Blood disorders genetics problems
advertisement

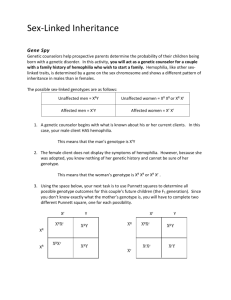
Name:________________________________________________Date____________________ Anatomy & Physiology - Genetics of Blood Disorders 1. If a female is a carrier for hemophilia X H X h and is married to a man with hemophilia X h Y , what is the probability that she will have a daughter with hemophilia? 2. A normal female marries a man who has hemophilia . (You’ll need to figure out the genotypes). What percentage of their sons will have hemophilia? 3. If a female has hemophilia and is married to a normal man..... What percentage of her sons will have hemophilia? What percentage of her daughters will have hemophilia? 4. A woman with sickle cell anemia is married to a man who is a carrier for the trait. ( a a x A a). What is the chance of their children having sickle cell anemia? 5. What is the chance that two people (both being carriers for sickle cell anemia) will have a child with the disease? 6, What is the chance that a female who is a carrier for sickle cell anemia will have a child with sickle cell anemia if she marries a normal man? 7. Von Willebrand Disease is an autosomal dominant disorder (not located on the sex chromosomes) where blood will not clot properly. What would be the two possible genotypes of a person who has the disorder? If a person is heterozygous for the trait (having the disease) is married to a normal spouse (dd), what is the chance that their children will have the disorder. Blood Type Problems 8. List all the possible genotypes for each of the 4 blood types: Type O ____________ Type A ____________ Type B ____________ Type AB ____________ 9. A man with AB blood is married to a woman with AB blood. What blood types will their children be and in what proportion? 10. A man who has type B blood (genotype: BB) is married to a woman with type O blood. What blood type will their children have? 11. A woman with type A blood (genotype: AO) is married to a type B person (genotype: BO). What blood types will their children have? 12. A woman with type A blood is claiming that a man with type AB blood is the father of her child, who is also type AB. Could this man be the father? Show the possible crosses; remember the woman can have AO or AA genotypes. 13. A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type O blood. They have two natural children, and one adopted child. The children's blood types are: A, B, and O. Which child was adopted? 14. A person with type A blood (unknown genotype) marries a person with type O blood. What blood types are possible among their children. (Show 2 crosses 15. Two people, both with AB blood have four children. What blood types should the children be? 16. A person with type B blood (genotype BO) has children with a type AB person. What blood types are possible among their children? 17. A person with type O blood is married to a person with type A blood (unknown genotype). They have 6 children, 3 of them have type A blood, three of them have type O blood. What is the genotype of the two parents? 18. A person has type B blood. What are ALL the possible blood types of his parents. Show the crosses to prove your answer. 19. A man of unknown genotype has type B blood, his wife has type A blood (also unknown genotype). List ALL the blood types possible for their children. (you may need to do multiple crosses to consider the different possible genotypes of the parents) 20. Two people with type O blood have three children. How many of those three children also have type O blood? 21. Why is a person with type O blood called a “universal donor”? 22. Why is a person with type AB blood called a “universal acceptor”? Name:_______________________________________________ Study Guide (Blood) 1. Describe a blood sample (with percentages). Define: hematocrit. 2. Describe the shape of a blood cell. How many red blood cells would you find in a ml of blood? 3. List all of the scientific names for red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. 4. What are platelets? Why are they important? 5. Describe the events in blood clot formation, such as what would occur after an injury. 6. List the 4 blood types and their associated genotypes. 7. List the two white blood cells that are classified as agranulocytes. List the ones that are granulocytes. 8. Describe how antibodies and antigens work (related to blood transfusions) What blood type can give to what blood type? What type of antibodies with a person with type O blood have in their bloodstream? 8. What is plasma and what is it composed of? 9. What is sickle cell anemia? How is it inherited (genetics)? What is the treatment for sickle cell disease? Ex. Aa x aa 10. What is hemophilia? How is it inherited (genetics)? What is the treatment for hemophilia? Ex. X H X h x X H Y 11. What is the Rh factor? How can it affect a pregnancy? 12. What is leukemia? What does a blood sample look like if someone has leukemia? How is leukemia treated? 13. What is anemia (general)? What are the different types of anemia? What is the most common type? 14. What is septicemia? How does a person become septic? 15. What causes coagulation? What chemical prevents it? What is an embolism? Thrombus? 16. What organ removes damaged or old blood cells? What do you call cells that destroy (eat) other cells? 17. List the plasma proteins. Which one is responsible for maintaining blood pressure? 18. What is hematopoeisis? Where does this occur in adults? 19. Be able to do a variety of genetic crosses (punnett squares) to show what blood types are possible. Ex. AB x O AB x A what are all the possible offspring? 20. Describe the events of hemostasis. Define hemostasis. What is vasoconstriction and what chemical causes it? 21. Identify a type of white blood cell on a picture (neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil, monocyte, lymphocyte). 22. What causes an inflammatory reaction? What white blood cell secretes this substance? 23. What is carbon monoxide and why is it dangerous? 24. What white blood cell attacks parasites? _________________ Which one has a large round nucleus and is responsible for making cell antibodies? __________________________ What is an active phagocyte, and also the most common white blood cell? __________________________ Anatomy & Physiology - Genetics of Blood Disorders (Answer Key) 1. If a female is a carrier for hemophilia X H X h and is married to a man with hemophilia X h Y , what is the probability that she will have a daughter with hemophilia? 1/4 2. A normal female marries a man who has hemophilia . (You’ll need to figure out the genotypes). What percentage of their sons will have hemophilia? 0 3. If a female has hemophilia and is married to a normal man. What percentage of her sons will have hemophilia? all sons What percentage of her daughters will have hemophilia? none, but they will be carriers X H X h 4. A woman with sickle cell anemia is married to a man who is a carrier for the trait. ( a a x A a). What is the chance of their children having sickle cell anemia? 1/2 5. What is the chance that two people (both being carriers for sickle cell anemia) will have a child with the disease? 1/4 6, What is the chance that a female who is a carrier for sickle cell anemia will have a child with sickle cell anemia if she marries a normal man? 0 7. Von Willebrand Disease is an autosomal dominant disorder (not located on the sex chromosomes) where blood will not clot properly. What would be the two possible genotypes of a person who has the disorder? DD or Dd If a person is heterozygous for the trait (having the disease) is married to a normal spouse (dd), what is the chance that their children will have the disorder. 1/2