03s
advertisement
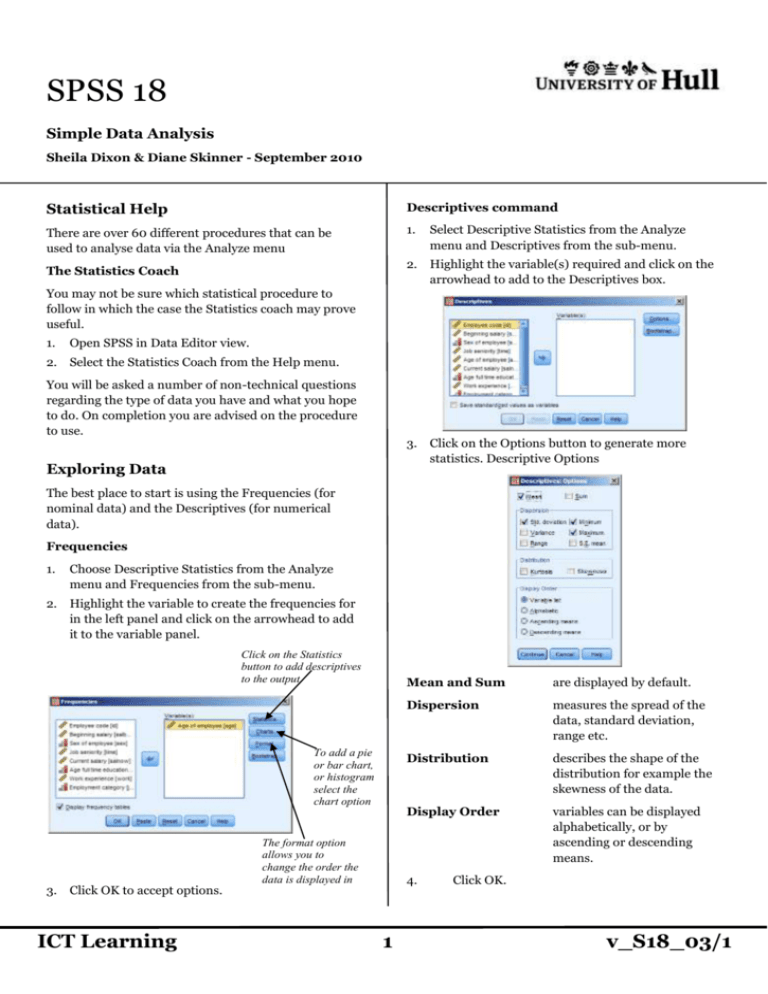
SPSS 18 Simple Data Analysis Sheila Dixon & Diane Skinner - September 2010 Statistical Help Descriptives command There are over 60 different procedures that can be used to analyse data via the Analyze menu 1. Select Descriptive Statistics from the Analyze menu and Descriptives from the sub-menu. 2. Highlight the variable(s) required and click on the arrowhead to add to the Descriptives box. The Statistics Coach You may not be sure which statistical procedure to follow in which the case the Statistics coach may prove useful. 1. Open SPSS in Data Editor view. 2. Select the Statistics Coach from the Help menu. You will be asked a number of non-technical questions regarding the type of data you have and what you hope to do. On completion you are advised on the procedure to use. 3. Click on the Options button to generate more statistics. Descriptive Options Exploring Data The best place to start is using the Frequencies (for nominal data) and the Descriptives (for numerical data). Frequencies 1. Choose Descriptive Statistics from the Analyze menu and Frequencies from the sub-menu. 2. Highlight the variable to create the frequencies for in the left panel and click on the arrowhead to add it to the variable panel. Click on the Statistics button to add descriptives to the output. To add a pie or bar chart, or histogram select the chart option 3. Click OK to accept options. ICT Learning The format option allows you to change the order the data is displayed in Mean and Sum are displayed by default. Dispersion measures the spread of the data, standard deviation, range etc. Distribution describes the shape of the distribution for example the skewness of the data. Display Order variables can be displayed alphabetically, or by ascending or descending means. 4. 1 Click OK. v_S18_03/1 Crosstabs Selecting Cases to Analyse Crosstabs are two way tables. They allow you to specify a row and column variable, and a layer. For example using educational level as the row and Sex as a layer would list the educational levels for Females, then Males as shown below. (If no statistics are defined, a count of cases is displayed.) Column You may want to restrict your analysis to a few specific cases based on a particular variable, for example only those aged 30 or less, or female and 20 or less. Row s 1. Choose Select Cases from the Data Menu. 2. Click on the If condition is satisfied button. s 3. Click the If button. 4. Double click on the variable to be tested. Layers 5. Add the comparison operator. 6. Add the value to test against. 7. Statistics Creating a Crosstab 1. Click on Continue, then OK. A new variable will have been created entitled filter_$. Choose Descriptive Statistics from the Analyze menu. 2. From the Sub-menu select Crosstabs. Those cases not selected will have a diagonal line across the row number. Any analysis will be performed on the selected rows only. Comparison operators To obtain statistics such as Chi Squared, click on the Statistics button. Tick the statistics required, then Continue. The comparison criteria can be an exact match or an expression such as >100 (greater than 100). If comparing a string variable the criteria should be entered in speech marks e.g. = “Hull” 3. Add a minimum of a row and column variable. Click OK. In the example below the age variable is used. Weighting cases If the data you have is already in the form of a table, it can be weighted to allow you to perform simple statistical tests on it. 1. Select Weight Cases from the Data menu. 2. Add the variable to be weighted by. Operator Selects if age is: =35 Equal to 35 >35 Greater than more than 35 <35 Less than less than 35 >=35 Greater than or equal to 35 or more <=35 Less than or equal to 35 or less ~= 35 Not any value except 35 Removing Selection 3. Click OK. ICT Learning Criteria 2 1. Select Cases from the Data menu. 2. Choose the All cases option. v_S18_03/1 T Test Non-parametric tests T Tests compare the means of two samples with a normal distribution. If normal distribution cannot be assumed it is said to be Non-parametric, so there are different tests to compare means. Paired sample T-test 1. Wilcoxon Select Analyze, Compare Means, Paired Samples T test. Used for related (dependent) samples 2. Highlight variables to be compared. 1. 3. Click on the arrow head to add the variables to the Paired Variables box Select Analyze, Nonparametric tests, Legacy Dialogs, 2 related samples. If the arrowhead is greyed out, make sure you have two variables selected 4. Click OK and the statistic is displayed in the Output window. Independent 2 sample T test 1. The data must be entered as value, group as shown opposite 2. Highlight the variables to be compared and add to the Test Pair(s) list. 3. Click OK. 2. Select Analyze, Compare Means, Independentsamples T Test. Mann-Whitney U Test Is similar to the two sample T-test. It is used for independent samples. 3. Add the variable(s) whose mean you want to compare to the Test Variable. 4. The group variable should be added to the Grouping Variable box. 5. Click on the Define Groups button. 1. Select Analyze, Nonparametric tests, Legacy Dialogs, 2 Independent samples. 2. Add the variable(s) whose mean you want to compare to the Test Variable List. 3. The group variable should be added to the Grouping Variable box. 6. Enter the values to be assigned to each group. 4. Click on the Define Groups button. 7. 5. Click Continue, then OK. Add the groups required 6. Click Continue, then OK. ICT Learning 3 v_S18_03/1