Matter Packet - Mr. P`s AP Science Site
advertisement
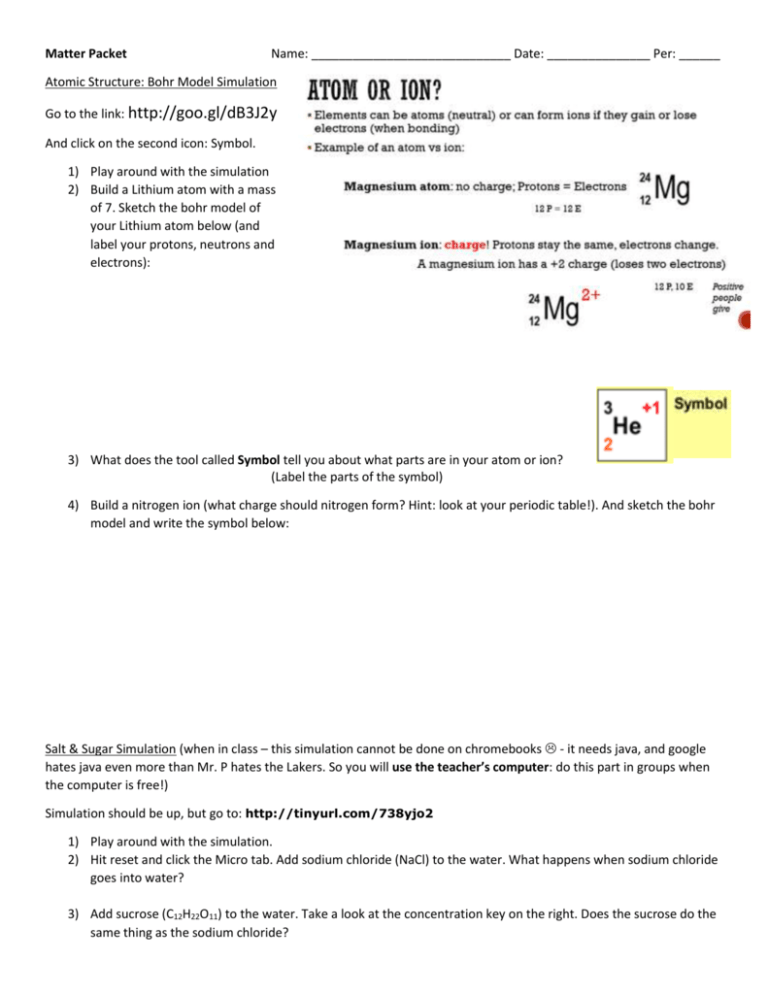
Matter Packet Name: _____________________________ Date: _______________ Per: ______ Atomic Structure: Bohr Model Simulation Go to the link: http://goo.gl/dB3J2y And click on the second icon: Symbol. 1) Play around with the simulation 2) Build a Lithium atom with a mass of 7. Sketch the bohr model of your Lithium atom below (and label your protons, neutrons and electrons): 3) What does the tool called Symbol tell you about what parts are in your atom or ion? (Label the parts of the symbol) 4) Build a nitrogen ion (what charge should nitrogen form? Hint: look at your periodic table!). And sketch the bohr model and write the symbol below: Salt & Sugar Simulation (when in class – this simulation cannot be done on chromebooks - it needs java, and google hates java even more than Mr. P hates the Lakers. So you will use the teacher’s computer: do this part in groups when the computer is free!) Simulation should be up, but go to: http://tinyurl.com/738yjo2 1) Play around with the simulation. 2) Hit reset and click the Micro tab. Add sodium chloride (NaCl) to the water. What happens when sodium chloride goes into water? 3) Add sucrose (C12H22O11) to the water. Take a look at the concentration key on the right. Does the sucrose do the same thing as the sodium chloride? Information: Ionic compounds dissolve (break into its ions) in water while molecular compounds do not. Water molecules which have one side positive (the hydrogens) and one side that is negative (oxygen) pulls on the ions in the ionic compounds (positive ion and negative ion) and breaks them apart. Which is the ionic compound? _____________________________. 4) Find out which of the two substance conducts electricity using the light bulb! Electrolytes conduct electricity and non-electrolytes do not. Fill out the table: Substance What happens in water? Ionic or Electrolyte Click the water tab and sketch the molecular Molecular or nonview when adding the substance Compound electrolyte? Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Sucrose (C12H22O11) Information: A solute dissolves in the solvent. In salt water, sodium chloride is the solute and the solvent is water. The universal solvent is water. There are two types of substances that dissolve in water: ionic compounds and other polar substances (water is a polar molecule). The substances that do not dissolve in water are non-polar substances. Water is polar because one side of a water molecule is positive (hydrogens) and one side of the molecule is negative (oxygen). If a molecule is asymmetrical it may be polar; if a molecule is symmetrical it may be nonpolar. Molecular compounds can only be polar or nonpolar (not ionic). 1) After making a cup of lemonade from lemon mix. Label the solute and solvent. 2) Based on the symmetry of the molecules, label the following molecular molecules as polar or non-polar. 3) Circle the compounds when dissolved in water would make good electrolytes: KF C2H2 Li2S F2 IF3 Atoms vs Compounds vs Mixtures Information: Take a look at the picture to the right, the molecular view of an element is shown in A and B. Picture B is a diatomic element because there are 2 atoms stuck together. (Diatomic – those 7 elements when by itself always exist in pairs!) Picture C is a molecular view of a compound. Different atoms stuck together. (chemically combined). Picture D is a mixture because it is a physical mixture of more than one type