View
advertisement

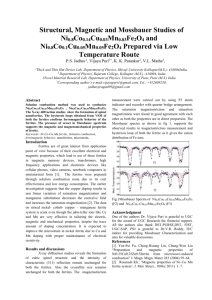
Cation distribution in ferrimagnetic Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 :57Fe Mossbauer and Raman spectroscopy study Sanjay Kumar Upadhaya and V.Raghavendra Reddy* UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Khandwa Road, Indore – 452 001, India * e-mail:vrreddycsr73@gmail.com; vrreddy@csr.res.in Introduction Polycrystalline Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 (x= 0 to 1 @ 0.2) samples are prepared by conventional solid-state reaction starting from the oxide precursors. The prepared A 2g (3 (2 2g T T ) (1 X=0.2 ) ) nfo . 1g X=0 g It is well know that the magnetic properties of ferrites are governed by the distribution of cations at tetrahedral and octahedral sites [1]. Many experimental methods viz., x-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, 57Fe Mossbauer etc., are used to measure the cation distribution in ferrites [1,2]. It may be noted that out of all the techniques, 57Fe Mossbauer under the application of external magnetic fields is extensively used to study the ferrites [2]. One can get the information regarding the Fe distribution, spin canting etc., using Mossbauer measurements. However, in systems such as Ni1xZnxFe2O4, where one is having more than one magnetic cations, Mossbauer measurements cannot give the distribution of all the cations as the Mossbauer is sensitive to Fe only. In such cases, it is required to use other complementary methods to corroborate the results that are obtained from Mossbauer measurements. Recently, Silva et al., have used Raman measurements in addition to the Mossbauer measurements to find out the degree of inversion in Zn1-xMgxFe2O4 [3]. In the present work, series of Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 samples are prepared and cation distribution is estimated using Raman spectroscopy and 57Fe Mossbauer measurements under the application of external magnetic fields. The prepared samples are phase pure (from the XRD) and the magnetization values are found to vary as a function of Ni concentration (not shown) matching with the literature. Figure 1 show the 57Fe Mossbauer data of all the samples measured at 5K and with the application of 5Tesla magnetic field parallel to the gamma rays and Raman data measured at room temperature. Both the data are used to find the distribution of cations in the system. The obtained distribution is cross checked with magnetization data as obtained from VSM data. E Introduction Results 2g Keywords: Ferrites, Mossbauer spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy samples are studied using x-ray diffraction for phase purity. Magnetic measurements are carried out using PPMS-VSM. Raman measurements are carried out using micro Raman spectrometer. High field Mossbauer measurements are carried out using standard PC based spectrometer. T The present study reports the preparation and study of ferromagnetic Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 (x= 0 to 1 @ 0.2) using x-ray diffraction, magnetization, Mossbauer and Raman spectroscopy techniques. The cation distribution is estimated using low temperature 57Fe Mossbauer and Raman spectroscopy measurements and the results are correlated with magnetization measurements. ni8 Intensity (arb.units) Abstract X=0.4 ni6 ni4 ni2 X=0.6 zfo X=0.8 200 300 400 500 600 700 -1 Raman Shift (cm ) X=1.0 -10 -5 0 5 10 Velocity (mm/s) Fig. 1: 57Fe Mossbauer, Raman data of Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 Acknowledgments Authors thank Dr.Mukul Gupta, Dr.V.Sathe and Dr. A.Banerjee for XRD, Raman and magnetization data. References [1] L.K.Leung et al., Phys. Rev. B., 8 (1973) 29 [2] N. Lakshmi et al., Phys. Rev. B., 80 (2009) 174425 [3] S.W.de Silva et al., J. Nanopart Res (2012) 14, 798