1. Linguistic Background I
advertisement

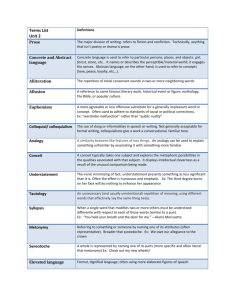
1. Linguistic Background I 1. Denotation, connotation and collocation Task 1: Match the following linguistic terms with their definitions below. 1. A denotation is __________. 2. A connotation is __________. 3. A collocation is __________. a) the habitual juxtaposition of a particular word with another word or words with a frequency greater than chance b) the literal or primary meaning of a word, in contrast to the feelings or ideas that the word suggests c) an idea or feeling which a word invokes for a person in addition to its literal or primary meaning Task 2: What are the denotations and connotations of the following words? 1. war 2. Washington 3. Iraq 4. communism 6. mother 7. soledier 8. Christmas 9. Brussels 5. demonstration 10. abortion Task 3: The following terms are all used as political labels. Although a number can be used as adjectives, for the sake of this activity they are all used as nouns. For each category, rearrange the order of the words so that you have a list which begins with the most negative connotations and moves to the most positive. There is no correct answer to this activity, so having come up with your own list, compare them with others to see at what points you agree/disagree and why this is so. a) government, regime, junta, democracy, dictatorship, faction, one man rule (used as nouns to describe forms of government) b) revolutionary, fundamentalist, dissident, zealot, critic, partisan, militant, separatist, paramilitary, protester, liberator (used as nouns to describe opponents of those in power) c) militant, hawk, dove, extremist, radical, moderate (used as nouns to describe strength of attitude to a political issue) Task 4: Match the common collocations. In some cases more options might be possible. 1. general service 2. direct aid 3. political vote 4. prime information 5. corruption state 6. exile government 7. financial minister 8. police party 9. confidential scandal 10. inteligence election 2. Metaphor, metonymy and synecdoche Task 5: Match the following linguistic terms with their definitions below. 1. A metaphor is __________. 2. A metonymy is __________. 3. A synecdoche is __________. a) a figure of speech in which a part is made to represent the whole or vice versa, as in England lost by six wickets (meaning ‘ the English cricket team’) b) the substitution of the name of an attribute or adjunct for that of the thing meant, for example suit for business executive, or the turf for horse racing c) a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is applied to an object or action to which it is not literally applicable Task 6: The following text is taken from an imaginary news report about a music award ceremony. It has been deliberately constructed to show examples of metaphor and metonymy. 1) Identify the examples of metaphor and metonymy 2) Explain the comparisons that are being made. British music triumphed when home-grown bands swept the board at the World Pop Awards. The Albert Hall was treated to a feast of celebration as many of the world’s leading bands received their accolades. There was also a morsel of controversy when the Deputy Prime Minister was half-drowned by a water jug hurled by rising star Jake Thrower. 2. Traineeships in the European Commission Task 7: Listen to the following short talk giving information on traineeships with the European Commission. Take notes and summarize the most important points of the talk. The table below will help you organize your notes. Main Points Aims of traineeship Adviser’s role Trainees’ tasks Additional info Website / email Important information