20 Chlorine Cl 17 Aluminum Al 13 Sulphur S 16 Beryllium Be 4 Phosphorus P 15 Oxygen O 8 Sodium Na 11 Complete the following table. Compounds Glass Water Table Salt Sugar Chalk 5Q. Complete the following table. Elements Contained 6 6Q. Compounds Chemical Formulas Carbon Dioxide CO2 Water H2O Sodium Chloride Na Cl Calcium Carbonate CaCO3 Copper Sulphate Cu SO4 Sulphur Dioxide SO2 Sugar C6H12O6 Hydrogen Chloride HCL Sodium Hydroxide Na OH Hydrogen Sulphate H2SO4 Hydrogen Nitrate HNO3 Complete the following table. Element Element (Metal) (Non-metal) Properties Atomic Number Colorless gas; essential for life; does not burn but supports combustion 1 Aluminum Chlorine Yellow powdery solid; Poisonous; soluble in organic solvent (e.g., alcohol) but not in water 12 Nitrogen