of element and/or more than one type of compound. These mixtures can either be homogenous (evenly distributed) or heterogeneous. All materials can be classified as either pure substances (P) or mixtures (M). On the first line for each substance, write P or M. For all pure substances, write either E or C on the second line. For all mixtures, write heterogeneous (He) or homogeneous (Ho). ____ ____ Beaker of distilled water (H2O) ____ ____ Glass of Kool-Aid ____ ____ Beaker of lake water ____ ____ Piece of copper wire ____ ____ Balloon filled with air ____ ____Tank of carbon dioxide (CO2) ____ ____ Slab of concrete ____ ____ Carbon ____ ____ Bowl of chicken noodle soup ____ ____ Salt water ____ ____ Fresh orange juice Separation of Substances Filtration works because of particle size. ____ ____ Piece of Copper Wire Filtration is commonly the mechanical or physical operation which is used for the separation of solids from fluids (liquids or gases) by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass. The fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Distillation is used to separate substances based on the strength of intermolecular interactions. If a solution of two or more liquids are being distilled, then the difference in their boiling points make the separation possible. 2) Condense the vapor as it escapes and collect it -Higher the intermolecular forces (attraction between different elements/compounds), the more the molecules “stick” together boiling point is higher. Takes more energy for the substance to boil if it has strong intermolecular forces. 1) Boil the solution Chromatography is used to separate mixtures of substances into their components. All forms of chromatography work on the same principle. Chromatography means “colored writing.” Chromatography is a way of separating out a mixture of chemicals, which are in gas or liquid form, by letting them creep slowly past another substance, which is typically a liquid or solid. So, with the ink and paper trick for example, we have a liquid (the ink) dissolved in water or another solvent creeping over the surface of a solid (the paper). A mixture of chemicals (unknown) are at the base line (like a start of a race) and when the race starts, they take off and each go a certain distance based on their abilities (properties). In any type of chromatography, we have the chemicals at the front (gas or liquid) moving over the surface of something else (liquid or solid that stays put). The moving substance is called the mobile phase and the substance that stays put is called the stationary phase. As the mobile phase moves, it separates out into its components on the stationary phase; we can then identify them one by one. The unequal solubilities cause the various color molecules to leave solution at different places as the solvent Why? Like dissolves like. Polar continues to move up the paper. substances dissolve in other polar The more soluble a molecule is, substances and non-polar substances the higher it will migrate up the dissolve in other non-polar substances. paper. If a chemical is very nonpolar it will not dissolve at all So if we have a polar substance in water in a very polar solvent and will (polar solvent) it will travel far with it drop off. because it is dissolved in it. 1) Which method would you use if you want to separate by: (a) particle size (b) polarity (c) boiling points 2) Oil is a nonpolar substance, what is more likely to dissolve in oil: water (polar) or gasoline (non-polar)?