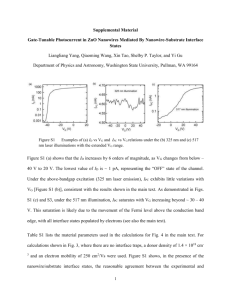
(IPC) to communicate with other applications?
advertisement
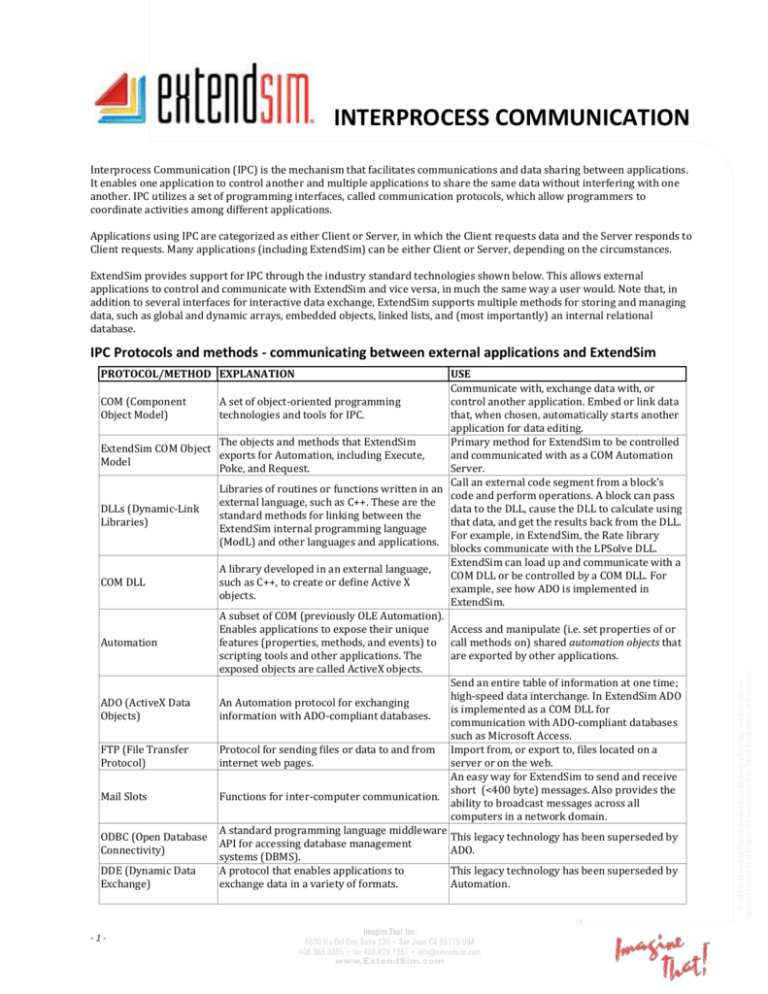
INTERPROCESS COMMUNICATION Interprocess Communication (IPC) is the mechanism that facilitates communications and data sharing between applications. It enables one application to control another and multiple applications to share the same data without interfering with one another. IPC utilizes a set of programming interfaces, called communication protocols, which allow programmers to coordinate activities among different applications. Applications using IPC are categorized as either Client or Server, in which the Client requests data and the Server responds to Client requests. Many applications (including ExtendSim) can be either Client or Server, depending on the circumstances. ExtendSim provides support for IPC through the industry standard technologies shown below. This allows external applications to control and communicate with ExtendSim and vice versa, in much the same way a user would. Note that, in addition to several interfaces for interactive data exchange, ExtendSim supports multiple methods for storing and managing data, such as global and dynamic arrays, embedded objects, linked lists, and (most importantly) an internal relational database. IPC Protocols and methods - communicating between external applications and ExtendSim PROTOCOL/METHOD EXPLANATION USE Communicate with, exchange data with, or COM (Component A set of object-oriented programming control another application. Embed or link data Object Model) technologies and tools for IPC. that, when chosen, automatically starts another application for data editing. The objects and methods that ExtendSim Primary method for ExtendSim to be controlled ExtendSim COM Object exports for Automation, including Execute, and communicated with as a COM Automation Model Poke, and Request. Server. Call an external code segment from a block's Libraries of routines or functions written in an code and perform operations. A block can pass external language, such as C++. These are the DLLs (Dynamic-Link data to the DLL, cause the DLL to calculate using standard methods for linking between the Libraries) that data, and get the results back from the DLL. ExtendSim internal programming language For example, in ExtendSim, the Rate library (ModL) and other languages and applications. blocks communicate with the LPSolve DLL. ExtendSim can load up and communicate with a A library developed in an external language, COM DLL or be controlled by a COM DLL. For COM DLL such as C++, to create or define Active X example, see how ADO is implemented in objects. ExtendSim. A subset of COM (previously OLE Automation). Enables applications to expose their unique Access and manipulate (i.e. set properties of or Automation features (properties, methods, and events) to call methods on) shared automation objects that scripting tools and other applications. The are exported by other applications. exposed objects are called ActiveX objects. Send an entire table of information at one time; high-speed data interchange. In ExtendSim ADO ADO (ActiveX Data An Automation protocol for exchanging is implemented as a COM DLL for Objects) information with ADO-compliant databases. communication with ADO-compliant databases such as Microsoft Access. FTP (File Transfer Protocol for sending files or data to and from Import from, or export to, files located on a Protocol) internet web pages. server or on the web. An easy way for ExtendSim to send and receive short (<400 byte) messages. Also provides the Mail Slots Functions for inter-computer communication. ability to broadcast messages across all