LP 13 Marriage and Marriage Theories
advertisement
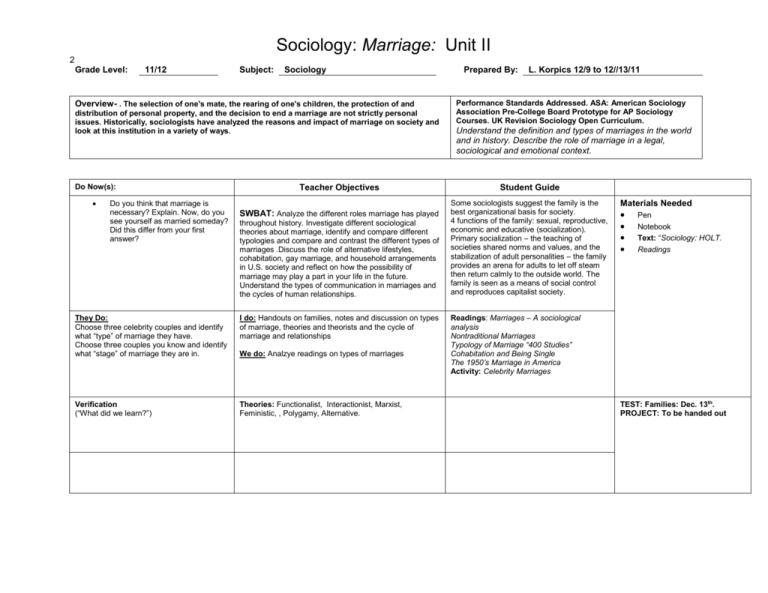
Sociology: Marriage: Unit II 2 Grade Level: 11/12 Subject: Sociology Overview- . The selection of one's mate, the rearing of one's children, the protection of and distribution of personal property, and the decision to end a marriage are not strictly personal issues. Historically, sociologists have analyzed the reasons and impact of marriage on society and look at this institution in a variety of ways. Do Now(s): Do you think that marriage is necessary? Explain. Now, do you see yourself as married someday? Did this differ from your first answer? Teacher Objectives SWBAT: Analyze the different roles marriage has played throughout history. Investigate different sociological theories about marriage, identify and compare different typologies and compare and contrast the different types of marriages .Discuss the role of alternative lifestyles, cohabitation, gay marriage, and household arrangements in U.S. society and reflect on how the possibility of marriage may play a part in your life in the future. Understand the types of communication in marriages and the cycles of human relationships. They Do: Choose three celebrity couples and identify what “type” of marriage they have. Choose three couples you know and identify what “stage” of marriage they are in. I do: Handouts on families, notes and discussion on types of marriage, theories and theorists and the cycle of marriage and relationships Verification (“What did we learn?”) Theories: Functionalist, Interactionist, Marxist, Feministic, , Polygamy, Alternative. We do: Analzye readings on types of marriages Prepared By: L. Korpics 12/9 to 12//13/11 Performance Standards Addressed. ASA: American Sociology Association Pre-College Board Prototype for AP Sociology Courses. UK Revision Sociology Open Curriculum. Understand the definition and types of marriages in the world and in history. Describe the role of marriage in a legal, sociological and emotional context. Student Guide Some sociologists suggest the family is the best organizational basis for society. 4 functions of the family: sexual, reproductive, economic and educative (socialization). Primary socialization – the teaching of societies shared norms and values, and the stabilization of adult personalities – the family provides an arena for adults to let off steam then return calmly to the outside world. The family is seen as a means of social control and reproduces capitalist society. Materials Needed Pen Notebook Text: “Sociology: HOLT. Readings Readings: Marriages – A sociological analysis Nontraditional Marriages Typology of Marriage “400 Studies” Cohabitation and Being Single The 1950’s Marriage in America Activity: Celebrity Marriages TEST: Families: Dec. 13th. PROJECT: To be handed out