computers in a network domain. A standard programming language middleware ODBC (Open Database This legacy technology has been superseded by API for accessing database management Connectivity) ADO. systems (DBMS). DDE (Dynamic Data A protocol that enables applications to This legacy technology has been superseded by Exchange) exchange data in a variety of formats. Automation. -1- Interprocess Communication Communicating between external applications and ExtendSim The IPC technologies listed above have been developed as industry standards to allow applications to share and access data independent of programming language, operating system, and file type. You can incorporate IPC into ExtendSim models by: 1. Using ExtendSim menu commands and blocks for import/export 2. Embedding objects (Windows only) 3. Using the ExtendSim I/O functions – ExtendSim as IPC Client 4. Using an external language to access ExtendSim Automation protocols - ExtendSim as IPC Server ExtendSim can act as a Client, connecting to and requesting data and services from a Server application. It can also act as a Server application that is controlled by any Windows application that can be configured as an Automation controller. The table below shows how ExtendSim can communicate with other applications and with ExtendSim models running on other computers, even while the simulation is running. This allows ExtendSim to work on a wide variety of tasks jointly with external applications such as spreadsheets, external databases, word processors, statistics packages, and so forth. ExtendSim uses and supports IPC technologies through: Read or Write blocks Data Import Export block Text File Excel X X X X Command block Internal Database ExtendSim DB Add-In ADOCompliant Databases X X X External databases X External languages control ExtendSim Other applications Other applications, COM DLLs OLE/COM functions DLL functions ADO (user-defined functions) Mailslot functions Internet Access Serial I/O functions FTP site Excel Macro, DDE command OLE Automation ExtendSim as Server IPC functions X Notes Value and Item libraries. UG 755. X X Other Communication & Control X Other applications X Other computers Web, internet Equipment Value library – UG 763; Import and Export commands – UG 766. Value library. Select a command to send and choose when it is sent. Integrated in ExtendSim. UG 728742. Allows Excel to create, edit, and export an ExtendSim DB file. UG 742-747. DR 111-118. See examples in folder ExtendSim9\Examples\Developer Tips\OLE Automation. DR 239-241; UG 765-771. DR 241-249; UG 767-769. Example in ModL library>OLE category. DR 254-256. Example in the folder ExtendSim9\Examples\Developer Tips\DLLs. DR 380-383 & UG 769 for ADO; DR 79 for Include Files. DR 249 DR 236. DR 253-254. DR 250-253. Example in ModL Tips library > Input/Output category. All references are to the ExtendSim 9 User Guide (UG) or Developer Reference (DR), released February 13, 2015. ODBC functions X Communicating with external devices and equipment There are two methods you can use to communicate with external devices such as scientific equipment and other hardware: 1. Dynamic Link Libraries (DLLs) on Windows or Shared Libraries for Mac OS. DLLs and Shared Libraries are segments of code written in a language other than the ExtendSim ModL language, such as Visual Basic or C++. A standardized interface provides a method for linking between other languages and ModL. DLLs can also be used to perform complex calculations utilizing specialized hardware. 2. Serial port functions on Windows. To pass data through serial devices, use the serial port functions. (Note that this is a legacy technology.) -2- www.ExtendSim.com August 2015